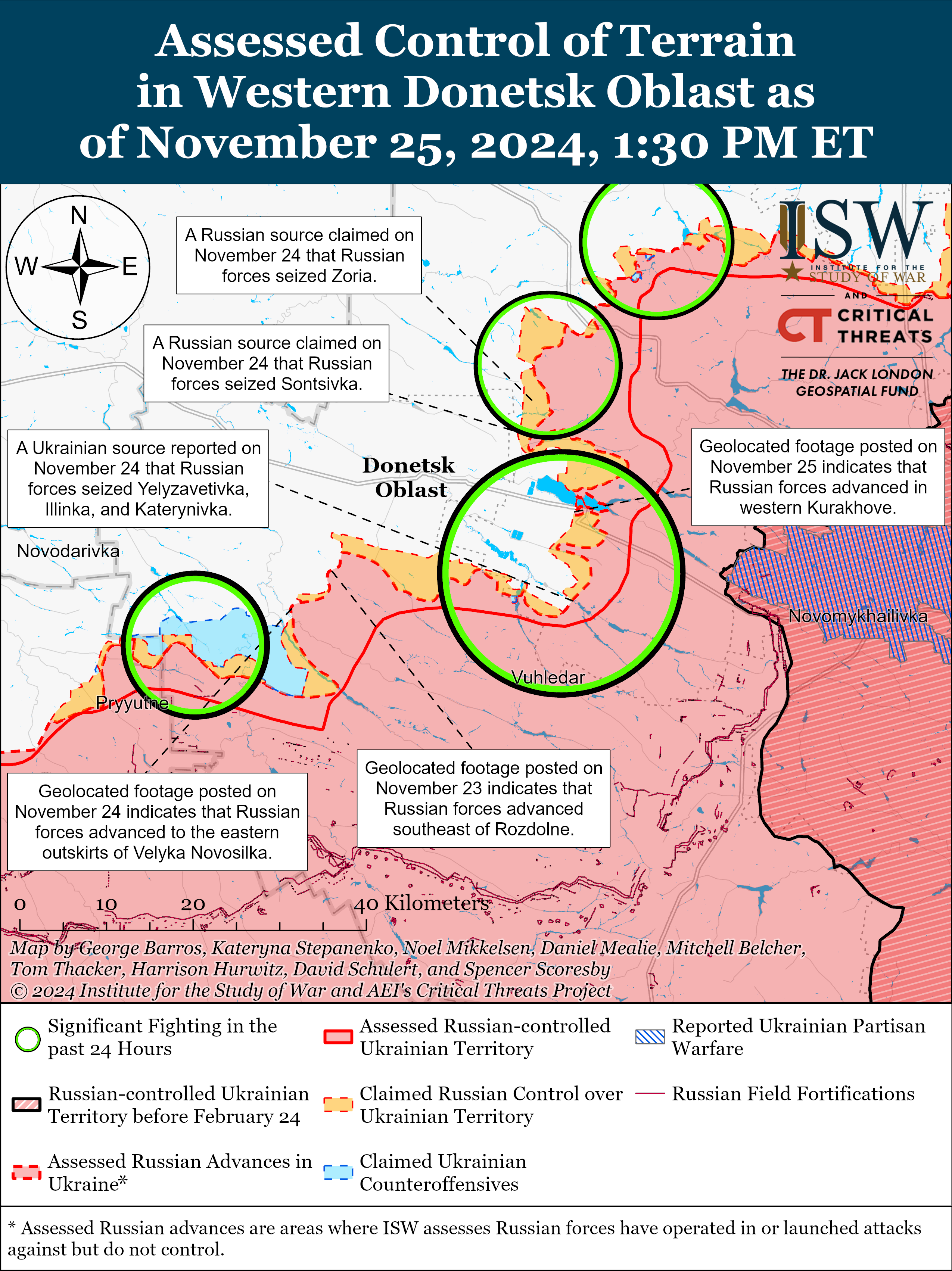
After over a decade of meticulous knowledge assortment, scientists on the H.E.S.S. observatory — which stands for “Top Power Stereoscopic Device” and is positioned in Namibia — have made a groundbreaking discovery. They have got detected probably the most full of life cosmic electrons ever seen, unlocking new avenues in our figuring out of the universe.”Cosmic rays are a century-old thriller,” Mathieu de Naurois, a researcher on the French Nationwide Centre for Medical Analysis and deputy director of the H.E.S.S. collaboration, instructed House.com.First reported in 1912 via Austrian physicist Victor Hess, cosmic rays had been came upon after a sequence of balloon ascents supposed to discover ionizing radiation that used to be first detected on an electroscope. Then again, after achieving an altitude of five,300 meters, Hess unveiled a herbal supply of high-energy debris from area. Lately, we name the ones debris cosmic rays.Now, H.E.S.S. scientists are excited as a result of they’ve detected the easiest calories electrons and positrons up to now (a positron is just like the “reverse” of an electron as it has the mass of an electron, however is undoubtedly charged like a proton), which make up one part of high-energy cosmic rays.The discovering is thrilling as it supplies tangible proof of utmost cosmic processes unleashing colossal quantities of calories.Similar: Earth were given hammered via cosmic rays 41,000 years in the past because of a vulnerable magnetic box”Working out those cosmic rays permits us to unveil large particle accelerators within the universe which might be incessantly related to probably the most violent phenomena: the explosion of stars; very compact gadgets with massive gravitational and electromagnetic fields, comparable to neutron stars and pulsars; cataclysmic mergers; and black holes,” mentioned de Naurois.The cool section is, as a result of electrons at this calories lose calories briefly, the workforce believes they will have to be coming from moderately within sight. “Within the neighborhood of our sun machine, there [are] very environment friendly cosmic accelerators of electrons,” de Naurois mentioned. “Inside of a couple of hundred light-years, there are lots of stars, with the closest ones generally mendacity two light-years from the Earth. We might due to this fact additionally be expecting to have a couple of ‘useless stars’ on this area, comparable to pulsars or supernova remnants, which might be the assets of those electrons.”Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!Detecting those excessive calories electrons and positrons with energies of a number of teraelectronvolts — larger than any particle accelerators on Earth are ready to reach — has been in particular difficult for a few causes.At the beginning, galactic magnetic fields motive electrons to deviate from a instantly trail, arriving on Earth from apparently random instructions. Secondly, space-based tools are too small to seize sufficient of those debris, partially because of the debris’ asymmetric calories distribution in area.In different phrases, cosmic ray assets boost up debris progressively, with higher-energy debris being much more likely to flee their methods. As a result of achieving the easiest energies takes time, this results in an abundance of low-energy debris and steadily fewer debris at larger calories ranges. “At excessive energies, the cosmic ray flux falls all of a sudden, that means area tools gather too few of them,” de Naurois defined.Then again, alternatively, ground-based telescopes that discover cosmic rays not directly have a troublesome time differentiating cosmic ray electrons from numerous different kinds of cosmic rays bombarding Earth’s setting.”H.E.S.S., against this, has an enormous efficient space, making it in particular appropriate to review the excessive calories a part of the electron spectrum,” de Naurois mentioned.The H.E.S.S. Observatory, consisting of 5 massive telescopes unfold throughout a space of concerning the measurement of a soccer box, used to be designed to seize atmospheric showers that emit Cherenkov radiation. This radiation happens when high-energy debris collide with the Earth’s setting, growing particle showers that the telescopes can discover and analyze.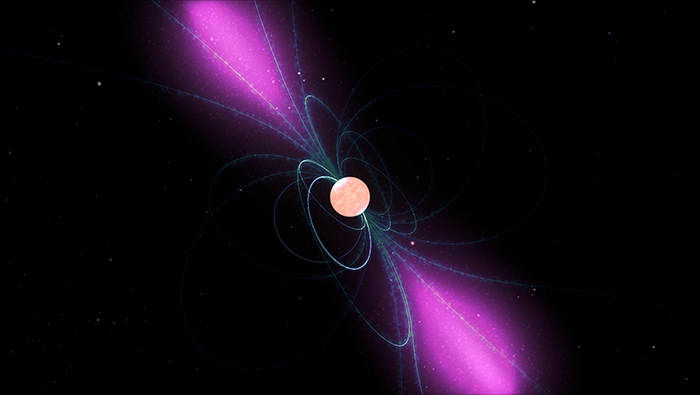 Artist’s impact of a pulsar with its robust magnetic box rotating round it. The clouds of charged debris shifting alongside the sector traces emit gamma rays which might be centered via the magnetic fields, moderately just like the beams of sunshine from a lighthouse. In those magnetic fields, pairs of positrons and electrons are created and speeded up, making pulsars possible assets of high-energy cosmic electrons and positrons. (Symbol credit score: NASA/Goddard House Flight Heart Conceptual Symbol Lab)Although its major objective is to discover gamma rays and to find their assets, the workforce repurposed the information to seek for those excessive calories cosmic ray electrons. “The set of rules used here’s according to a pixel-by-pixel comparability, the use of refined statistical modeling — particularly probability research — between a pre-calculated fashion and the pictures recorded via the digital camera,” mentioned de Naurois.Firstly, the set of rules used to be tailored to discover electrons, which can be subtly other from gamma rays. In addition they had in an effort to differentiate the electrons from background indicators. And, as a result of electrons are uncommon within the knowledge, the set of rules needed to be adjusted to reject different cosmic ray debris via making use of stricter standards, however this additionally led to fewer electrons being detected.To enhance accuracy, “each and every telescope statement used to be totally simulated, offering a deeper figuring out of the way the tools behave,” mentioned de Naurois.This led to an remarkable set of statistical knowledge for examining cosmic-ray electrons. The workforce showed that the electron calories spectrum extends as much as no less than 40 TeV, which is 400 instances larger than the energy-detection features of Earth-based accelerators. A pointy “spoil” within the spectrum round 1 TeV signifies that electrons at this calories lose calories all of a sudden inside the Milky Approach, suggesting, as de Naurois mentioned, that they originate from moderately within sight assets.”The sharpness of this spoil signifies that only some, or perhaps only one, cosmic supply is liable for those electrons,” he added. “If more than one assets had been concerned, the spectrum can be smoother, with breaks happening at other calories ranges. The most productive applicants are moderately outdated supernovas, or robust stellar winds from WR stars [the bare cores of initially massive stars whose original hydrogen-rich envelope has been removed by stellar winds], however there are different probabilities that we can not rule out.”The workforce says its research no longer best supplies a very powerful knowledge, but additionally knowledge that can act as a benchmark for long run research.
Artist’s impact of a pulsar with its robust magnetic box rotating round it. The clouds of charged debris shifting alongside the sector traces emit gamma rays which might be centered via the magnetic fields, moderately just like the beams of sunshine from a lighthouse. In those magnetic fields, pairs of positrons and electrons are created and speeded up, making pulsars possible assets of high-energy cosmic electrons and positrons. (Symbol credit score: NASA/Goddard House Flight Heart Conceptual Symbol Lab)Although its major objective is to discover gamma rays and to find their assets, the workforce repurposed the information to seek for those excessive calories cosmic ray electrons. “The set of rules used here’s according to a pixel-by-pixel comparability, the use of refined statistical modeling — particularly probability research — between a pre-calculated fashion and the pictures recorded via the digital camera,” mentioned de Naurois.Firstly, the set of rules used to be tailored to discover electrons, which can be subtly other from gamma rays. In addition they had in an effort to differentiate the electrons from background indicators. And, as a result of electrons are uncommon within the knowledge, the set of rules needed to be adjusted to reject different cosmic ray debris via making use of stricter standards, however this additionally led to fewer electrons being detected.To enhance accuracy, “each and every telescope statement used to be totally simulated, offering a deeper figuring out of the way the tools behave,” mentioned de Naurois.This led to an remarkable set of statistical knowledge for examining cosmic-ray electrons. The workforce showed that the electron calories spectrum extends as much as no less than 40 TeV, which is 400 instances larger than the energy-detection features of Earth-based accelerators. A pointy “spoil” within the spectrum round 1 TeV signifies that electrons at this calories lose calories all of a sudden inside the Milky Approach, suggesting, as de Naurois mentioned, that they originate from moderately within sight assets.”The sharpness of this spoil signifies that only some, or perhaps only one, cosmic supply is liable for those electrons,” he added. “If more than one assets had been concerned, the spectrum can be smoother, with breaks happening at other calories ranges. The most productive applicants are moderately outdated supernovas, or robust stellar winds from WR stars [the bare cores of initially massive stars whose original hydrogen-rich envelope has been removed by stellar winds], however there are different probabilities that we can not rule out.”The workforce says its research no longer best supplies a very powerful knowledge, but additionally knowledge that can act as a benchmark for long run research.
Scientists to find easiest calories cosmic ray electrons ever noticed