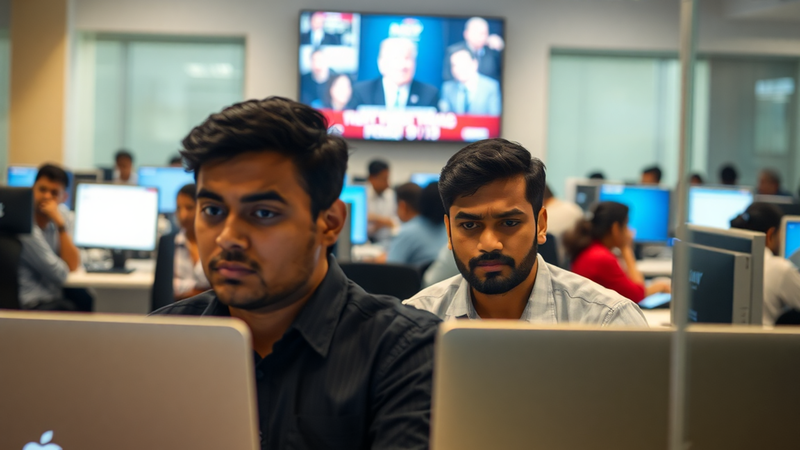
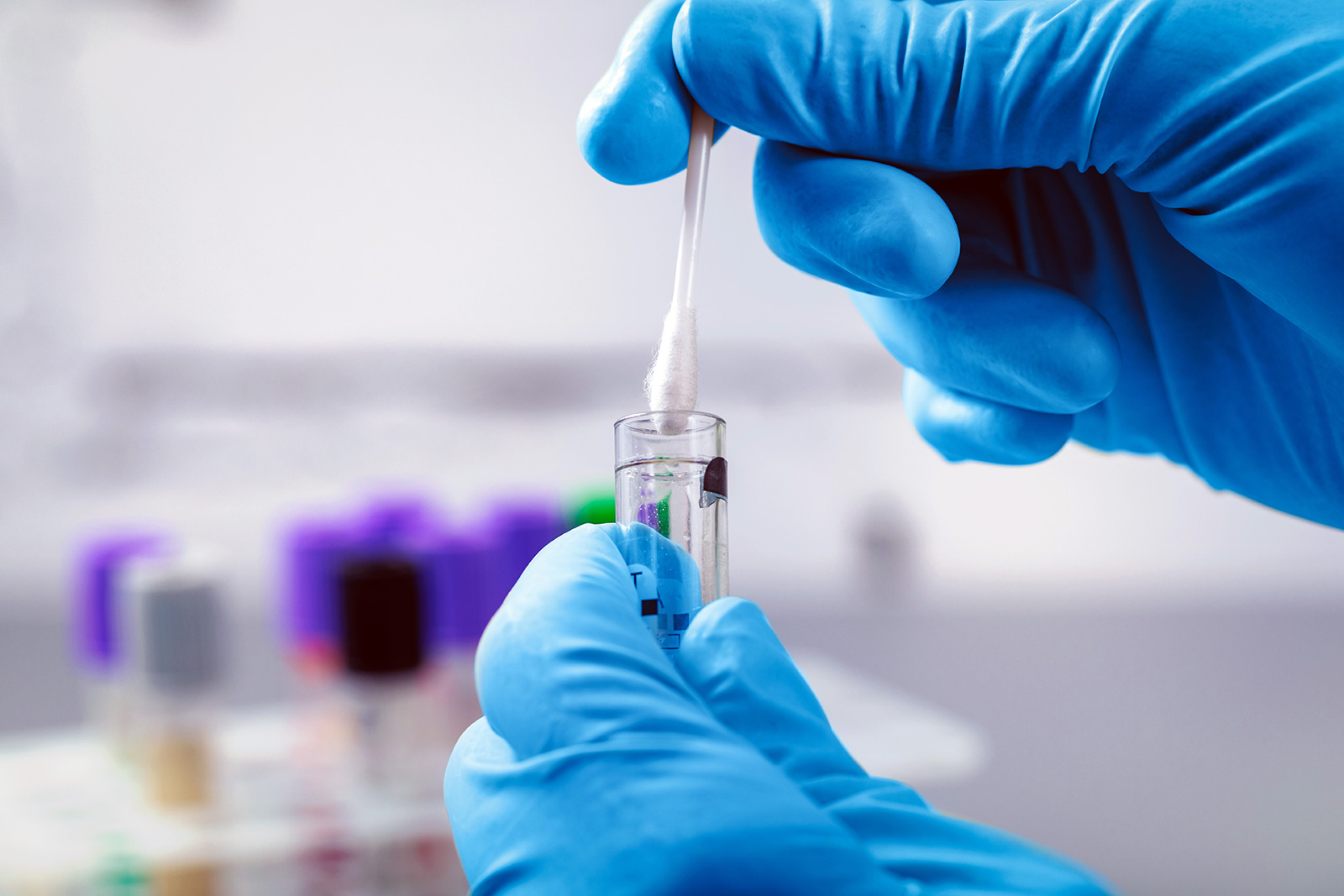
The mouse at the left is a chimeric with darkish eyes and patches of black fur, a results of stem cells derived from a choanoflagellate Sox gene. The wildtype mouse at the proper has crimson eyes and all white fur. The color distinction is because of genetic markers used to tell apart the stem cells, now not a right away impact of the gene itself. Credit score: Gao Ya and Alvin Relations Shing Lee, with because of the Centre for Comparative Drugs Analysis (CCMR) for his or her toughen.
A global group of researchers has completed an extraordinary milestone: the introduction of mouse stem cells in a position to producing a completely evolved mouse the use of genetic gear from a unicellular organism, with which we percentage a not unusual ancestor that predates animals.
This step forward reshapes our figuring out of the genetic origins of stem cells, providing a brand new point of view at the evolutionary ties between animals and their historic single-celled family members. The analysis is revealed within the magazine Nature Communications.
In an experiment that seems like science fiction, Dr. Alex de Mendoza of Queen Mary College of London collaborated with researchers from The College of Hong Kong to make use of a gene present in choanoflagellates, a single-celled organism associated with animals, to create stem cells which they then used to present upward thrust to a residing, respiring mouse.
Choanoflagellates are the nearest residing family members of animals, and their genomes comprise variations of the genes Sox and POU, recognized for using pluripotency—the mobile attainable to grow to be any mobile sort—inside mammalian stem cells. This sudden discovery demanding situations a longstanding trust that those genes developed completely inside animals.
“By way of effectively making a mouse the use of molecular gear derived from our single-celled family members, we are witnessing an atypical continuity of serve as throughout just about a thousand million years of evolution,” mentioned Dr. de Mendoza. “The find out about means that key genes all in favour of stem mobile formation would possibly have originated a ways previous than the stem cells themselves, in all probability serving to pave the way in which for the multicellular lifestyles we see these days.”
The 2012 Nobel prize to Shinya Yamanaka demonstrated that it’s conceivable to acquire stem cells from “differentiated” cells simply by expressing 4 elements, together with a Sox (Sox2) and a POU (Oct4) gene. On this new analysis, thru a suite of experiments performed in collaboration with Dr. Ralf Jauch’s lab in The College of Hong Kong / Heart for Translational Stem Cellular Biology, the group offered choanoflagellate Sox genes into mouse cells, changing the local Sox2 gene attaining reprogramming against the pluripotent stem mobile state.
To validate the efficacy of those reprogrammed cells, they have been injected right into a growing mouse embryo. The ensuing chimeric mouse displayed bodily characteristics from each the donor embryo and the lab triggered stem cells, reminiscent of black fur patches and darkish eyes, confirming that those historic genes performed a the most important position in making stem cells appropriate with the animal’s building.
The find out about lines how early variations of Sox and POU proteins, which bind DNA and keep watch over different genes, have been utilized by unicellular ancestors for purposes that might later develop into integral to stem mobile formation and animal building. “Choanoflagellates do not need stem cells, they are single-celled organisms, however they have got those genes, prone to keep an eye on fundamental mobile processes that multicellular animals most probably later repurposed for development complicated our bodies,” defined Dr. de Mendoza.
Uncover the newest in science, tech, and area with over 100,000 subscribers who depend on Phys.org for day by day insights.
Join our unfastened publication and get updates on breakthroughs,
inventions, and analysis that topic—day by day or weekly.
This novel perception emphasizes the evolutionary versatility of genetic gear and provides a glimpse into how early lifestyles bureaucracy would possibly have harnessed identical mechanisms to power mobile specialization, lengthy prior to true multicellular organisms got here into being, and into the significance of recycling in evolution.
This discovery has implications past evolutionary biology, doubtlessly informing new advances in regenerative medication. By way of deepening our figuring out of ways stem mobile equipment developed, scientists might determine new tactics to optimize stem mobile remedies and enhance mobile reprogramming ways for treating sicknesses or repairing broken tissue.
“Finding out the traditional roots of those genetic gear we could us innovate with a clearer view of ways pluripotency mechanisms can also be tweaked or optimized,” Dr. Jauch mentioned, noting that developments may just rise up from experimenting with artificial variations of those genes that would possibly carry out even higher than local animal genes in sure contexts.
Additional info:
Ya Gao et al, The emergence of Sox and POU transcription elements predates the origins of animal stem cells, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54152-x
Supplied via
Queen Mary, College of London
Quotation:
Genes of historic animal family members used to develop a mouse: Find out about unearths hidden historical past of stem cells (2024, November 15)
retrieved 15 November 2024
from
This report is matter to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal find out about or analysis, no
phase is also reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions best.