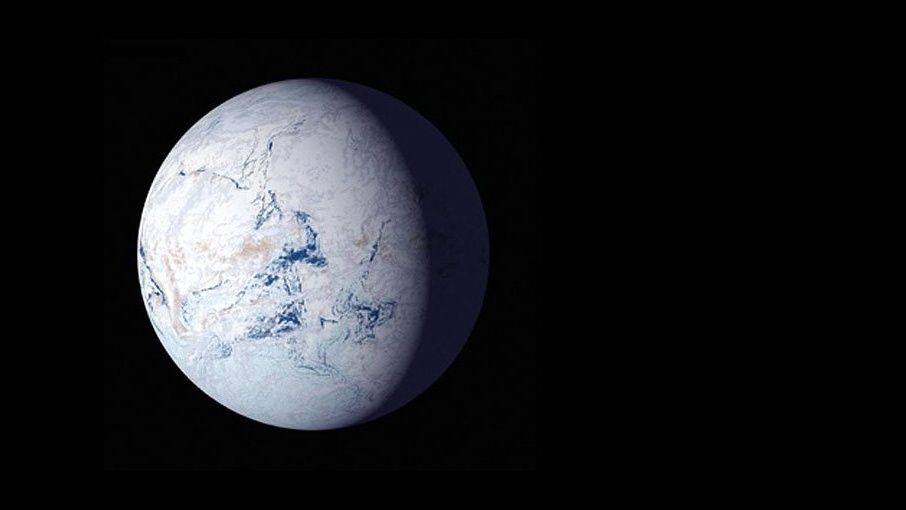
Any person residing on Earth between 720 million and 635 million years in the past almost definitely would’ve wanted a jacket.Geologists have lengthy suspected that Earth’s temperature dropped dramatically all through this time, leading to a frigid “Snowball Earth.” However they have argued slightly a little about simply how icy the planet were given — particularly, whether or not thick glacial ice coated all the globe, all of the means all the way down to the equator.Now, new proof discovered on the Tavakaiv, or “Tava,” sandstones within the Rocky Mountains of Colorado helps the perception that Snowball Earth was once certainly an international phenomenon.”This learn about gifts the primary bodily proof that Snowball Earth reached the center of continents on the equator,” Liam Courtney-Davies, lead writer of the brand new learn about and a postdoctoral researcher within the Division of Geological Sciences on the College of Colorado, Boulder, mentioned in a remark.Comparable: Our luscious blue Earth was a frozen snowballWhy are the Tava sandstones a very powerful piece of this puzzle? All through the Snowball Earth duration, Colorado wasn’t at its present northern latitude; somewhat, it sat on the equator as a landlocked a part of the traditional supercontinent Laurentia. Recently, options of the Tava sandstones jut out from the bottom at a couple of places alongside Colorado’s Entrance Vary, particularly round Pikes Height. For geologists, those options inform an enchanting tale; they started as sands on the floor however had been then shoved underground.”Those are vintage geological options known as injectites that ceaselessly shape under some ice sheets, together with in modern day Antarctica,” Courtney-Davies mentioned.Breaking area information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!If ice sheets had been certainly liable for pushing those rocks down into the subsurface, Courtney-Davies and his crew sought after to determine precisely when this procedure was once going down.The researchers took good thing about a courting methodology known as laser ablation mass spectrometry. Mineral samples had been gathered from the Tava rock, which might be wealthy in iron oxide, and the crew then hit them with a laser, liberating small amounts of the radioactive component uranium.As uranium atoms decay at a identified charge, the researchers had been in a position to discern when the rocks had been most probably buried underground — someday between 690 and 660 million years in the past, which is smack-bang in the midst of Earth’s suspected Snowball section.Courtney-Davies additionally added that figuring out extra about this era in Earth’s historical past can lend a hand scientists perceive the connection between Earth’s local weather and primary evolutionary transitions within the historical past of existence. As an example, the primary multicellular organisms, the ancestors of modern day animals and crops, are idea to have emerged within the oceans now not lengthy after Snowball Earth sooner or later thawed.”You’ve got the local weather evolving, and you’ve got existence evolving with it. All of this stuff came about all through Snowball Earth upheaval,” Courtney-Davies mentioned. “We need to higher symbolize this complete time frame to know how we and the planet advanced in combination.”The learn about was once revealed on-line Monday (Nov. 11) within the magazine Complaints of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences.
‘Snowball Earth:’ Whole planet was once most probably coated in ice greater than 600 million years in the past