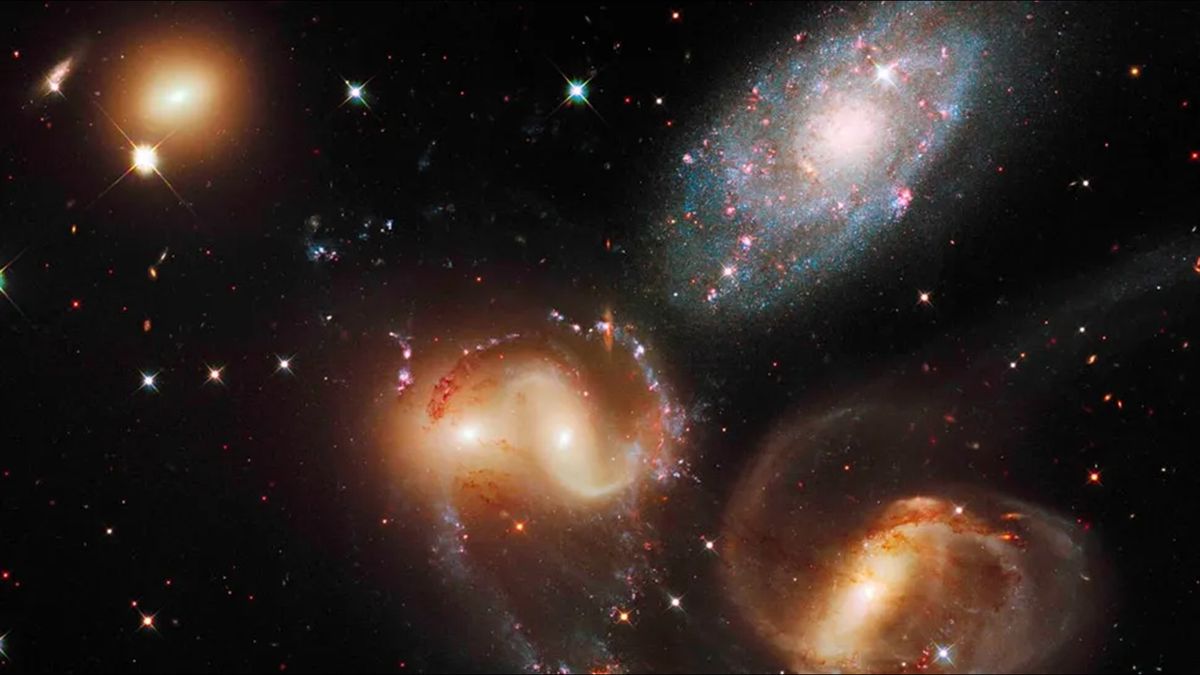
The use of probably the most tough telescopes on Earth, astronomers have witnessed an intimidating 2-million-mile-per-hour (3.2-million-kilometer-per-hour) smash-up between galaxies at a perilous “cosmic crossroads,” the website online of a couple of earlier collisions.The collision befell when the galaxy NGC 7318b ripped in the course of the website online of earlier galactic smash-ups, a galactic grouping referred to as “Stephan’s Quintet.” The influence created an impressive shockwave on this advanced subject of cosmic particles that “reawakened” the quintet.A crew of over 60 astronomers noticed the collision the usage of the William Herschel Telescope Enhanced House Speed Explorer (WEAVE) wide-field spectrograph connected to the William Herschel Telescope in Los angeles Palma, Spain. The team blended those observations with knowledge from the James Webb House Telescope (JWST) and the Low-Frequency Array (LOFAR) to research the collision website online. Such an investigation may lend a hand expose how galaxies just like the Milky Means are constructed up by way of violent occasions and mergers over billions of years.”Since its discovery in 1877, Stephan’s Quintet has captivated astronomers as it represents a galactic crossroad the place previous collisions between galaxies have left in the back of a posh subject of particles,” Marina Arnaudova, crew chief and a College of Hertfordshire researcher, in a remark. “Dynamical process on this galaxy team has now been reawakened by way of a galaxy smashing via it at an out of this world velocity of over 2 million mph (3.2 million km/h), resulting in an immensely tough surprise, just like a sonic increase from a jet fighter.”The highest velocity of an SR-71 Blackbird jet fighter is Mach 3.4, or simply over 2,500 mph (4,023 kph). That signifies that the galaxy NGC 7318b was once in fact outpacing a jet fighter by way of round 800 occasions. The surprise entrance observed by way of the crew additionally has a curious twin nature.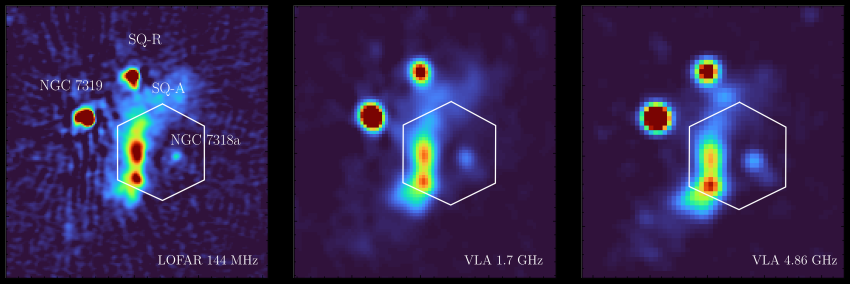 Radio observations of Stephan’s Quintet at other frequencies, taken by way of the Low Frequency Array (LOFAR) and the Very Huge Array (VLA). The pink colours point out sturdy radio emissions coming from the surprise entrance, in addition to from one of the crucial galaxies within the team and past. (Symbol credit score: College of Hertfordshire)Arnaudova defined that, because the surprise strikes via wallet of chilly fuel or the “intergalactic medium” of Stephan’s Quintet at hypersonic speeds, it’s tough sufficient to tear electrons clear of atoms. This leaves in its wake a sparkling path of charged fuel, or “plasma,” this is visual with WEAVE.The touring surprise weakens when it encounters scorching fuel surrounding the galactic collision website online.”As a substitute of inflicting important disruption, the vulnerable surprise compresses the recent fuel, leading to radio waves which are picked up by way of radio telescopes like LOFAR,” Soumyadeep Das, a College of Hertfordshire scientist, stated within the remark.Breaking area information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!
Radio observations of Stephan’s Quintet at other frequencies, taken by way of the Low Frequency Array (LOFAR) and the Very Huge Array (VLA). The pink colours point out sturdy radio emissions coming from the surprise entrance, in addition to from one of the crucial galaxies within the team and past. (Symbol credit score: College of Hertfordshire)Arnaudova defined that, because the surprise strikes via wallet of chilly fuel or the “intergalactic medium” of Stephan’s Quintet at hypersonic speeds, it’s tough sufficient to tear electrons clear of atoms. This leaves in its wake a sparkling path of charged fuel, or “plasma,” this is visual with WEAVE.The touring surprise weakens when it encounters scorching fuel surrounding the galactic collision website online.”As a substitute of inflicting important disruption, the vulnerable surprise compresses the recent fuel, leading to radio waves which are picked up by way of radio telescopes like LOFAR,” Soumyadeep Das, a College of Hertfordshire scientist, stated within the remark.Breaking area information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!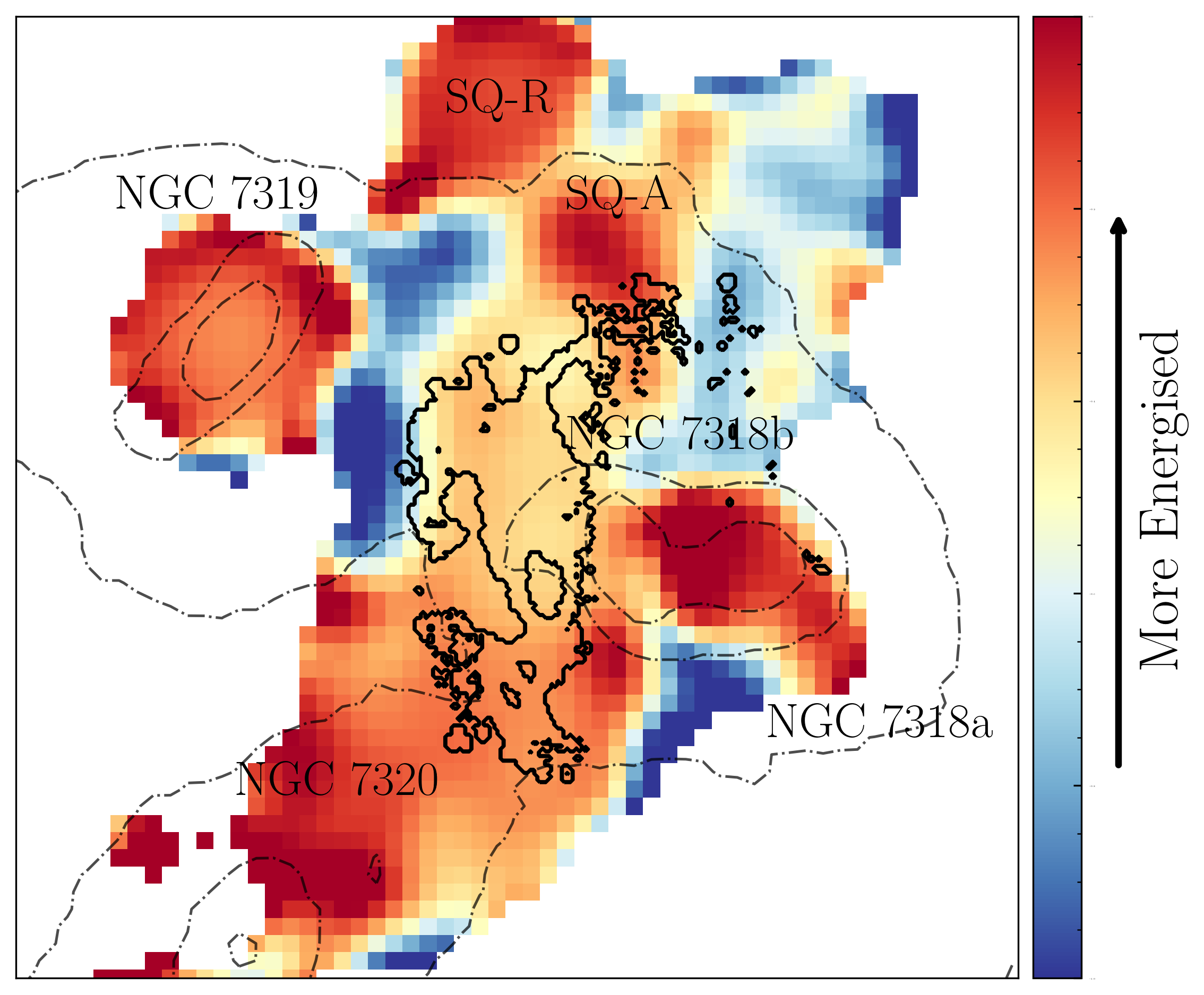 A picture revealing high-energy plasma in Stephan’s Quintet, as captured by way of radio observations with the VLA and LOFAR. The blue colors point out older, low-energy plasma, whilst the orange and yellow spaces mark areas which are being actively energised. (Symbol credit score: College of Hertfordshire)WEAVE foremost investigator and College of Oxford researcher Gavin Dalton praised the extent of element attained within the tool’s observations of Stephan’s Quintet.”In addition to the main points of the surprise and the unfolding collision that we see in Stephan’s Quintet, those observations supply a outstanding point of view on what could also be going down within the formation and evolution of the hardly resolved faint galaxies that we see on the limits of our present features,” he stated.The consequences are a tantalizing preview of the way WEAVE may collaborate with area telescopes just like the JWST to fortify our perspectives of faint galaxies.”I am excited to peer that the knowledge collected on the WEAVE crack of dawn already supply a high-impact end result, and I am positive that is simply an early instance of the varieties of discoveries that will likely be made imaginable with WEAVE at the William Herschel Telescope within the coming years,” Marc Balcells, director of the Isaac Newton Workforce of Telescopes, stated within the remark.The crew’s effects have been printed on Friday (Nov. 22) in the magazine Per 30 days Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
A picture revealing high-energy plasma in Stephan’s Quintet, as captured by way of radio observations with the VLA and LOFAR. The blue colors point out older, low-energy plasma, whilst the orange and yellow spaces mark areas which are being actively energised. (Symbol credit score: College of Hertfordshire)WEAVE foremost investigator and College of Oxford researcher Gavin Dalton praised the extent of element attained within the tool’s observations of Stephan’s Quintet.”In addition to the main points of the surprise and the unfolding collision that we see in Stephan’s Quintet, those observations supply a outstanding point of view on what could also be going down within the formation and evolution of the hardly resolved faint galaxies that we see on the limits of our present features,” he stated.The consequences are a tantalizing preview of the way WEAVE may collaborate with area telescopes just like the JWST to fortify our perspectives of faint galaxies.”I am excited to peer that the knowledge collected on the WEAVE crack of dawn already supply a high-impact end result, and I am positive that is simply an early instance of the varieties of discoveries that will likely be made imaginable with WEAVE at the William Herschel Telescope within the coming years,” Marc Balcells, director of the Isaac Newton Workforce of Telescopes, stated within the remark.The crew’s effects have been printed on Friday (Nov. 22) in the magazine Per 30 days Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
2-million-mile-per-hour galactic crash reawakens a perilous ‘cosmic crossroads’















