Huge stars about 8 instances extra large than the Solar explode as supernovae on the finish in their lives. The explosions, which depart in the back of a black hollow or a neutron superstar, are so full of life they may be able to outshine their host galaxies for months. On the other hand, astronomers seem to have noticed an enormous superstar that skipped the explosion and became immediately right into a black hollow.
Stars are balancing acts between the outward power of fusion and the inward power of their very own gravity. When an enormous superstar enters its ultimate evolutionary phases, it starts to expire of hydrogen, and its fusion weakens. The outward power from its fusion can not counteract the superstar’s tough gravity, and the superstar collapses in on itself. The result’s a supernova explosion, a calamitous match that destroys the superstar and leaves in the back of a black hollow or a neutron superstar.
On the other hand, it sounds as if that on occasion those stars fail to blow up as supernovae and as an alternative flip immediately into black holes.
New analysis presentations how one large, hydrogen-depleted supergiant superstar within the Andromeda galaxy (M31) did not detonate as a supernova. The analysis is “The disappearance of an enormous superstar marking the beginning of a black hollow in M31.” The lead writer is Kishalay De, a postdoctoral student on the Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Area Analysis at MIT.
A lot of these supernovae are referred to as core-collapse supernovae, often referred to as Sort II. They’re fairly uncommon, with one happening about each 100 years within the Milky Method. Scientists are thinking about supernovae as a result of they’re chargeable for growing lots of the heavy parts, and their surprise waves can cause superstar formation. Additionally they create cosmic rays that may succeed in Earth.
This new analysis presentations that we won’t perceive supernovae in addition to we concept.
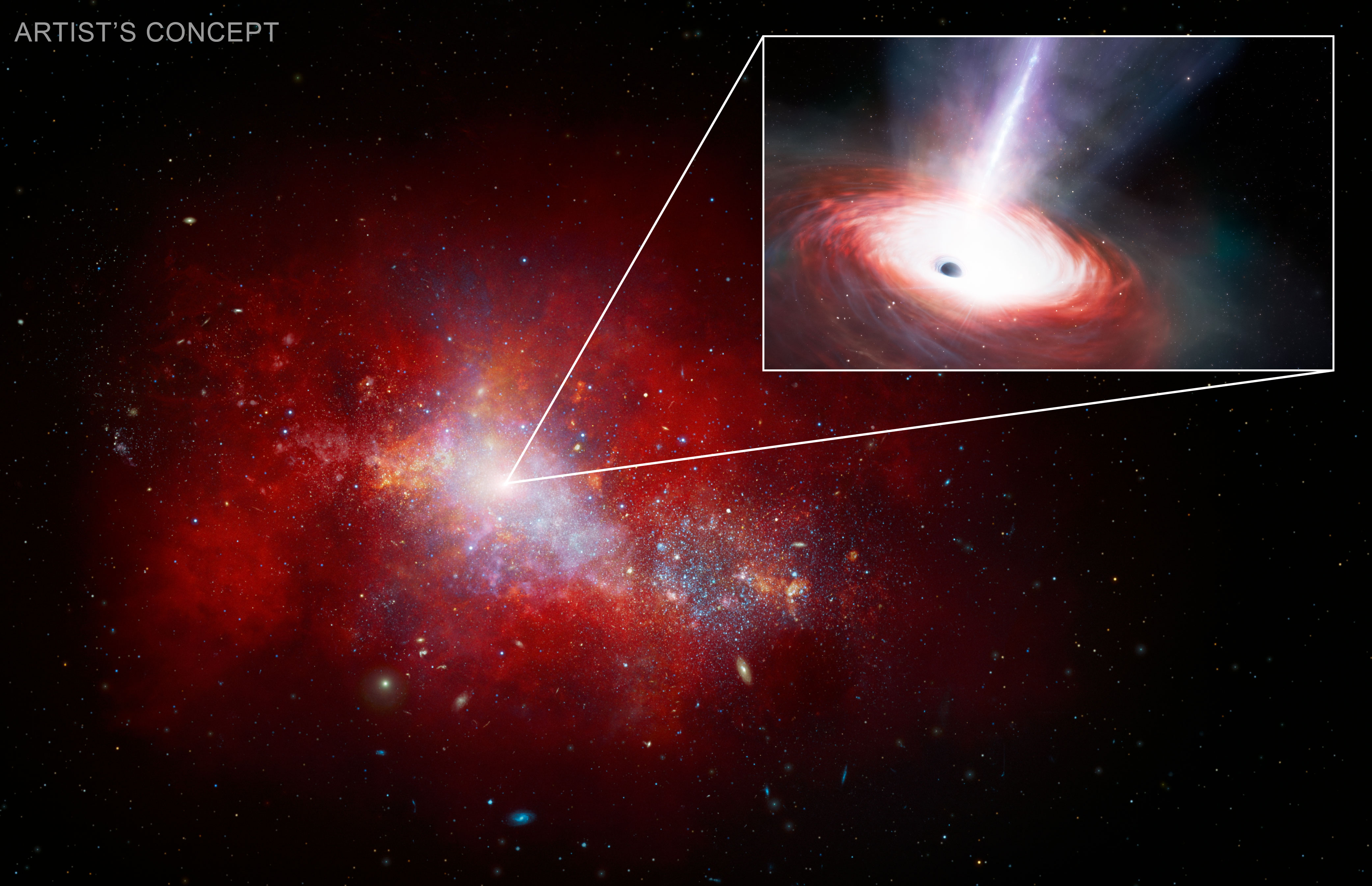
 Artist’s affect of a Sort II supernova explosion. Those supernovae explode when an enormous superstar nears the tip of its existence and leaves in the back of both a black hollow or a neutron superstar. However on occasion, the supernova fails to blow up and collapses immediately right into a black hollow. Symbol Credit score: ESO
Artist’s affect of a Sort II supernova explosion. Those supernovae explode when an enormous superstar nears the tip of its existence and leaves in the back of both a black hollow or a neutron superstar. However on occasion, the supernova fails to blow up and collapses immediately right into a black hollow. Symbol Credit score: ESO
The superstar in query is known as M31-2014-DS1. Astronomers spotted it brightening in mid-infrared (MIR) in 2014. For 1000 days, its luminosity was once consistent. Then, for some other thousand days between 2016 and 2019, it light dramatically. It’s a variable superstar, however that may’t give an explanation for those fluctuations. In 2023, it was once undetected in deep optical and near-IR (NIR) imaging observations.
The researchers say that the superstar was once born with an preliminary mass of about 20 stellar plenty and reached its terminal nuclear-burning segment with about 6.7 stellar plenty. Their observations counsel that the superstar is surrounded through a not too long ago ejected mud shell, in keeping with a supernova explosion, however there’s no proof of an optical outburst.
“The dramatic and sustained fading of M31-2014-DS1 is phenomenal within the panorama of variability in large, advanced stars,” the authors write. “The unexpected decline of luminosity in M31-2014-DS1 issues to the cessation of nuclear burning along with a next surprise that fails to conquer the infalling subject material.” A supernova explosion is so tough that it utterly overcomes infalling subject material.
“Missing any proof for a luminous outburst at such proximity, the observations of M31-2014-DS1 bespeak signatures of a ‘failed’ SN that results in the cave in of the stellar core,” the authors give an explanation for.
What may just make a celebrity fail to blow up as a supernova, although it’s the proper mass to blow up?
Supernovae are advanced occasions. The density within a collapsing core is so excessive that electrons are pressured to mix with protons, growing each neutrons and neutrinos. This procedure is known as neutronization, and it creates an impressive burst of neutrinos that carries about 10% of the superstar’s leisure mass power. The outburst is known as a neutrino surprise.
Neutrinos get their title from the truth that they’re electrically impartial and infrequently have interaction with common topic. Each 2nd, about 400 billion neutrinos from our Solar cross all the way through each individual on Earth. However in a dense stellar core, the neutrino density is so excessive that a few of them deposit their power into the encompassing stellar subject material. This heats the fabric, which generates a surprise wave.
The neutrino surprise all the time stalls, however on occasion it revives. When it revives, it drives an explosion and expels the outer layer of the supernova. If it’s no longer revived, the surprise wave fails, and the superstar collapses and paperwork a black hollow.
 This symbol illustrates how the neutrino surprise wave can stall, resulting in a black hollow with no supernova explosion. A presentations the preliminary surprise wave with cyan traces representing neutrinos being emitted and the purple circle representing the surprise wave propagating outward. B presentations the neutrino surprise stalling, with white arrows representing infalling topic. The outer layers fall inward, and the neutrino heating isn’t tough sufficient to restore the surprise. C presentations the failed surprise dissipating as a dotted purple line and the more potent white arrows constitute the cave in accelerating. The outer layers are falling in unexpectedly, and the core is changing into extra compact. D presentations the black hollow forming, with the blue circle representing the development horizon and the remainder subject material forming an accretion disk. (Credit score: Unique representation created for this text.)
This symbol illustrates how the neutrino surprise wave can stall, resulting in a black hollow with no supernova explosion. A presentations the preliminary surprise wave with cyan traces representing neutrinos being emitted and the purple circle representing the surprise wave propagating outward. B presentations the neutrino surprise stalling, with white arrows representing infalling topic. The outer layers fall inward, and the neutrino heating isn’t tough sufficient to restore the surprise. C presentations the failed surprise dissipating as a dotted purple line and the more potent white arrows constitute the cave in accelerating. The outer layers are falling in unexpectedly, and the core is changing into extra compact. D presentations the black hollow forming, with the blue circle representing the development horizon and the remainder subject material forming an accretion disk. (Credit score: Unique representation created for this text.)
In M31-2014-DS1, the neutrino surprise was once no longer revived. The researchers had been in a position to constrain the quantity of subject material ejected through the superstar, and it was once a long way beneath what a supernovae would eject. “Those constraints indicate that almost all of stellar subject material (?5 sun plenty) collapsed into the core, exceeding the utmost mass of a neutron superstar (NS) and forming a BH,” they conclude. About 98% of the superstar’s mass collapsed and created a black hollow with about 6.5 sun plenty.
M31-2014-DS1 isn’t the one failed supernova, or candidate failed supernova, that astronomers have discovered. They’re tricky to identify as a result of they’re characterised through what doesn’t occur relatively than what does. A supernova is tricky to pass over as it’s so vivid and looks within the sky unexpectedly. Historic astronomers recorded a number of of them.
In 2009, astronomers came upon the one different showed failed supernova. It was once a supergiant purple superstar in NGC 6946, the “Fireworks Galaxy.” It’s named N6946-BH1 and has about 25 sun plenty. After disappearing from view, it left just a faint infrared glow. In 2009, its luminosity larger to one million sun luminosities, however through 2015, it had disappeared in optical gentle.
A survey with the Huge Binocular Telescope monitored 27 close by galaxies, searching for disappearing large stars. The consequences counsel that between 20% and 30% of huge stars can finish their lives as failed supernovae. On the other hand, M31-2014-DS1 and N6946-BH1 are the one showed observations.
Like this:Like Loading…