Human footprints stir the creativeness. They invite you to apply, to bet what any person was once doing and the place they have been going. Fossilized footprints preserved in rock do the similar – they file instants within the lives of many various extinct organisms, again to the earliest creatures that walked on 4 toes, 380 million years in the past.
Discoveries in japanese Africa of tracks made through hominins – our historical family members – are telling paleontologists like ourselves in regards to the conduct of hominin species that walked on two toes and resembled us however weren’t but human like we’re nowadays. Our new analysis specializes in footprints that amazingly file two other species of hominins strolling alongside the similar Kenyan lakeshore on the identical time, more or less 1.5 million years in the past.
Finding out historical tracks like those fills in thrilling items of the human evolution tale as a result of they supply proof for hominin conduct and locomotion that scientists can’t be informed from fossilized bones.
Discovering first fossilized footprints in Kenya
The primary discovery of tracks of early hominins in Kenya’s Lake Turkana area took place accidentally in 1978. A staff led through considered one of us (Behrensmeyer) and paleoecologist Léo Laporte was once exploring the geology and fossils of the wealthy paleontological file of East Turkana. We considering documenting the animals and environments represented in a single “time slice” of in style sediments deposited about 1.5 million years in the past.
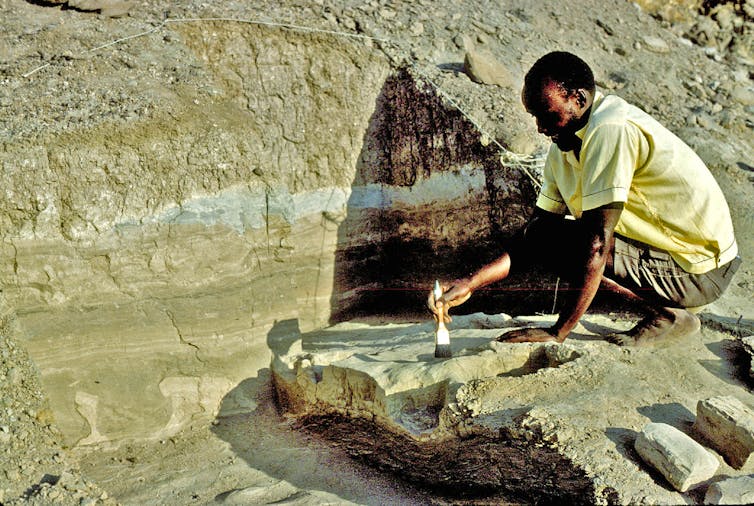

Kimolo Mulwa on the website of the primary hominin footprint discovery in 1978. Deep, sand-filled depressions to his left display hippopotamus tracks in pass segment.
Anna Okay. Behrensmeyer
We accumulated fossils from the skin and dug geological step trenches to file the sediment layers that preserved the fossils. The again wall of one of the crucial trenches confirmed deep depressions in a layer of solidified dust that we concept could be hippo tracks. We have been interested in what they gave the impression of from the highest down – what scientists name the “plan view” – so we determined to reveal 1 sq. meter of the footprint floor subsequent to the ditch.
After I returned from extra fossil bone surveys, Kimolo Mulwa, one of the crucial professional Kenyan box assistants at the mission, had moderately excavated the highest of the mudstone layer and there was once a large smile on his face. He stated, “Mutu!” – that means “individual” – and pointed to a shallow humanlike print in a number of the deep hippo tracks.
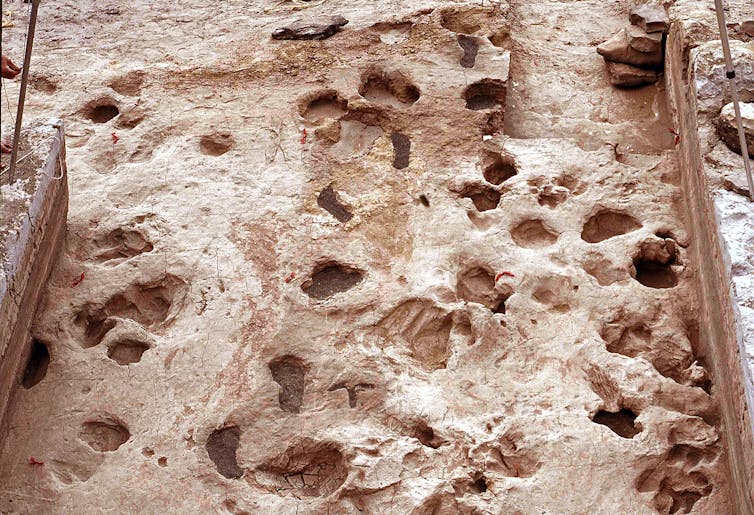

The excavated floor presentations the hominin trackway at the side of footprints of hippos, a big fowl and different animals. For the picture, scientists stuffed the hominin tracks and a couple of different footprints with darkish sand so they might stand out towards the light-colored sediment.
Anna Okay. Behrensmeyer
I may hardly ever consider it, however, sure, a humanlike footprint was once obviously recognizable at the excavated floor. And there have been extra hominin tracks, coming our means out of the strata. It was once awe-inspiring to comprehend we have been connecting with a second within the lifetime of a hominin that walked right here 1½ million years in the past.
We excavated extra of the skin and in the end discovered seven footprints in a line, appearing that the hominin had walked eastward out of softer dust onto a tougher, most likely shallower floor. At one level the person’s left foot had slipped right into a deep hippo print and the hominin stuck itself on its proper foot to steer clear of falling – lets see this obviously alongside the trackway.
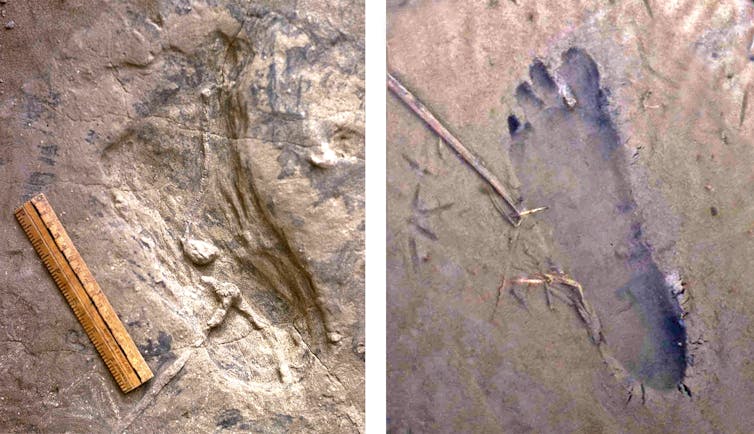

Comparability of the best-preserved 1978 hominin tune, left, with a contemporary tune (girls’s measurement 7) made through Behrensmeyer at the muddy coastline of Lake Turkana. The white gadgets throughout the fossil footprint are calcified fillings of malicious program burrows or roots that shaped within the sediment after the tune was once buried.
Anna Okay. Behrensmeyer
Even nowadays at the shore of contemporary Lake Turkana, it’s simple to slide into hippo prints, particularly if the water is a little cloudy. We joked about being sorry our hominin track-maker didn’t fall on its fingers, or face, so we will have a file of the ones portions, too.
Some other set of tracks
Over 4 a long time later, in 2021, paleontologist Louise Leakey and her Kenyan analysis staff have been excavating hominin fossils found out in the similar house when staff member Richard Loki exposed a portion of some other hominin trackway. Leakey invited considered one of us (Hatala) and paleoanthropologist Neil Roach to excavate and find out about the brand new trackway, as a result of our enjoy running on different hominin footprint websites.
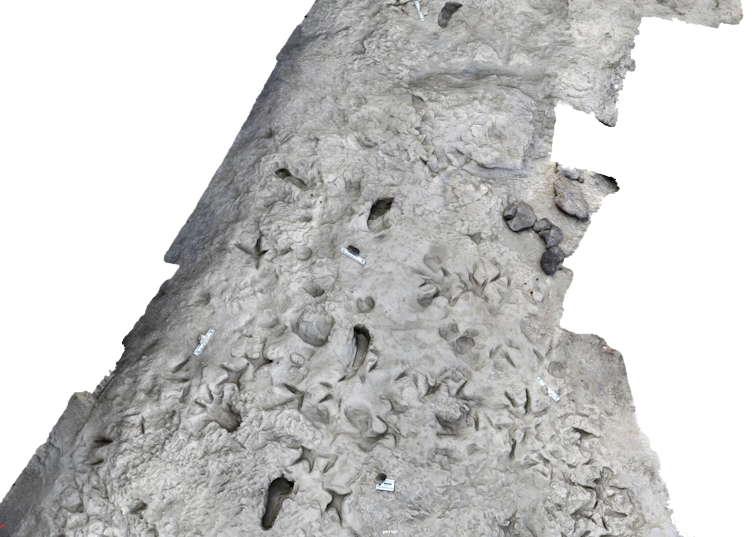

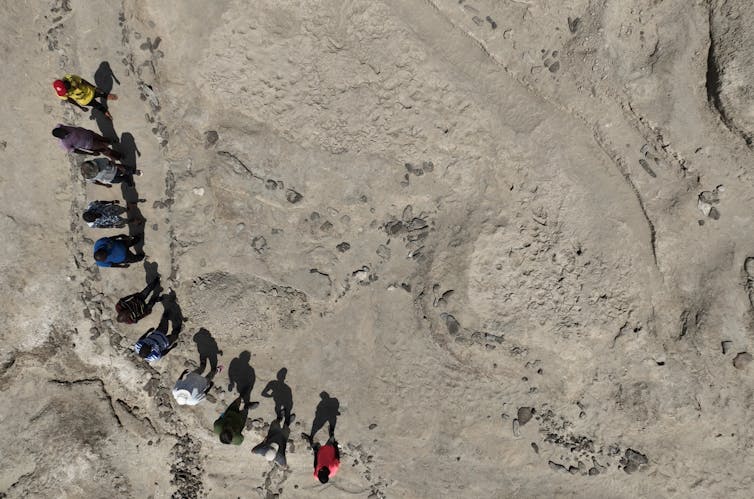
A three-D symbol of a part of the 2021 excavated floor made through photogrammetry, which presentations the tracks of 2 hominin species crossing.
Kevin Hatala
The staff, together with 10 professional Kenyan box researchers led through Cyprian Nyete, excavated the skin and documented the tracks with photogrammetry – a technique for three-D imaging. That is the easiest way to gather tune surfaces for the reason that sediments don’t seem to be laborious sufficient – what geologists name lithified – to take away from the bottom safely and take to a museum.
The newly found out tracks have been made roughly 1.5 million years in the past. They happen at an previous stratigraphic stage than those we present in 1978 and are a couple of hundred thousand years older, in keeping with relationship of volcanic deposits within the East Turkana strata.
Analysis staff participants alongside the fringe of the traditional footprint trackway.
Louise N. Leakey
Who was once passing thru?
Those footprints are particularly thrilling as a result of cautious anatomical and useful research in their shapes presentations that two other sorts of hominins made tracks at the identical lakeshore, inside hours to a couple of days of one another, perhaps even inside mins!
We all know the footprints have been made very shut in combination in time as a result of experiments at the trendy coastline of Lake Turkana display {that a} muddy floor appropriate for conserving transparent tracks doesn’t remaining lengthy earlier than being destroyed through waves or cracked through publicity to the Solar.

A trackway of footprints scientists hypothesize have been created through a Paranthropus boisei particular person.
Neil T. Roach
That is the primary time ever that scientists were in a position to mention that Homo erectus and Paranthropus boisei – one our most likely ancestor and the opposite a extra far away relative – in fact coexisted on the identical time and position. Along side many various species of mammals, they have been each participants of the traditional group that inhabited the Turkana Basin.
Now not simplest that, however with the brand new tracks as references, our analyses counsel that different prior to now described hominin tracks in the similar area point out that those two hominins coexisted on this house of the Turkana Basin for no less than 200,000 years, many times leaving their footprints within the shallow lake margin habitat.
Different animals left tracks there as neatly – massive storks, smaller birds corresponding to pelicans, antelope and zebra, hippos and elephants – however hominin tracks are strangely not unusual for a land-based species. What have been they doing, returning over and over to this habitat, when different primates, corresponding to baboons, it seems that didn’t discuss with the lakeshore and depart tracks there?
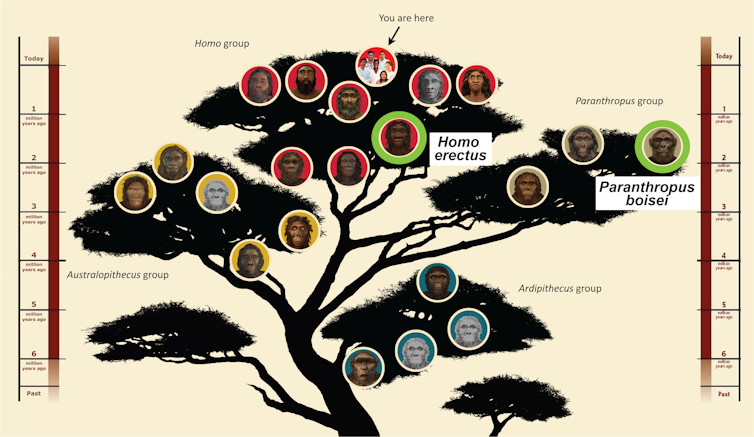
The track-making species Homo erectus and Paranthropus boisei are on two other branches of the hominin circle of relatives tree.
Smithsonian Human Origins Program, changed through writer from authentic paintings
Those footprints galvanize new ideas and questions on our early family members. Had been they consuming vegetation that grew at the lakeshore? Some paleontologists have proposed this risk for the powerful Paranthropus boisei for the reason that chemistry of its enamel point out a particular herbivorous nutrition of grasslike and reedlike vegetation. The similar chemical assessments on enamel of Homo erectus – the ancestral species to Homo sapiens – display a combined nutrition that most likely incorporated animal protein in addition to vegetation.
The lake margin habitat presented meals within the type of reeds, freshwater bivalves, fish, birds and reptiles corresponding to turtles and crocodiles, regardless that it would were bad for bipedal primates 4 or 5 toes (1.2 to one.5 meters) tall. Even nowadays, folks residing alongside the shore on occasion are attacked through crocodiles, and native hippos will also be competitive as neatly. So, no matter drew the hominins to the lakeshore should were value some chance.
For now it’s unimaginable to grasp precisely how the 2 species interacted. New clues about their conduct might be published with long term excavations of extra trackway surfaces. However it’s attention-grabbing to believe those two hominin “cousins” being shut neighbors for masses of 1000’s of years.
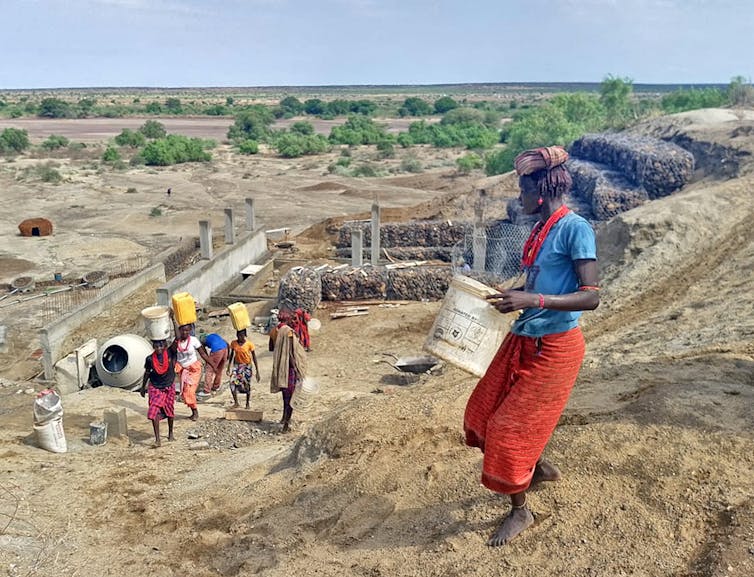

Building of the Ileret footprint website museum, with Daasanach girls wearing water for blending concrete.
Nationwide Museums of Kenya Audio Visible
Historic footprints you’ll discuss with
Previous excavations of hominin trackways close to a village referred to as Ileret, 25 miles (40 km) to the north of our new website, are being advanced as a museum thru a mission through the Nationwide Museums of Kenya. The general public, the native Daasanach folks, tutorial teams and vacationers will have the ability to see numerous 1.5-million-year-old hominin footprints on one excavated floor.
That layer preserves tracks of no less than 8 hominin people, and we now consider they constitute participants of each Homo erectus and Paranthropus boisei. Amongst those is a subset of people, all about the similar grownup measurement, who have been shifting in the similar route and seem to have been touring as a bunch alongside the lake margin.
The museum constructed over the tune website is designed to stop erosion of the website and to offer protection to it from seasonal rains. A group outreach and schooling heart related to the museum goals to have interaction native tutorial teams and younger folks in finding out and instructing others about this remarkable file of human prehistory preserved of their yard. The brand new website museum is scheduled to open in January 2025.





![Samsung by accident presentations off One UI 7 as leaked apps divulge deeper updates [Gallery] Samsung by accident presentations off One UI 7 as leaked apps divulge deeper updates [Gallery]](https://9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2024/10/one-ui-7-icons-sg-1.jpg?quality=82&strip=all&w=1600)




![[UPDATE] Even at 38% off for Black Friday, I will be able to’t counsel this mediocre gaming hand held when there’s a inexpensive and a lot better choice [UPDATE] Even at 38% off for Black Friday, I will be able to’t counsel this mediocre gaming hand held when there’s a inexpensive and a lot better choice](https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/n7V9VJYEvH6H2xXWxhZEf7.jpg)