In 2015, David Hollow used to be prospecting in Maryborough Regional Park close to Melbourne, Australia.Armed with a steel detector, he found out one thing out of the bizarre – an overly heavy, reddish rock resting in some yellow clay.
He took it house and attempted the whole thing to open it, certain that there used to be a gold nugget within the rock – finally, Maryborough is within the Goldfields area, the place the Australian gold rush peaked within the nineteenth century.
To wreck open his to find, Hollow attempted a rock noticed, an perspective grinder, a drill, even dousing the article in acid. Alternatively, now not even a sledgehammer may just make a crack. That is as a result of what he used to be making an attempt so tough to open used to be no gold nugget.
As he discovered years later, it used to be a unprecedented meteorite. frameborder=”0″ permit=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>”It had this sculpted, dimpled glance to it,” Melbourne Museum geologist Dermot Henry informed The Sydney Morning Bring in in 2019.
“That is shaped once they come in the course of the setting, they’re melting at the outdoor, and the ambience sculpts them.”
Not able to open the ‘rock’, however nonetheless intrigued, Hollow took the nugget to the Melbourne Museum for identity.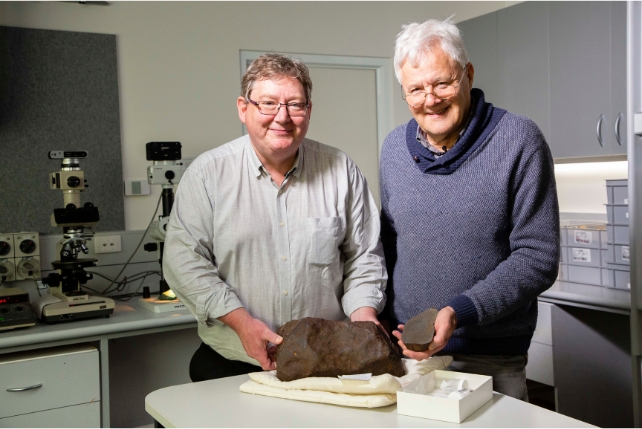 Dermot Henry and Melbourne Museum geologist Invoice Birch with the Maryborough meteorite. (Museums Victoria)”I have checked out a large number of rocks that individuals suppose are meteorites,” Henry informed Channel 10 Information.
Dermot Henry and Melbourne Museum geologist Invoice Birch with the Maryborough meteorite. (Museums Victoria)”I have checked out a large number of rocks that individuals suppose are meteorites,” Henry informed Channel 10 Information.
Actually, after 37 years of operating on the museum and analyzing hundreds of rocks, Henry mentioned most effective two of the choices had ever grew to become out to be actual meteorites.
This used to be some of the two.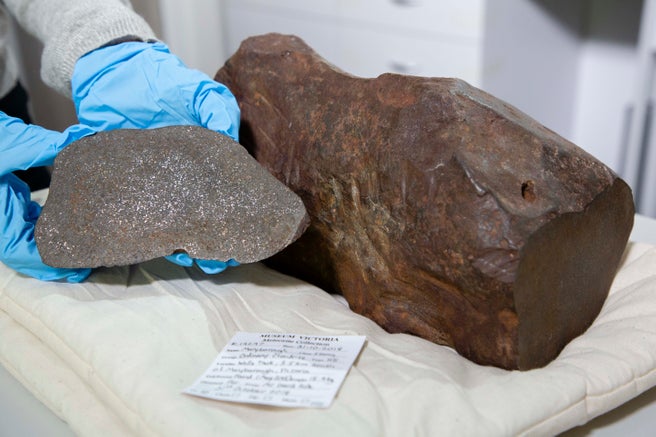 The Maryborough meteorite, with a slab lower from the mass. (Museums Victoria)”For those who noticed a rock on Earth like this, and also you picked it up, it should not be that heavy,” Melbourne Museum geologist, Invoice Birch, defined to The Sydney Morning Bring in.
The Maryborough meteorite, with a slab lower from the mass. (Museums Victoria)”For those who noticed a rock on Earth like this, and also you picked it up, it should not be that heavy,” Melbourne Museum geologist, Invoice Birch, defined to The Sydney Morning Bring in.
The researchers printed a systematic paper describing the 4.6 billion-year-old meteorite, which they known as Maryborough after the city close to the place it used to be discovered.
It weighs a whopping 17 kilograms (37.5 kilos), and after the usage of a diamond noticed to bring to an end a small slice, the researchers found out its composition had a prime proportion of iron, making it a H5 bizarre chondrite.
As soon as open, you’ll additionally see the tiny crystallized droplets of metal minerals all through it, known as chondrules.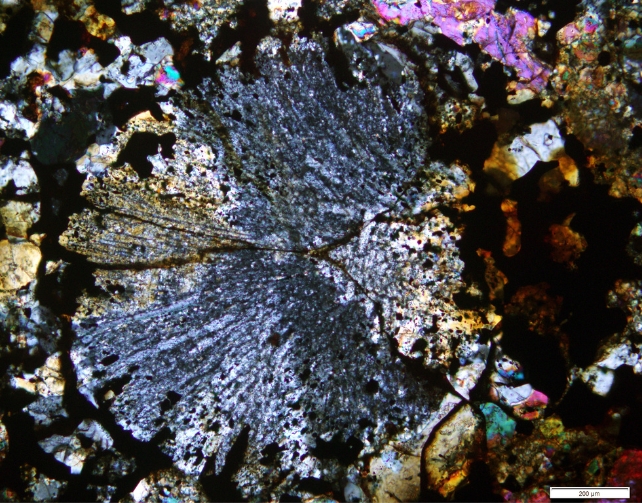 Radial pyroxene chondrule shaped within the Maryborough meteorite. (Birch et al., PRSV, 2019)”Meteorites give you the most cost-effective type of area exploration. They shipping us again in time, offering clues to the age, formation, and chemistry of our Sun Gadget (together with Earth),” mentioned Henry.
Radial pyroxene chondrule shaped within the Maryborough meteorite. (Birch et al., PRSV, 2019)”Meteorites give you the most cost-effective type of area exploration. They shipping us again in time, offering clues to the age, formation, and chemistry of our Sun Gadget (together with Earth),” mentioned Henry.
“Some supply a glimpse on the deep inner of our planet. In some meteorites, there may be ‘stardust’ even older than our Sun Gadget, which displays us how stars shape and evolve to create parts of the periodic desk.
“Different uncommon meteorites include natural molecules similar to amino acids; the construction blocks of existence.” A slab lower from the Maryborough meteorite. (Birch et al., PRSV, 2019)Even though the researchers do not but know the place the meteorite got here from and the way lengthy it will were on Earth, they do have some guesses.
A slab lower from the Maryborough meteorite. (Birch et al., PRSV, 2019)Even though the researchers do not but know the place the meteorite got here from and the way lengthy it will were on Earth, they do have some guesses.
Our Sun Gadget used to be as soon as a spinning pile of mud and chondrite rocks. Sooner or later gravity pulled a large number of this subject material in combination into planets, however the leftovers most commonly ended up in an enormous asteroid belt.
“This actual meteorite almost certainly comes out of the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, and it is been nudged out of there by means of some asteroids smashing into every different, then in the future it smashes into Earth,” Henry informed Channel 10 Information.
Carbon courting suggests the meteorite has been on Earth between 100 and 1,000 years, and there may be been various meteor sightings between 1889 and 1951 that would correspond to its arrival on our planet.
The researchers argue that the Maryborough meteorite is way rarer than gold, making it way more precious to science.
It is certainly one of most effective 17 meteorites ever recorded within the Australian state of Victoria, and it is the second one greatest chondritic mass, after an enormous 55-kilogram specimen recognized in 2003.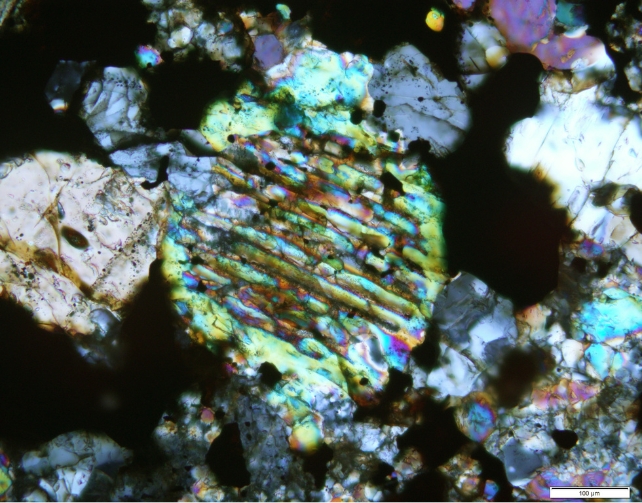 Barred Olivine chondrule shaped within the Maryborough meteorite. (Birch et al., PRSV, 2019)”That is most effective the seventeenth meteorite present in Victoria, while there may be been hundreds of gold nuggets discovered,” Henry informed Channel 10 Information.
Barred Olivine chondrule shaped within the Maryborough meteorite. (Birch et al., PRSV, 2019)”That is most effective the seventeenth meteorite present in Victoria, while there may be been hundreds of gold nuggets discovered,” Henry informed Channel 10 Information.
“Having a look on the chain of occasions, it is reasonably, chances are you’ll say, astronomical it being found out in any respect.”
It isn’t even the primary meteorite to take a couple of years to make it to a museum. In a in particular superb tale ScienceAlert coated in 2018, one area rock took 80 years, two homeowners, and a stint as a doorstop earlier than in spite of everything being published for what it in point of fact used to be.
Now’s almost definitely as just right a time as any to test your yard for in particular heavy and hard-to-break rocks – you may well be sitting on a metaphorical gold mine.
The find out about used to be printed in Complaints of the Royal Society of Victoria.An previous model of this text used to be printed in July 2019.
Guy Helps to keep a Rock For Years Hoping It is Gold. It Turns Out to Be A ways Extra Precious.












