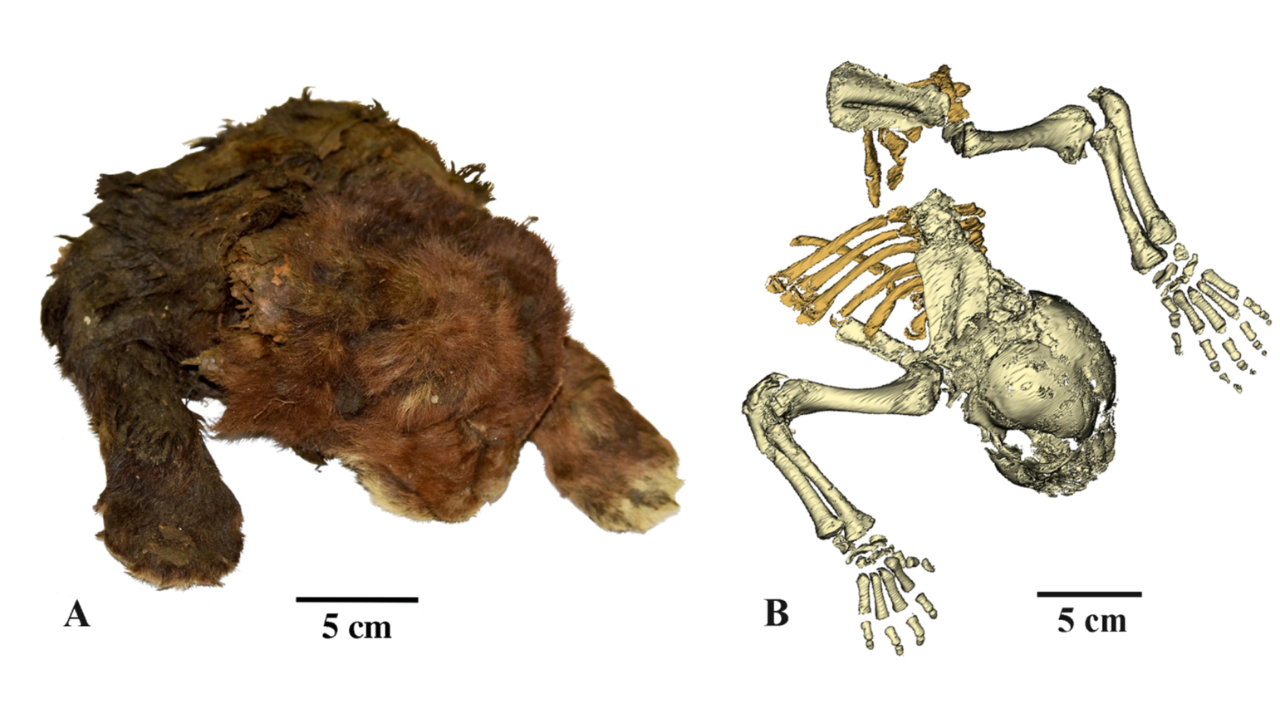
For the primary time, scientists have recovered the mummified, frozen frame of a juvenile saber-toothed cat from the Arctic permafrost in Siberia. Regardless of being over 35,000 years outdated, the sub-zero temperatures have stored the specimen in a outstanding state of preservation, with its fur, head, torso, and limbs nonetheless intact.The frozen carcass of the saber-toothed cat (Homotherium latidens) used to be found out in 2020, buried inside the permafrost close to the Badyarikha River within the northeast of Yakutia, Russia. Detailing the invention in a brand new learn about, researchers from the Russian Academy of Sciences wrote: “For the primary time within the historical past of paleontology, the semblance of an extinct mammal that has no analogues within the trendy fauna has been studied.”This particular person used to be necessarily a kitten, perishing simply 3 weeks after its delivery. Sadly, its extraordinarily younger age manner it had no longer but advanced the exceptionally lengthy higher dog enamel which are function of the genus. Scientists have lengthy contemplated the semblance of the saber-toothed cat, and this specimen is proving to be a useful useful resource for figuring out those extinct animals.The learn about authors word that the juvenile saber-tooth has “important variations from a contemporary lion cub of equivalent age.” In comparison to a lion of equivalent age, the saber-tooth cat has an “ordinary” form of the muzzle, a big mouth opening, small ears, elongated forelimbs, a corpulent neck area, and a depressing coat colour. The researchers famous that those are all vintage variations to dwelling in chilly climates. The exterior fur of the saber-tooth cat (left) and a CT scan of the specimen appearing its bones (proper).Homotherium, an extinct genus of saber-toothed cats, used to be standard all over the Ice Age, inhabiting areas throughout Eurasia, Africa, and the Americas, with other species tailored to each and every area.The lately found out particular person from Russia belongs to the species H. latidens, which lived in Eurasia till round 10,000 years in the past when the ultimate Ice Age got here to a detailed. It’s distinct from its counterpart that lived in North The united states, H. serum, in addition to the African species, H. problematicum and H. africanum. Maximum Homotherium stays were found out in North The united states, making this newest discover a treasured alternative to make clear the Eurasian department of the genus.”The invention of H. latidens mummy in Yakutia radically expands the figuring out of distribution of the genus and confirms its presence within the Overdue Pleistocene of Asia,” the learn about authors wrote.Lately, a number of different animal species were excavated from the permafrost of Siberia, together with woolly rhinoceros, mammoths, wolves, cave lions, and birds. Since Neanderthals and Denisovans additionally inhabited Eurasia all over this era, it raises the query of whether or not we would possibly in the future uncover an extinct human species preserved in permafrost.The learn about is revealed within the magazine Clinical Studies.
The exterior fur of the saber-tooth cat (left) and a CT scan of the specimen appearing its bones (proper).Homotherium, an extinct genus of saber-toothed cats, used to be standard all over the Ice Age, inhabiting areas throughout Eurasia, Africa, and the Americas, with other species tailored to each and every area.The lately found out particular person from Russia belongs to the species H. latidens, which lived in Eurasia till round 10,000 years in the past when the ultimate Ice Age got here to a detailed. It’s distinct from its counterpart that lived in North The united states, H. serum, in addition to the African species, H. problematicum and H. africanum. Maximum Homotherium stays were found out in North The united states, making this newest discover a treasured alternative to make clear the Eurasian department of the genus.”The invention of H. latidens mummy in Yakutia radically expands the figuring out of distribution of the genus and confirms its presence within the Overdue Pleistocene of Asia,” the learn about authors wrote.Lately, a number of different animal species were excavated from the permafrost of Siberia, together with woolly rhinoceros, mammoths, wolves, cave lions, and birds. Since Neanderthals and Denisovans additionally inhabited Eurasia all over this era, it raises the query of whether or not we would possibly in the future uncover an extinct human species preserved in permafrost.The learn about is revealed within the magazine Clinical Studies.
Global First 35,000-12 months-Outdated Saber-Toothed Kitten Discovered Mummified In Permafrost



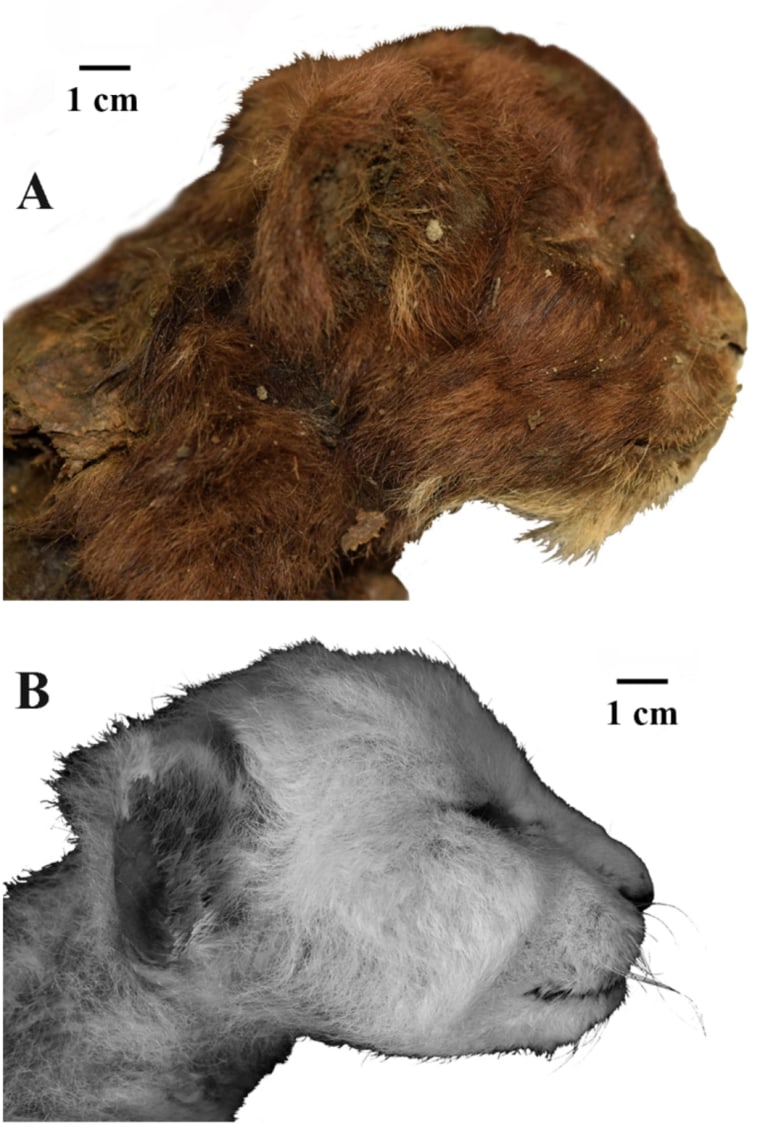







/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25735437/HT057_BLUESKY_CVirginia_A.jpg)