Join the Begins With a Bang e-newsletter
Shuttle the universe with Dr. Ethan Siegel as he solutions the most important questions of all
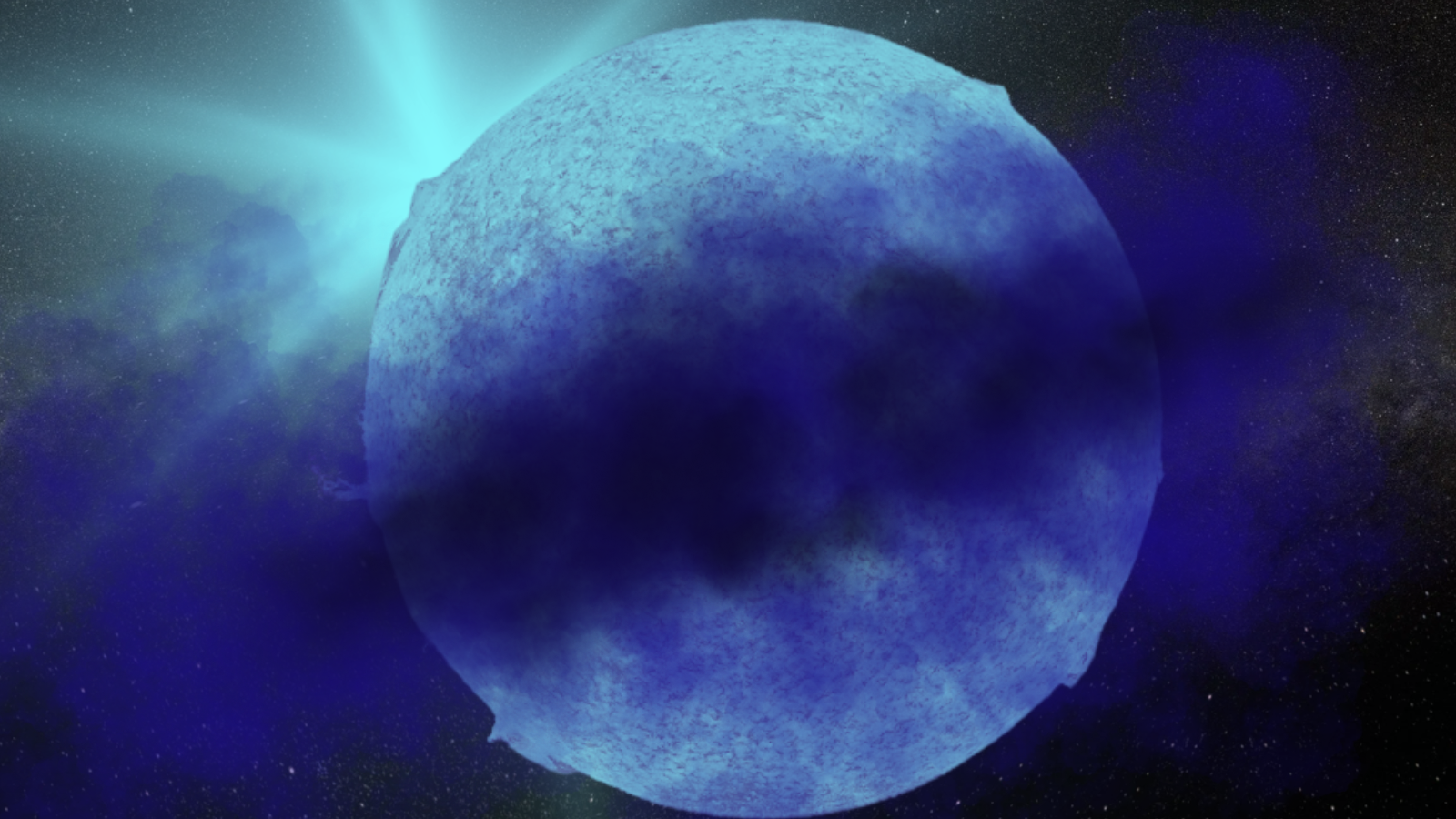
The celebrities within the night time sky, as we usually understand them, are typically static and unchanging to our eyes. Positive, there are variable stars that brighten and fainten, however maximum of the ones accomplish that periodically and frequently, with only some exceptions. Some of the outstanding exceptions is Betelgeuse, the crimson supergiant that makes up one of the vital “shoulders” of the constellation Orion. Over the last 5 years, now not solely has it been fluctuating in brightness, however its dimming in overdue 2019 and early 2020, adopted by way of a unusual brightening in 2023, signifies variation in a manner by no means earlier than witnessed by way of dwelling people.Betelgeuse is usually the tenth brightest big name in our sky, however fell out of the highest 20 all over its faintest in 2020 and rose as excessive because the seventh brightest in 2023. As a crimson supergiant, it’s just a subject of time earlier than it undergoes a core-collapse supernova, despite the fact that nobody is aware of how one can are expecting when that may happen. There’s no medical reason why to imagine that Betelgeuse is in any longer threat of going supernova lately than at any random day over the following ~100,000 years or so, however many people — together with a really perfect {many professional} and newbie astronomers — are hoping to witness the primary naked-eye supernova in our galaxy since 1604. Even if it received’t pose a threat to us, it’s going to be impressive. Right here’s what we’ll have the ability to practice from right here on Earth.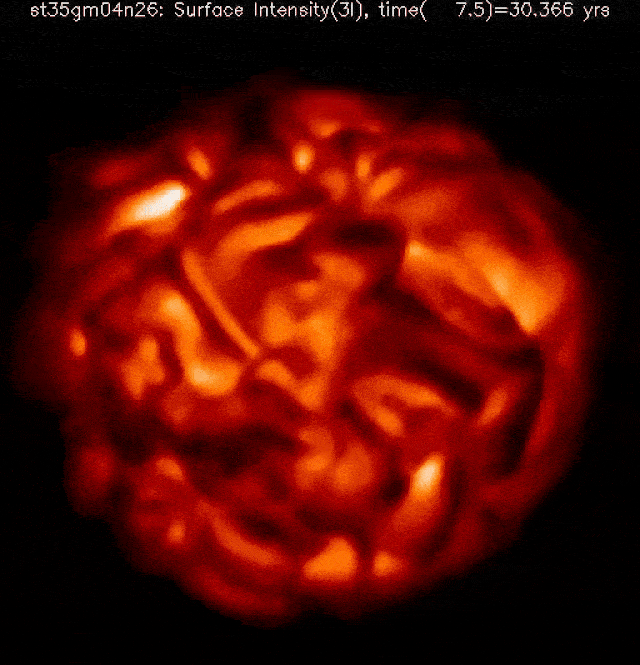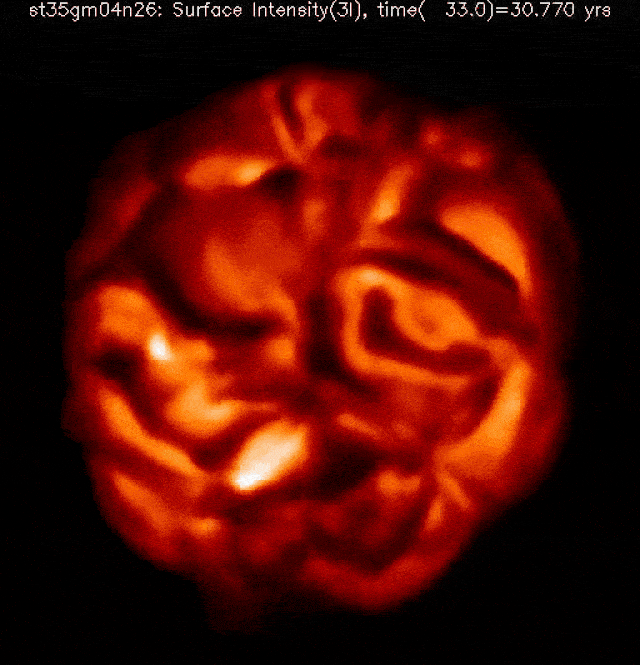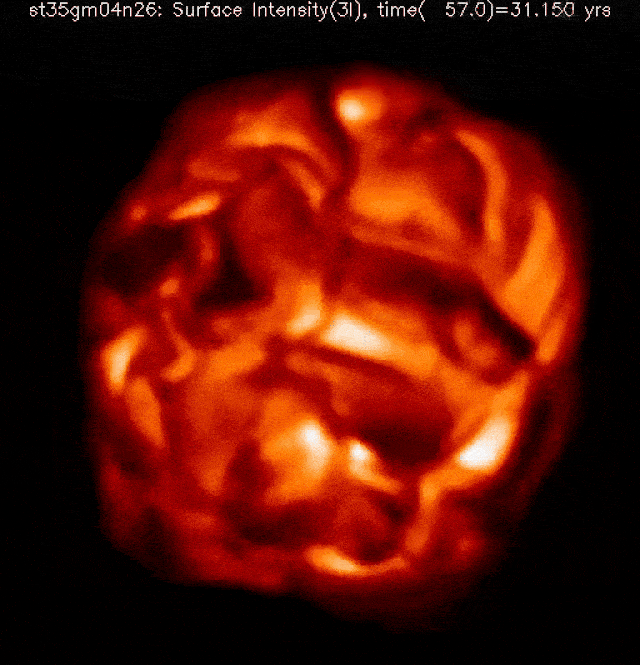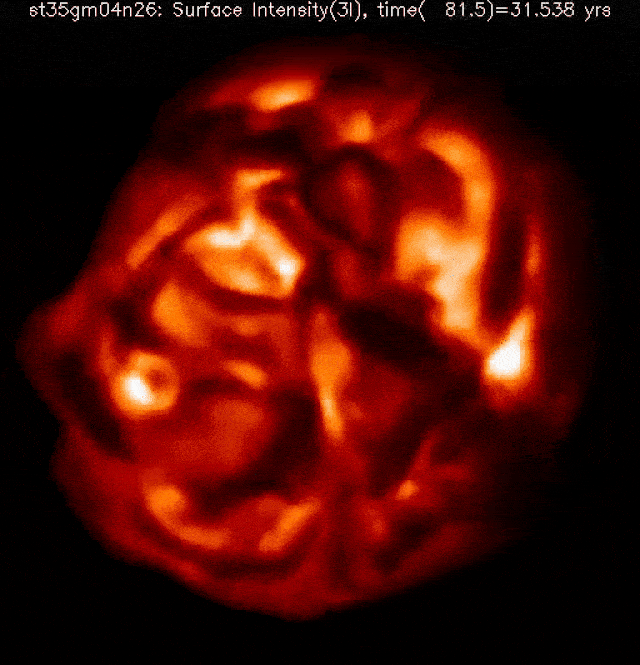 This simulation of a crimson supergiant’s floor, sped as much as show a whole yr of evolution in only a few seconds, displays how a “standard” crimson supergiant evolves all over a rather quiet length with out a perceptible adjustments to its inside processes. The enormity of its floor and the volatility of the tenuous outer layers results in super variability on brief however abnormal timescales.Credit score: Bernd Freytag, Susanne Höfner & Sofie Liljegren
This simulation of a crimson supergiant’s floor, sped as much as show a whole yr of evolution in only a few seconds, displays how a “standard” crimson supergiant evolves all over a rather quiet length with out a perceptible adjustments to its inside processes. The enormity of its floor and the volatility of the tenuous outer layers results in super variability on brief however abnormal timescales.Credit score: Bernd Freytag, Susanne Höfner & Sofie Liljegren
At this time, Betelgeuse is:
completely huge,
irregularly formed,
and with an asymmetric floor temperature.
Situated roughly 640 light-years away, it’s greater than 2,000 °C cooler than our Solar, but in addition a lot better, at roughly 900 instances our Solar’s radius and occupying some 700,000,000 instances our Solar’s quantity. In the event you had been to exchange our Solar with Betelgeuse, it might engulf Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, the asteroid belt, or even Jupiter!However there also are huge, prolonged emissions round Betelgeuse from subject material that’s been blown off over the last few dozen millennia: subject and gasoline that extends out farther than Neptune’s orbit round our Solar. Over the years, because the inevitable supernova approaches, Betelgeuse will shed extra mass, proceed to enlarge, dim-and-brighten chaotically, and can burn gradually heavier parts in its core.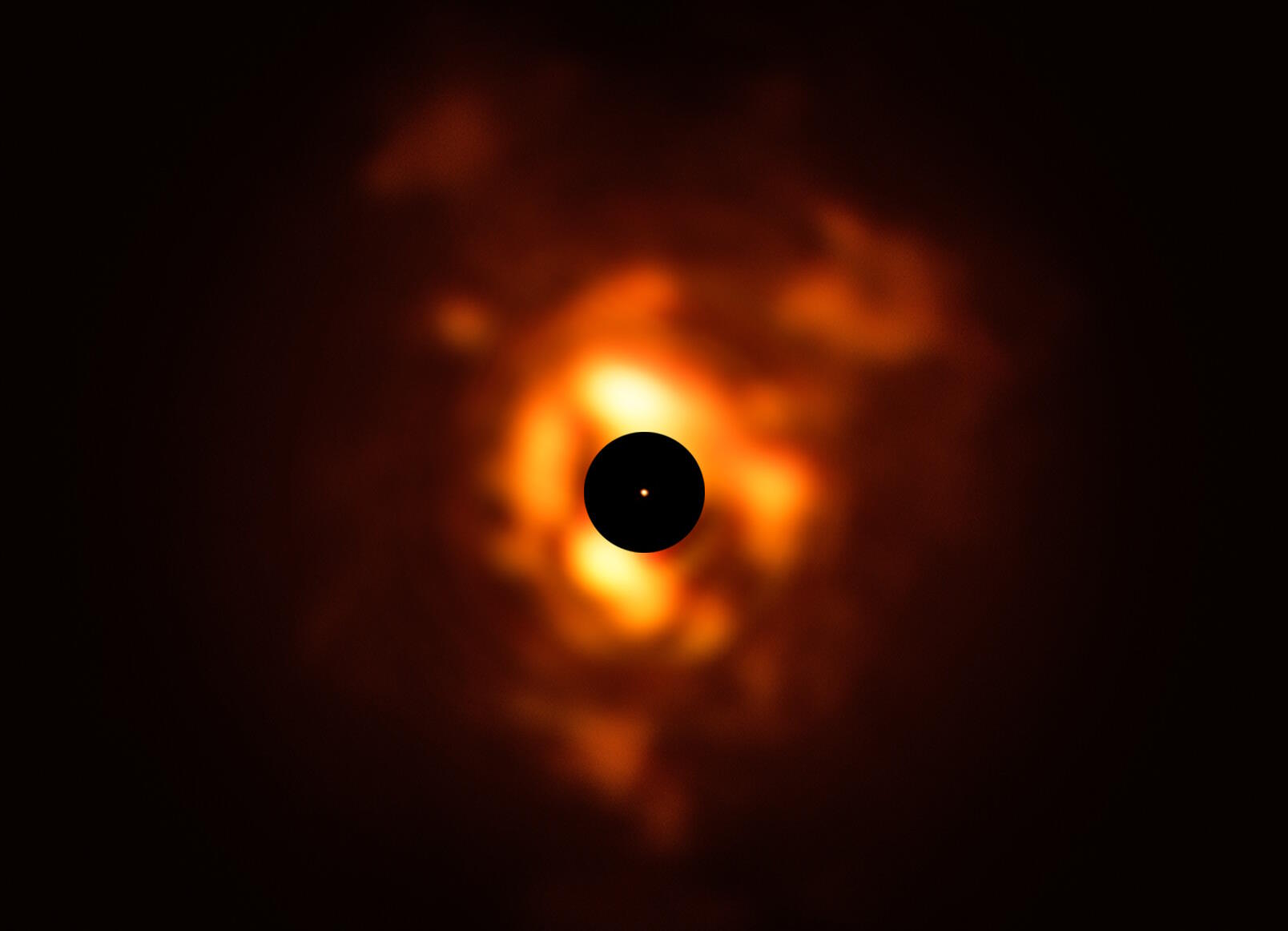 The nebula of expelled subject created round Betelgeuse, which, for scale, is proven within the inside crimson circle. This construction, comparable to flames emanating from the big name, paperwork since the behemoth is dropping its subject material into area. The prolonged emissions transcend the an identical of Neptune’s orbit across the Solar. Statistically, there’s round a 1-in-4000 probability that Betelgeuse has already exploded, and we’re simply looking ahead to the coming of its gentle.
The nebula of expelled subject created round Betelgeuse, which, for scale, is proven within the inside crimson circle. This construction, comparable to flames emanating from the big name, paperwork since the behemoth is dropping its subject material into area. The prolonged emissions transcend the an identical of Neptune’s orbit across the Solar. Statistically, there’s round a 1-in-4000 probability that Betelgeuse has already exploded, and we’re simply looking ahead to the coming of its gentle.
Credit score: ESO/P. Kervella/M. Montargès et al.; Acknowledgement: Eric Pantin
Even if it transitions to the extra complex phases of existence inside of its core, from carbon-burning to then neon and oxygen and ultimately silicon fusion, we received’t have any immediately observable signatures of the ones occasions. The velocity of the core’s fusion and effort output will alternate, however our figuring out of ways that has effects on the big name’s photosphere and chromosphere — the portions that we will be able to practice — is simply too deficient for us to extract concrete predictions about. The calories spectrum of the neutrinos produced within the core, the only observable we all know will alternate, will solely transform necessary all over the silicon-burning level, or even then, we’ll solely have a couple of days, most, to are expecting the eventual supernova.However at some crucial second within the big name’s evolutionary procedure, the interior core’s silicon burning will succeed in of completion, and the radiation power deep inside of Betelgeuse will plummet. As this power used to be the one factor maintaining the big name up in opposition to gravitational fall down, the interior core, composed of parts like iron, cobalt, and nickel, will then start to implode.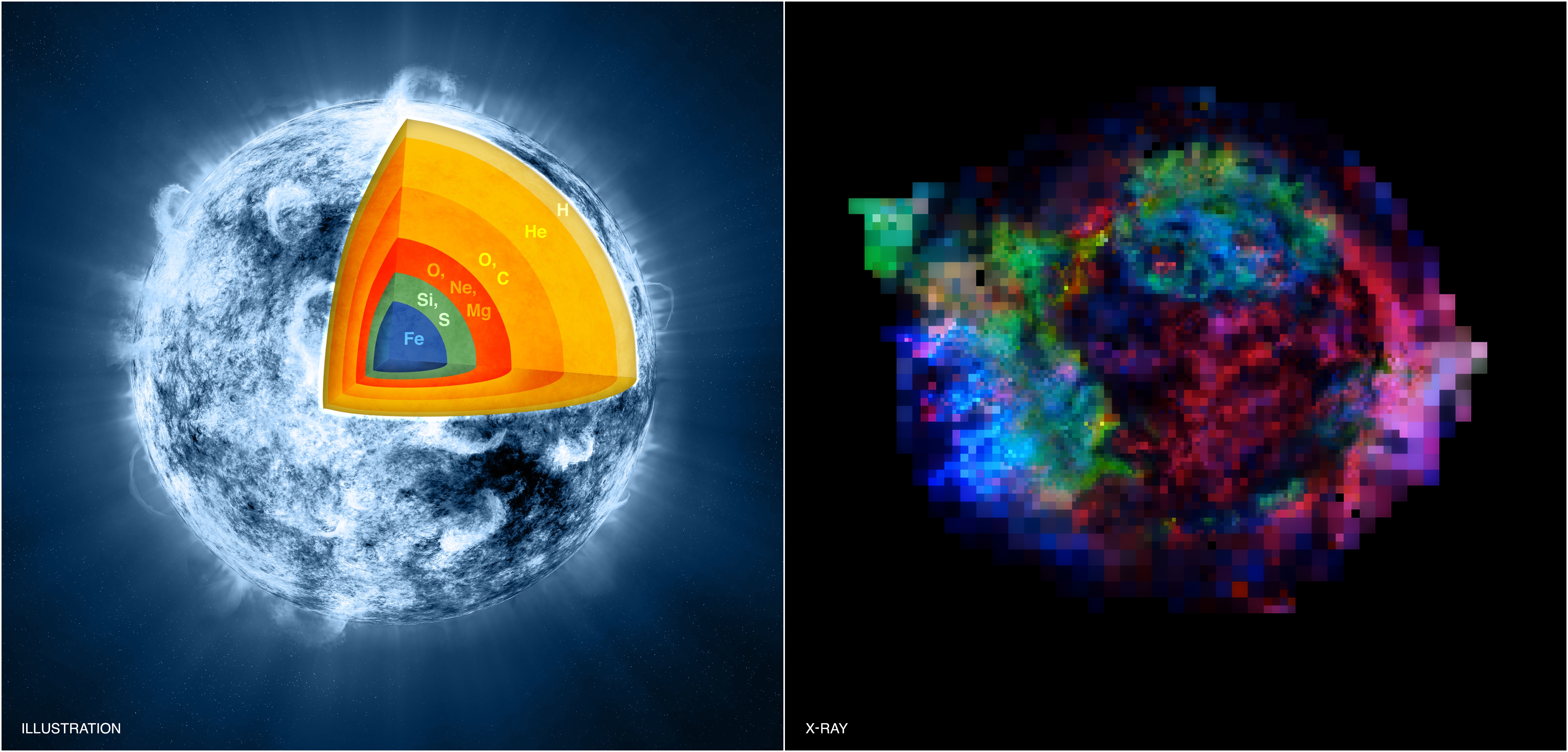 Artist’s representation (left) of the internal of an enormous big name within the ultimate phases, pre-supernova, of silicon-burning. (Silicon-burning is the place iron, nickel, and cobalt shape within the core.) A Chandra symbol (proper) of the Cassiopeia A supernova remnant lately displays parts like Iron (in blue), sulphur (inexperienced), and magnesium (crimson). Betelgeuse is predicted to practice an overly identical pathway to in the past noticed core-collapse supernovae.Credit: NASA/CXC/M.Weiss (representation, left) NASA/CXC/GSFC/U. Hwang & J. Laming (symbol, proper)
Artist’s representation (left) of the internal of an enormous big name within the ultimate phases, pre-supernova, of silicon-burning. (Silicon-burning is the place iron, nickel, and cobalt shape within the core.) A Chandra symbol (proper) of the Cassiopeia A supernova remnant lately displays parts like Iron (in blue), sulphur (inexperienced), and magnesium (crimson). Betelgeuse is predicted to practice an overly identical pathway to in the past noticed core-collapse supernovae.Credit: NASA/CXC/M.Weiss (representation, left) NASA/CXC/GSFC/U. Hwang & J. Laming (symbol, proper)
It’s tricky to believe the size of this: an object totaling about 20 sun lots, unfold out over the quantity of Jupiter’s orbit, whose internal core is similar to (and extra huge than) the scale of the Solar, starts to unexpectedly fall down. As huge because the gravitational pressure used to be pulling the whole thing in on itself, it used to be counterbalanced by way of the radiation power coming from nuclear fusion within the inside. Now, that fusion (and that outward power) is long gone, and fall down proceeds uninhibited.The innermost atomic nuclei — a dense number of iron, nickel, cobalt, and different identical parts — get forcefully scrunched in combination, the place they fuse into a huge ball of neutrons. The layers atop them additionally fall down, however rebound in opposition to the dense proto-neutron big name within the core, which triggers a fantastic burst of nuclear fusion. Because the layers pile up, they rebound, growing waves of fusion, radiation, and power that cascade throughout the big name.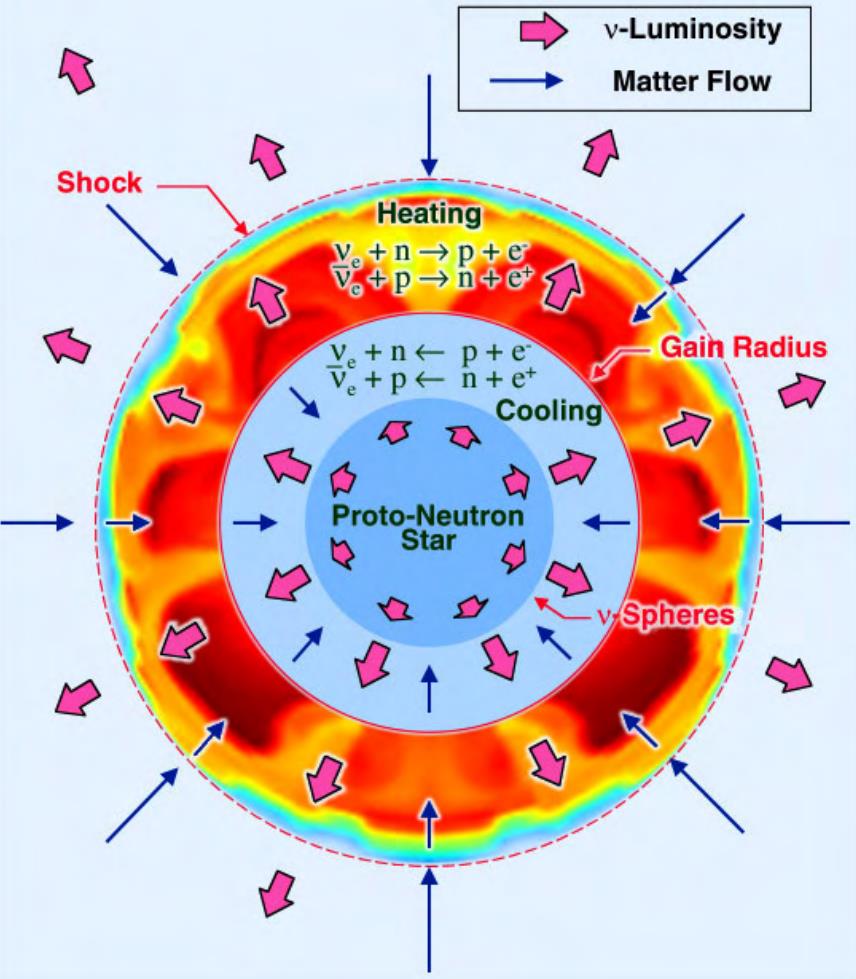 Within the internal areas of a celebrity that undergoes a core-collapse supernova, a neutron big name starts to shape within the core, whilst the outer layers crash in opposition to it and go through their very own runaway fusion reactions. Neutrons, neutrinos, radiation, and strange quantities of calories are produced, with neutrinos and antineutrinos wearing nearly all of the core-collapse supernova’s calories away. Whether or not the remnant turns into a neutron big name or black hollow, in the long run, depends upon how a lot mass stays within the core all over this procedure.
Within the internal areas of a celebrity that undergoes a core-collapse supernova, a neutron big name starts to shape within the core, whilst the outer layers crash in opposition to it and go through their very own runaway fusion reactions. Neutrons, neutrinos, radiation, and strange quantities of calories are produced, with neutrinos and antineutrinos wearing nearly all of the core-collapse supernova’s calories away. Whether or not the remnant turns into a neutron big name or black hollow, in the long run, depends upon how a lot mass stays within the core all over this procedure.
Credit score: TeraScale Supernova Initiative/Oak Ridge Nationwide Lab
Those fusion reactions happen over a shockingly transient timescale of solely roughly 10 seconds, and the vast majority of the calories is over excited within the type of neutrinos, which rarely engage with subject. The remainder energy-carrying debris, together with neutrons, nuclei, electrons, and photons, even with the serious quantities of calories imparted to them, must have their calories cascade and propagate via all the outer layers of the big name.On account of this, the neutrinos transform the primary indicators to flee, and the primary sign to reach on Earth. With the energies that supernovae impart to those debris — at the order of round ~10–50 MeV according to quantum of calories — the neutrinos will transfer at speeds indistinguishable from the velocity of sunshine. On every occasion the supernova in reality happens (or came about, which will have been anytime from the 14th century onward), it’s going to be the neutrinos that arrive right here on Earth first, some 640 years later. A neutrino match, identifiable by way of the rings of Cherenkov radiation that display up alongside the photomultiplier tubes lining the detector partitions, exhibit the a hit technique of neutrino astronomy. This symbol displays a couple of occasions, and is a part of the suite of experiments paving our approach to a better figuring out of neutrinos. The neutrinos detected in 1987 marked the daybreak of each neutrino astronomy and the rebranding of nucleon decay experiments as neutrino detector experiments.
A neutrino match, identifiable by way of the rings of Cherenkov radiation that display up alongside the photomultiplier tubes lining the detector partitions, exhibit the a hit technique of neutrino astronomy. This symbol displays a couple of occasions, and is a part of the suite of experiments paving our approach to a better figuring out of neutrinos. The neutrinos detected in 1987 marked the daybreak of each neutrino astronomy and the rebranding of nucleon decay experiments as neutrino detector experiments.
Credit score: Tremendous-Kamiokande Collaboration
In 1987, a supernova from 168,000 light-years away wound up making a sign of slightly over 20 neutrinos throughout 3 small neutrino detectors that had been running on the time. There are lots of other neutrino observatories in operation lately, a lot better and extra delicate than those we had at our disposal some 37 years in the past, and Betelgeuse, simply 640 light-years away solely, would ship a sign some 70,000 instances more potent on Earth because of its shut proximity.Now, on the finish of 2024, if Betelgeuse had been to move supernova, our first surefire signature would come within the type of high-energy neutrinos flooding our neutrino detectors everywhere the arena in a burst spanning some 10–15 seconds. There would actually be tens of millions, most likely even tens of tens of millions, of neutrinos picked up suddenly by way of those observatories. A couple of hours later, when the primary vigorous ripples created by way of this cataclysm reached the big name’s outer layers, a “breakout” of photons would succeed in us: a swift spike that larger Betelgeuse’s optical brightness enormously.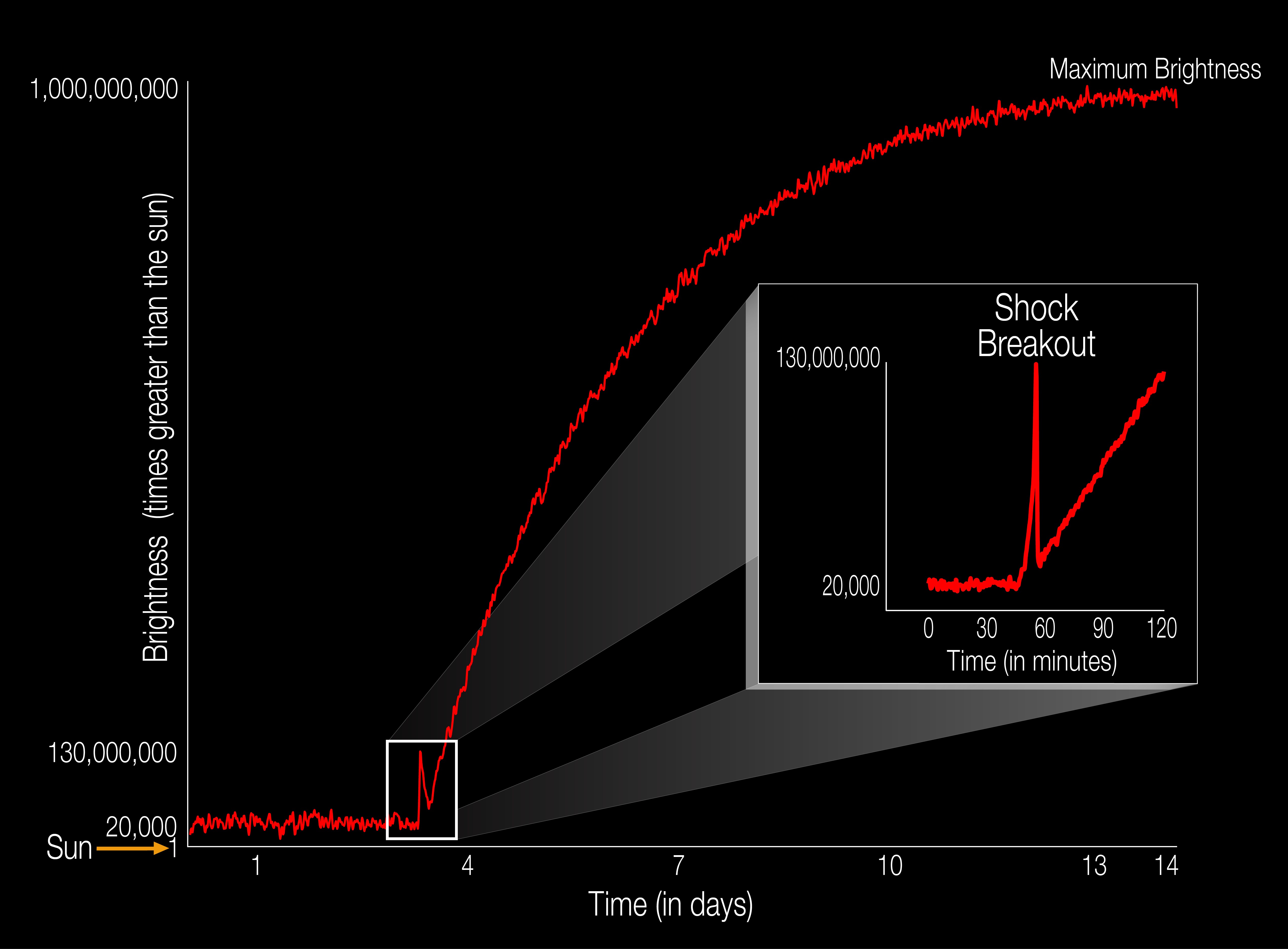 In 2011, one of the vital stars in a far off galaxy that came about to be within the box of view of NASA’s Kepler venture spontaneously and serendipitously went supernova. This marked the primary time {that a} supernova used to be stuck going on within the act of transitioning from a typical big name to a supernova match, with a stunning ‘breakout’ briefly expanding the big name’s brightness by way of an element of about 7,000 over its earlier price.
In 2011, one of the vital stars in a far off galaxy that came about to be within the box of view of NASA’s Kepler venture spontaneously and serendipitously went supernova. This marked the primary time {that a} supernova used to be stuck going on within the act of transitioning from a typical big name to a supernova match, with a stunning ‘breakout’ briefly expanding the big name’s brightness by way of an element of about 7,000 over its earlier price.
Credit score: NASA Ames/W. Stenzel
Unexpectedly, the luminosity of Betelgeuse would spike by way of a few issue of seven,000 from its in the past secure price. It might pass from one of the vital brightest stars within the night time sky to the brightness of a skinny crescent Moon: about 40 instances brighter than the planet Venus. That height brightness would solely remaining for a couple of mins earlier than falling once more again to being with reference to 5 instances brighter than it in the past used to be, however then the normal supernova upward push starts.Over a period of time of roughly 10 days, the brightness of Betelgeuse will step by step upward push, ultimately turning into about as shiny as the total Moon. Its brightness will surpass the entire stars and planets after about an hour, will succeed in that of a part Moon in 3 days, and can succeed in its most brightness after roughly 10 days. To skywatchers around the globe, Betelgeuse will seem to be even brighter than the total Moon, as as an alternative of being unfold out over part some extent (like the total Moon), all of its brightness will likely be concentrated right into a unmarried, solitary, saturated level.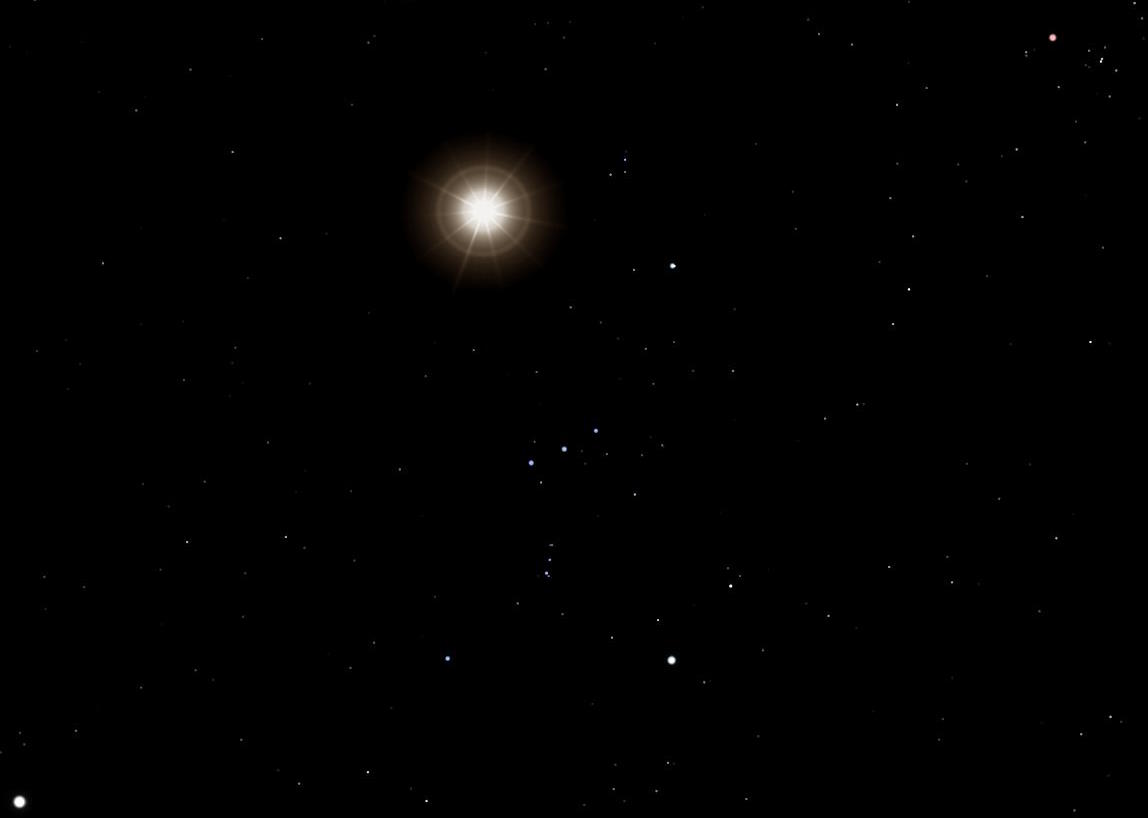 The constellation Orion as it might seem if Betelgeuse went supernova within the very close to long term. The big name would shine roughly as brightly as the total Moon, however the entire gentle could be concentrated to some extent, somewhat than prolonged over a disk that covers roughly part some extent. Top brightness must be completed more or less two weeks after the preliminary explosion.
The constellation Orion as it might seem if Betelgeuse went supernova within the very close to long term. The big name would shine roughly as brightly as the total Moon, however the entire gentle could be concentrated to some extent, somewhat than prolonged over a disk that covers roughly part some extent. Top brightness must be completed more or less two weeks after the preliminary explosion.
Credit score: HeNRyKus/Wikimedia Commons
As a kind II supernova, the sunshine from an exploded Betelgeuse will stay shiny for a somewhat very long time, despite the fact that there are huge diversifications inside of those categories of supernovae for precisely how shiny they transform and the way shiny they continue to be over lengthy sessions of time. (When such an match happens in our galaxy subsequent, it’s going to educate us an amazing quantity in regards to the dating between the progenitor big name and the supernova explosion that it produces!) The supernova, after attaining most brightness, will slowly start to fade over the timespan of a few month, turning into about as dim as a part Moon after 30 days time.Over the following two months, alternatively, its brightness will plateau, the place solely specialised tools and astrophotographers will have the ability to come across a minuscule dimming; the standard human eye won’t be able to discern a metamorphosis in brightness over this time. Following that length, alternatively, the brightness will drop precipitously and over the following (fourth) month since detonation: it’s going to return to slightly being brighter than Venus by way of the top of that point. And in any case, over the following yr or two, it’s going to step by step fade out of lifestyles, with the supernova remnant visual solely via telescopes.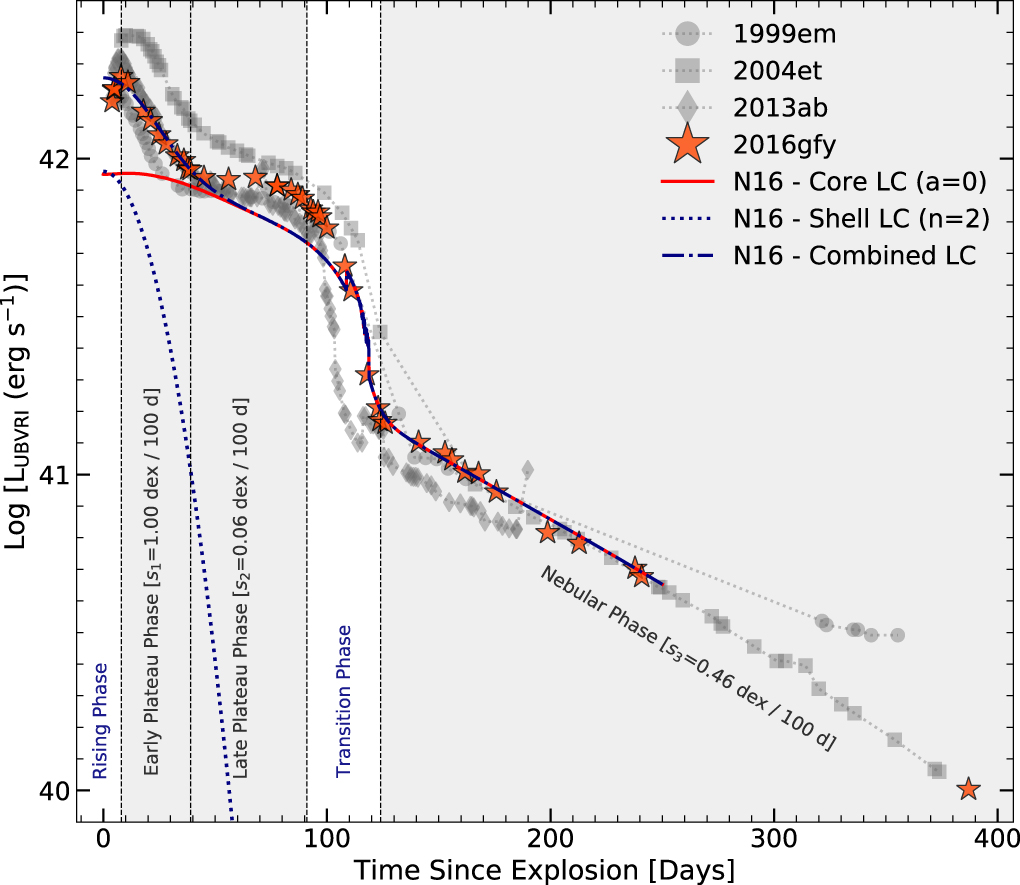 Sort II supernovae range between other sub-types and person occasions, however obey the similar common curve, with a upward push lasting roughly 10 days, a brief fall-off lasting a month, a plateau lasting every other two months, a steep drop lasting a month, after which a gentle fade-out lasting a yr or longer.
Sort II supernovae range between other sub-types and person occasions, however obey the similar common curve, with a upward push lasting roughly 10 days, a brief fall-off lasting a month, a plateau lasting every other two months, a steep drop lasting a month, after which a gentle fade-out lasting a yr or longer.
Credit score: A. Singh et al., Astrophysical Magazine, 2019
At height brightness, Betelgeuse will shine roughly as brightly as 10 billion Suns all packed in combination; by the point a few years have long gone by way of, it’s going to be too faint to be noticed with the bare human eye. The explanation the supernova stays so shiny for the primary 3 months or so isn’t even from the explosion itself, however somewhat from a mix of radioactive decays (from cobalt, for instance) and the increasing gases within the supernova remnant.All through the ones first 3 months or so, Betelgeuse will likely be so shiny that it’s going to be obviously visual all over the day in addition to the night time; solely after the fourth month or so will it transform a nighttime-only object. And because it starts to vanish from its brightness to seem like a typical big name as soon as once more, the prolonged buildings must stay illuminated via a telescope for many years, centuries, or even millennia to come back. It is going to transform the nearest supernova remnant in recorded historical past, and can stay a impressive sight (and astronomical object of research) for generations to come back.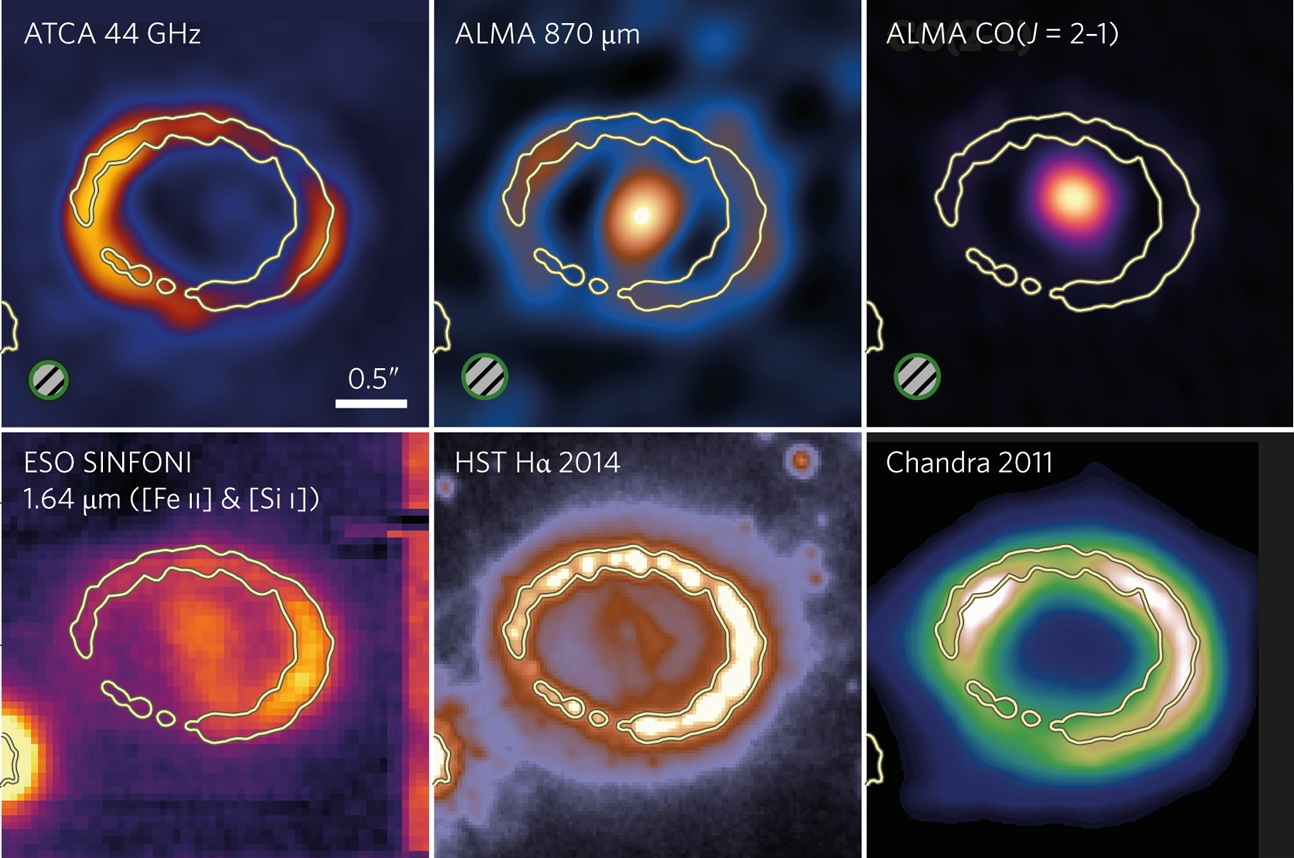 This symbol displays the supernova remnant of SN 1987A in six other wavelengths of sunshine. Even supposing it’s been 37 years since this explosion came about, and despite the fact that it’s proper right here in our personal yard, the fabric across the central engine has now not cleared sufficient to reveal the stellar remnant. For distinction, Cow-like items (often referred to as speedy blue optical transients) have their cores uncovered virtually right away.
This symbol displays the supernova remnant of SN 1987A in six other wavelengths of sunshine. Even supposing it’s been 37 years since this explosion came about, and despite the fact that it’s proper right here in our personal yard, the fabric across the central engine has now not cleared sufficient to reveal the stellar remnant. For distinction, Cow-like items (often referred to as speedy blue optical transients) have their cores uncovered virtually right away.
Credit score: Alak Ray, Nature Astronomy, 2017; ACTA/ALMA/ESO/Hubble/Chandra composite
On every occasion Betelgeuse (or a in a similar fashion shut crimson supergiant) in any case does pass supernova — and it may well be this night, subsequent decade, or 100,000 years from now — it’s going to transform the most-witnessed astronomical match in human historical past, visual to the majority of Earth’s population. The primary sign to reach received’t be visible in any respect, however will come within the type of neutrinos, a usually elusive particle that may flood our terrestrial detectors by way of the tens of millions.After that, a couple of hours later, the sunshine will first arrive in a spike, adopted by way of a gentle brightening over slightly greater than per week, which can fall off in phases over the approaching months earlier than step by step declining for years. The remnant, which is composed of gaseous outer layers illuminated for 1000’s of years, will proceed to please our descendants for generations to come back. We haven’t any concept when the display will start, however a minimum of we all know what to search for and be expecting when it in reality happens!
Join the Begins With a Bang e-newsletter
Shuttle the universe with Dr. Ethan Siegel as he solutions the most important questions of all