Find out about screening and normal traits of are studiesOur systematic evaluation and meta-analysis initiated with the method of literature seek and screening. The PRISMA glide diagram of the incorporated research is gifted in Fig. 1.Right through the literature screening procedure, D.S. took the lead position in making inclusion choices, each on the ‘name and summary degree’ and the ‘complete textual content screening degree,’ in session with different researchers. No important confrontation between authors was once discovered on this procedure. Desk S3 lists the research that investigated the associations of our pursuits from sure views but had been excluded because of their deviation from our evaluation’s exact scope, together with the explanations for his or her exclusion.Fig. 1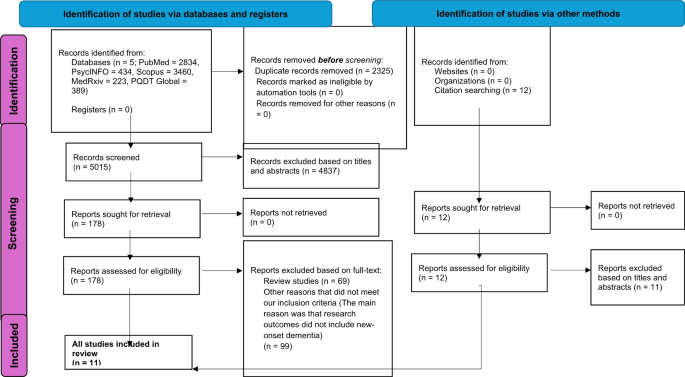 Most popular Reporting Pieces for Systematic Opinions and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) diagram demonstrating seek strategyThis process because of this resulted within the inclusion of knowledge from 939,824 post-COVID-19 circumstances and six,765,117 controls throughout 11 research [6, 9, 12, 13, 27,28,29,30,31,32,33], as detailed in Desk 1. Some of these research investigated the chance of NOD in older adults with and with out COVID-19 an infection over various observational classes. The full prevalence of NOD within the COVID-infected workforce was once round 1.82% (starting from 0.3 to six.4%), whilst the non-COVID-infected workforce exhibited an prevalence of round 0.35% (starting from 0.0 to five.0%), over an average remark duration of three hundred and sixty five days (starting from 3 to 24 months). To interpret, the whole prevalence was once calculated via aggregating the choice of NOD circumstances and the entire choice of people within the COVID-19-infected or non-COVID-infected teams throughout all incorporated research to procure an averaged prevalence. As an example, to calculate the averaged total prevalence within the COVID-infected workforce, we summed the NOD circumstances in particular from the COVID-infected workforce from every learn about and divided them via the entire choice of contributors within the COVID-infected teams. We implemented the similar technique to calculate the averaged total prevalence within the non-COVID-infected workforce, and the prevalence in particular person research. In research reporting incidences for various follow-up classes (e.g., 3, 6, 12, or 24 months), we used the longest to be had follow-up duration for consistency.Desk 1 A abstract of the overall traits of the 11 research incorporated on this reviewOf word, 5 research hired Propensity Ranking Matching (PSM) to ascertain 1:1 matched cohorts of older adults with out COVID-19, subsequently making sure comparison of baseline traits between COVID-positive and keep watch over teams [12, 27, 28, 30, 32]. The dementia possibility within the COVID-positive workforce was once in comparison to two varieties of keep watch over teams: non-COVID cohorts with different respiration infections [control group (C1)] [12, 28, 30, 31, 33], and non-COVID cohorts with another way unspecified well being standing [control group (C2)] [6, 9, 13, 27, 29, 32, 33]. As well as, whilst 9 research recorded definitive dementia diagnoses the usage of ICD-10, the TICS-40 in Liu et al.‘s research was once used to suggest, moderately than ascertain, dementia [6, 9]. The focal point was once on all-cause dementia (basically together with AD, vascular dementia, and unspecified dementia) in 8 research, whilst the rest 3 in particular tested AD [13, 32, 33]. In research addressing all-cause dementia, AD was once probably the most prevalent kind (in the event that they reported the proportions of every dementia subtype), adopted via vascular dementia [29, 31]. Discuss with Desk 1 for extra main points of alternative traits.High quality assessmentEvery learn about incorporated in our evaluation was once rated as excellent high quality (≥ 7 stars) according to the NOS high quality evaluation standards [34], as the main points proven in Desk S4(a) for 10 cohort research and Desk S4(b) for one cross-sectional learn about (longitudinal in nature with a cross-sectional evaluation). No confrontation in regards to the high quality appraisal amongst incorporated research between researchers was once discovered. The research via Park et al. and Qureshi et al. every misplaced one level for NOS comparison pieces, as they simply managed for demographic options, however now not for recognized dementia possibility components such because the frame mass index, alcohol intake, smoking historical past and bodily job [29, 30]. The research via Liu et al. in 2021 and 2022 every misplaced one level at the merchandise ‘evaluation of the end result’ for the reason that cognitive standing of the contributors was once self-reported [6, 9]. The learn about via Zarifkar et al. misplaced two issues on NOS comparison pieces, because of its failure to keep watch over for age, intercourse, and different components [33]. The research via Cohen et al. [27], Liu et al. in 2021 [6], Park et al. [29], and Taquet et al. in 2021 [31], misplaced one level at the NOS end result pieces because of their failure to offer a follow-up duration of a minimum of three hundred and sixty five days for results to happen.General pooled meta-analysis effects from all 11 incorporated studiesIn the primary pooled evaluation, the woodland plot in Fig. 2 confirmed the diversities in NOD dangers between COVID-infected workforce and non-COVID-infected workforce around the 11 incorporated research. A random-effects REML fashion was once used because of considerable heterogeneity. We didn’t distinguish between non-COVID-19 statuses, grouping in combination each wholesome people and the ones with different varieties of respiration infections as controls. The full pooled evaluation published a vital hyperlink between COVID-19 an infection and greater possibility for NOD in COVID-19 older grownup survivors (RR = 1.58, 95% CI 1.21–2.08, p < 0.001; I2 = 98.57%, p < 0.001).Amongst separate research, 9 out of eleven research reported an greater possibility for creating NOD in COVID-infected older adults, compared to their non-infected opposite numbers [6, 9, 12, 13, 27, 30,31,32,33]. Particularly, in comparison to 8 research indicating a RR from 1.28 to 4.87, one learn about confirmed that COVID-19 an infection ended in a chance of creating NOD that was once greater than 20 instances that of the ones uninfected (RR = 20.92, 95% CI 1.29-340.63) [6], albeit contributing minimally to the whole weight (0.87%). 0 dementia occasions within the non-COVID-infected workforce had been reported on this learn about, which might theoretically lead to an unlimited possibility ratio [6]. On the other hand, the statistical instrument addressed this problem in meta-analyses via using a continuity correction. For the learn about in query, this concerned including a nominal price of 0.5 to every mobile of the two × 2 contingency desk. This adjustment was once designed to mitigate the computational difficulties posed via 0 occasions and to permit for the estimation of an adjusted possibility ratio [35]. The similar approaches had been implemented throughout all meta-analyses, as essential.By contrast, one learn about steered no important distinction in NOD possibility between COVID-infected and non-infected teams (RR = 1.03, 95% CI 0.83–1.30) [28], whilst every other learn about via Park et al. steered a protecting impact of COVID-19 an infection in opposition to NOD possibility (RR = 0.64, 95% CI 0.48–0.86) [29]. On the other hand, we spotted that this possibility ratio (i.e., 0.64) was once calculated via us with out bearing in mind confounding covariates. Of their authentic article [29], a constantly upper possibility of NOD in COVID-infected people was once noticed throughout all age teams of their fashions adjusted for more than one covariates. Due to this fact, it may be inferred that, had changes for confounding components been conceivable (that have been now not carried out via us because of inaccessible related information), COVID-19 an infection may just nonetheless be related to an greater NOD possibility amongst older grownup survivors in our evaluation.Fig. 2
Most popular Reporting Pieces for Systematic Opinions and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) diagram demonstrating seek strategyThis process because of this resulted within the inclusion of knowledge from 939,824 post-COVID-19 circumstances and six,765,117 controls throughout 11 research [6, 9, 12, 13, 27,28,29,30,31,32,33], as detailed in Desk 1. Some of these research investigated the chance of NOD in older adults with and with out COVID-19 an infection over various observational classes. The full prevalence of NOD within the COVID-infected workforce was once round 1.82% (starting from 0.3 to six.4%), whilst the non-COVID-infected workforce exhibited an prevalence of round 0.35% (starting from 0.0 to five.0%), over an average remark duration of three hundred and sixty five days (starting from 3 to 24 months). To interpret, the whole prevalence was once calculated via aggregating the choice of NOD circumstances and the entire choice of people within the COVID-19-infected or non-COVID-infected teams throughout all incorporated research to procure an averaged prevalence. As an example, to calculate the averaged total prevalence within the COVID-infected workforce, we summed the NOD circumstances in particular from the COVID-infected workforce from every learn about and divided them via the entire choice of contributors within the COVID-infected teams. We implemented the similar technique to calculate the averaged total prevalence within the non-COVID-infected workforce, and the prevalence in particular person research. In research reporting incidences for various follow-up classes (e.g., 3, 6, 12, or 24 months), we used the longest to be had follow-up duration for consistency.Desk 1 A abstract of the overall traits of the 11 research incorporated on this reviewOf word, 5 research hired Propensity Ranking Matching (PSM) to ascertain 1:1 matched cohorts of older adults with out COVID-19, subsequently making sure comparison of baseline traits between COVID-positive and keep watch over teams [12, 27, 28, 30, 32]. The dementia possibility within the COVID-positive workforce was once in comparison to two varieties of keep watch over teams: non-COVID cohorts with different respiration infections [control group (C1)] [12, 28, 30, 31, 33], and non-COVID cohorts with another way unspecified well being standing [control group (C2)] [6, 9, 13, 27, 29, 32, 33]. As well as, whilst 9 research recorded definitive dementia diagnoses the usage of ICD-10, the TICS-40 in Liu et al.‘s research was once used to suggest, moderately than ascertain, dementia [6, 9]. The focal point was once on all-cause dementia (basically together with AD, vascular dementia, and unspecified dementia) in 8 research, whilst the rest 3 in particular tested AD [13, 32, 33]. In research addressing all-cause dementia, AD was once probably the most prevalent kind (in the event that they reported the proportions of every dementia subtype), adopted via vascular dementia [29, 31]. Discuss with Desk 1 for extra main points of alternative traits.High quality assessmentEvery learn about incorporated in our evaluation was once rated as excellent high quality (≥ 7 stars) according to the NOS high quality evaluation standards [34], as the main points proven in Desk S4(a) for 10 cohort research and Desk S4(b) for one cross-sectional learn about (longitudinal in nature with a cross-sectional evaluation). No confrontation in regards to the high quality appraisal amongst incorporated research between researchers was once discovered. The research via Park et al. and Qureshi et al. every misplaced one level for NOS comparison pieces, as they simply managed for demographic options, however now not for recognized dementia possibility components such because the frame mass index, alcohol intake, smoking historical past and bodily job [29, 30]. The research via Liu et al. in 2021 and 2022 every misplaced one level at the merchandise ‘evaluation of the end result’ for the reason that cognitive standing of the contributors was once self-reported [6, 9]. The learn about via Zarifkar et al. misplaced two issues on NOS comparison pieces, because of its failure to keep watch over for age, intercourse, and different components [33]. The research via Cohen et al. [27], Liu et al. in 2021 [6], Park et al. [29], and Taquet et al. in 2021 [31], misplaced one level at the NOS end result pieces because of their failure to offer a follow-up duration of a minimum of three hundred and sixty five days for results to happen.General pooled meta-analysis effects from all 11 incorporated studiesIn the primary pooled evaluation, the woodland plot in Fig. 2 confirmed the diversities in NOD dangers between COVID-infected workforce and non-COVID-infected workforce around the 11 incorporated research. A random-effects REML fashion was once used because of considerable heterogeneity. We didn’t distinguish between non-COVID-19 statuses, grouping in combination each wholesome people and the ones with different varieties of respiration infections as controls. The full pooled evaluation published a vital hyperlink between COVID-19 an infection and greater possibility for NOD in COVID-19 older grownup survivors (RR = 1.58, 95% CI 1.21–2.08, p < 0.001; I2 = 98.57%, p < 0.001).Amongst separate research, 9 out of eleven research reported an greater possibility for creating NOD in COVID-infected older adults, compared to their non-infected opposite numbers [6, 9, 12, 13, 27, 30,31,32,33]. Particularly, in comparison to 8 research indicating a RR from 1.28 to 4.87, one learn about confirmed that COVID-19 an infection ended in a chance of creating NOD that was once greater than 20 instances that of the ones uninfected (RR = 20.92, 95% CI 1.29-340.63) [6], albeit contributing minimally to the whole weight (0.87%). 0 dementia occasions within the non-COVID-infected workforce had been reported on this learn about, which might theoretically lead to an unlimited possibility ratio [6]. On the other hand, the statistical instrument addressed this problem in meta-analyses via using a continuity correction. For the learn about in query, this concerned including a nominal price of 0.5 to every mobile of the two × 2 contingency desk. This adjustment was once designed to mitigate the computational difficulties posed via 0 occasions and to permit for the estimation of an adjusted possibility ratio [35]. The similar approaches had been implemented throughout all meta-analyses, as essential.By contrast, one learn about steered no important distinction in NOD possibility between COVID-infected and non-infected teams (RR = 1.03, 95% CI 0.83–1.30) [28], whilst every other learn about via Park et al. steered a protecting impact of COVID-19 an infection in opposition to NOD possibility (RR = 0.64, 95% CI 0.48–0.86) [29]. On the other hand, we spotted that this possibility ratio (i.e., 0.64) was once calculated via us with out bearing in mind confounding covariates. Of their authentic article [29], a constantly upper possibility of NOD in COVID-infected people was once noticed throughout all age teams of their fashions adjusted for more than one covariates. Due to this fact, it may be inferred that, had changes for confounding components been conceivable (that have been now not carried out via us because of inaccessible related information), COVID-19 an infection may just nonetheless be related to an greater NOD possibility amongst older grownup survivors in our evaluation.Fig. 2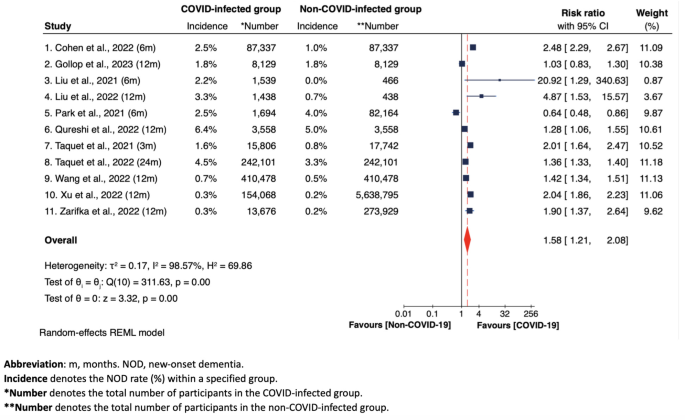 Wooded area plot of total pooled meta-analysis of NOD possibility between COVID-infected workforce and non-COVID-infected workforce throughout all 11 studiesSubgroup analysesFigures 3, 4 and 5, in conjunction with Supplementary Figures S1 to S5, show the result of subgroup analyses, analyzing: (i) NOD possibility only according to observational periods (i.e., at 3, 6, 12, 24 months) (Fig. 3); (ii) NOD possibility according to COVID-19 an infection standing [infected vs. other respiratory infections (C1) (Fig. 4), and infected vs. uninfected (C2) (Fig. 5)]; (iii) possibility of creating cognitive impairment in COVID-infected workforce in comparison to non-COVID-infected workforce (right here C1 and C2 had been grouped in combination), with cognitive impairment (together with each CIND and dementia circumstances) because the measured end result (Determine S1); (iv) NOD possibility throughout 3 teams – the ones trying out fine for COVID-19, the ones with different respiration infections, and the ones trying out unfavorable for COVID-19 another way unspecified, in particular according to intercourse variations (Determine S2); and (v). NOD possibility amongst COVID-19 sufferers, categorised via COVID-19 severity (Determine S3 and S4); and (vi) NOD possibility between COVID-infected and non-COVID-infected teams amongst research using propensity-score matching means (Determine S5). A majority of these subgroup meta-analyses implemented random-effects REML fashions because of considerable heterogeneity.Fig. 3
Wooded area plot of total pooled meta-analysis of NOD possibility between COVID-infected workforce and non-COVID-infected workforce throughout all 11 studiesSubgroup analysesFigures 3, 4 and 5, in conjunction with Supplementary Figures S1 to S5, show the result of subgroup analyses, analyzing: (i) NOD possibility only according to observational periods (i.e., at 3, 6, 12, 24 months) (Fig. 3); (ii) NOD possibility according to COVID-19 an infection standing [infected vs. other respiratory infections (C1) (Fig. 4), and infected vs. uninfected (C2) (Fig. 5)]; (iii) possibility of creating cognitive impairment in COVID-infected workforce in comparison to non-COVID-infected workforce (right here C1 and C2 had been grouped in combination), with cognitive impairment (together with each CIND and dementia circumstances) because the measured end result (Determine S1); (iv) NOD possibility throughout 3 teams – the ones trying out fine for COVID-19, the ones with different respiration infections, and the ones trying out unfavorable for COVID-19 another way unspecified, in particular according to intercourse variations (Determine S2); and (v). NOD possibility amongst COVID-19 sufferers, categorised via COVID-19 severity (Determine S3 and S4); and (vi) NOD possibility between COVID-infected and non-COVID-infected teams amongst research using propensity-score matching means (Determine S5). A majority of these subgroup meta-analyses implemented random-effects REML fashions because of considerable heterogeneity.Fig. 3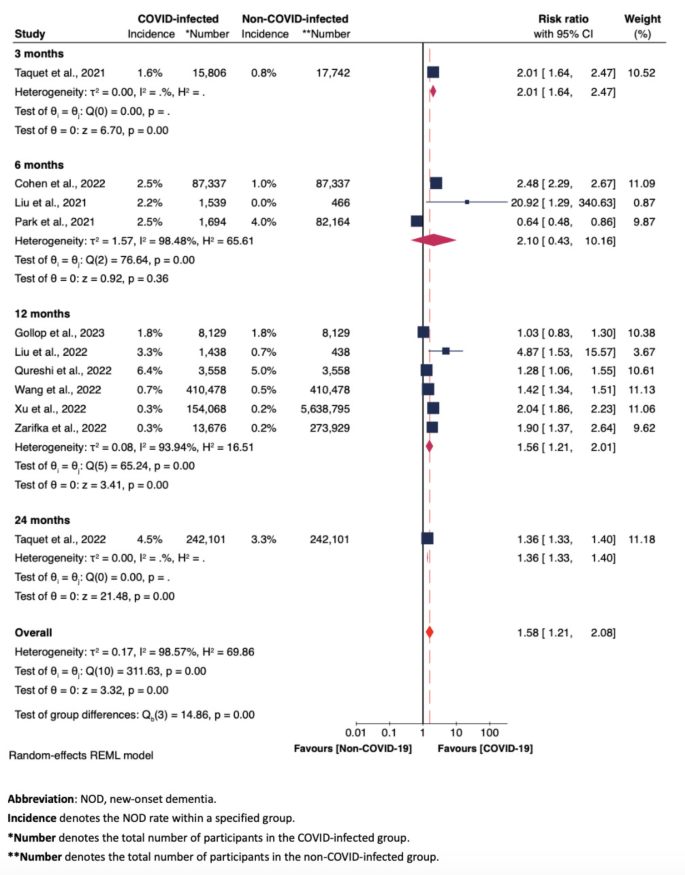 Wooded area plot of the meta-analysis of NOD possibility between COVID-infected workforce and non-COVID-infected workforce at 3, 6, 12, 24 months, involving all 11 studiesFig. 4
Wooded area plot of the meta-analysis of NOD possibility between COVID-infected workforce and non-COVID-infected workforce at 3, 6, 12, 24 months, involving all 11 studiesFig. 4 Wooded area plot of the meta-analysis of NOD possibility between COVID-infected workforce and C1 workforce at 3, 6, 12, 24 monthsFig. 5
Wooded area plot of the meta-analysis of NOD possibility between COVID-infected workforce and C1 workforce at 3, 6, 12, 24 monthsFig. 5 Wooded area plot of the meta-analysis of NOD possibility between COVID-infected workforce and C2 workforce at 3, 6, 12, 24 monthsNOD possibility amongst COVID-infected and non-COVID-infected teams, according to observational periodsFigure 3 illustrates that, when analyzing pooled effects from multiple particular person learn about, the chance ratio at three hundred and sixty five days was once considerably larger within the workforce contaminated with COVID-19 (RR = 1.56, 95% CI 1.21–2.01), carefully aligning with the whole pooled possibility ratio in Fig. 2 (RR = 1.58, 95% CI 1.21–2.08). Additionally, this subset shows diminished heterogeneity (I2 = 93.94%, Fig. 3) compared to the wider evaluation of all 11 research (I2 = 98.57%, Fig. 2). On the other hand, the rise in possibility ratio at six months was once now not statistically important (RR = 2.10, 95% CI 0.43–10.16). This loss of importance may also be attributed to the outlier possibility ratio of 0.64 reported via Park et al., which was once a price sooner than adjustment [29].NOD possibility amongst COVID-Inflamed, non-COVID-infected another way unspecified, and non-COVID-infected with different respiration infections teams throughout follow-up periodsFigure 4 displays no exceptional distinction about NOD possibility between the COVID-19 workforce and the non-COVID cohorts with different respiration infections [C1 group] (total RR = 1.13, 95% CI 0.92–1.38). Determine 5 displays a considerably greater possibility for NOD within the COVID-19 workforce in comparison to the non-COVID cohorts with another way unspecified well being statuses [C2 group] at three hundred and sixty five days post-COVID-19 (RR = 1.84, 95% CI 1.41–2.38). This greater possibility was once now not obtrusive at 3 months (RR = 0.87, 95% CI 0.46–1.65) or six months (RR = 1.73, 95% CI 0.72–4.14). Right here the loss of statistical importance at six months may also be attributed to the end result from Park et al. [29], which, as soon as adjusted, may just give a contribution to an total important build up in NOD possibility at six months.Comparability of newly evolved cognitive impairment possibility between COVID-infected and non-COVID-infected groupsFigure S1 displays that, a few of the 3 research which explored the chance of creating new-onset cognitive impairment between the COVID-Inflamed and the non-COVID-infected teams [6, 9, 27], a vital greater possibility for NOD was once noticed within the COVID-infected workforce (total RR = 1.93, 95% CI 1.52–2.43, p < 0.001; I2 = 79.04%, p < 0.001). In different phrases, cognitive impairment was once just about two times as most probably in COVID-19 older grownup survivors in comparison to the ones with out COVID-19 an infection.NOD possibility according to intercourse in COVID-positive, different respiration an infection, and COVID-negative another way unspecified teams, separatelyNotably, Determine S2 displays upper NOD dangers for girls on each the COVID-positive workforce (RR = 1.65, 95% CI 1.53–1.78, p < 0.001; I2 = 0.00%, p > 0.05) and COVID-negative another way unspecified keep watch over workforce (RR = 1.33, 95% CI 1.22–1.44, p < 0.001; I2 = 0.00%, p > 0.05), indicating that COVID-19 an infection itself was once now not a big underlying issue making ladies extra vulnerable to creating NOD when compared with males.NOD possibility amongst COVID-infected sufferers, according to COVID-19 severity (inpatient vs. outpatient)Each Figures S3 and S4 display considerably upper dangers for NOD amongst COVID-infected older grownup outpatients (RR = 1.91, 95% CI 1.06–3.45) and inpatients (RR = 3.06, 95% CI 2.78–3.37), as in comparison to COVID-negative older adults.NOD possibility between COVID-infected and non-COVID-infected teams, according to research with propensity rating matching (PSM)Determine S5 signifies that the one 5 research the usage of PSM reported an greater NOD possibility within the COVID-infected workforce (General RR = 1.46, 95% CI 1.10–1.94) [12, 27, 28, 30, 32]. This build up in NOD possibility is in step with the findings from our primary evaluation, which contains all 11 research (General RR = 1.58, Fig. 2).General heterogeneity and sensitivity analysesWe noticed considerable heterogeneity a few of the 11 incorporated research in our primary total pooled meta-analysis in Fig. 2 (I2 = 98.57%, p < 0.001). Additionally, L’Abbé and Galbraith plots, as proven in Determine S6 and Determine S7, visually point out the discrepancies amongst those research. Opposite to expectancies, the meta-regression effects, as proven in Determine S8, recommend that covariates comparable to observational periods (3, 6, 12, 24 months), varieties of keep watch over teams (non-COVID cohorts another way unspecified vs. non-COVID cohorts with different varieties of respiration infections), and dementia varieties assessed (all-cause dementia vs. AD) didn’t give a contribution to the range a few of the 11 research. The sensitivity evaluation, as proven in Determine S9, means that the whole effects remained constant in spite of the elimination of every particular person learn about (with applicable adjustments in impact dimension starting from 0.09 to 0.12), indicating that the findings of our primary meta-analysis in Fig. 2 had been powerful and now not overly depending on any unmarried learn about.E-newsletter biasThe contour-enhanced funnel plot, illustrated in Determine S10, visually signifies possible asymmetry, hinting at newsletter bias. Two imputed research had been strategically positioned to reflect the asymmetrical gaps. On the other hand, the regression-based Egger’s check (p = 0.052) and the nonparametric rank correlation Begg’s check (p = 0.978) don’t supply sturdy proof of important newsletter bias in our primary total pooled meta-analysis. In the meantime, incorporating the 2 imputed research into the evaluation yields a revised pooled impact dimension for a complete of 13 research (RR = 1.48, 95% CI 1.12–1.96), which nonetheless does now not markedly vary from the preliminary evaluation (RR = 1.58, 95% CI 1.21–2.08). As well as, the common high quality appraisal (NOS) rating of 8.1 [standard deviation (SD) = 0.79] is suggestive of a excellent methodological high quality of the 11 incorporated research. All incorporated research correctly constitute the objective inhabitants, investigating the have an effect on of COVID-19 at the NOD possibility in older adults, with sufficient pattern sizes all over.
Wooded area plot of the meta-analysis of NOD possibility between COVID-infected workforce and C2 workforce at 3, 6, 12, 24 monthsNOD possibility amongst COVID-infected and non-COVID-infected teams, according to observational periodsFigure 3 illustrates that, when analyzing pooled effects from multiple particular person learn about, the chance ratio at three hundred and sixty five days was once considerably larger within the workforce contaminated with COVID-19 (RR = 1.56, 95% CI 1.21–2.01), carefully aligning with the whole pooled possibility ratio in Fig. 2 (RR = 1.58, 95% CI 1.21–2.08). Additionally, this subset shows diminished heterogeneity (I2 = 93.94%, Fig. 3) compared to the wider evaluation of all 11 research (I2 = 98.57%, Fig. 2). On the other hand, the rise in possibility ratio at six months was once now not statistically important (RR = 2.10, 95% CI 0.43–10.16). This loss of importance may also be attributed to the outlier possibility ratio of 0.64 reported via Park et al., which was once a price sooner than adjustment [29].NOD possibility amongst COVID-Inflamed, non-COVID-infected another way unspecified, and non-COVID-infected with different respiration infections teams throughout follow-up periodsFigure 4 displays no exceptional distinction about NOD possibility between the COVID-19 workforce and the non-COVID cohorts with different respiration infections [C1 group] (total RR = 1.13, 95% CI 0.92–1.38). Determine 5 displays a considerably greater possibility for NOD within the COVID-19 workforce in comparison to the non-COVID cohorts with another way unspecified well being statuses [C2 group] at three hundred and sixty five days post-COVID-19 (RR = 1.84, 95% CI 1.41–2.38). This greater possibility was once now not obtrusive at 3 months (RR = 0.87, 95% CI 0.46–1.65) or six months (RR = 1.73, 95% CI 0.72–4.14). Right here the loss of statistical importance at six months may also be attributed to the end result from Park et al. [29], which, as soon as adjusted, may just give a contribution to an total important build up in NOD possibility at six months.Comparability of newly evolved cognitive impairment possibility between COVID-infected and non-COVID-infected groupsFigure S1 displays that, a few of the 3 research which explored the chance of creating new-onset cognitive impairment between the COVID-Inflamed and the non-COVID-infected teams [6, 9, 27], a vital greater possibility for NOD was once noticed within the COVID-infected workforce (total RR = 1.93, 95% CI 1.52–2.43, p < 0.001; I2 = 79.04%, p < 0.001). In different phrases, cognitive impairment was once just about two times as most probably in COVID-19 older grownup survivors in comparison to the ones with out COVID-19 an infection.NOD possibility according to intercourse in COVID-positive, different respiration an infection, and COVID-negative another way unspecified teams, separatelyNotably, Determine S2 displays upper NOD dangers for girls on each the COVID-positive workforce (RR = 1.65, 95% CI 1.53–1.78, p < 0.001; I2 = 0.00%, p > 0.05) and COVID-negative another way unspecified keep watch over workforce (RR = 1.33, 95% CI 1.22–1.44, p < 0.001; I2 = 0.00%, p > 0.05), indicating that COVID-19 an infection itself was once now not a big underlying issue making ladies extra vulnerable to creating NOD when compared with males.NOD possibility amongst COVID-infected sufferers, according to COVID-19 severity (inpatient vs. outpatient)Each Figures S3 and S4 display considerably upper dangers for NOD amongst COVID-infected older grownup outpatients (RR = 1.91, 95% CI 1.06–3.45) and inpatients (RR = 3.06, 95% CI 2.78–3.37), as in comparison to COVID-negative older adults.NOD possibility between COVID-infected and non-COVID-infected teams, according to research with propensity rating matching (PSM)Determine S5 signifies that the one 5 research the usage of PSM reported an greater NOD possibility within the COVID-infected workforce (General RR = 1.46, 95% CI 1.10–1.94) [12, 27, 28, 30, 32]. This build up in NOD possibility is in step with the findings from our primary evaluation, which contains all 11 research (General RR = 1.58, Fig. 2).General heterogeneity and sensitivity analysesWe noticed considerable heterogeneity a few of the 11 incorporated research in our primary total pooled meta-analysis in Fig. 2 (I2 = 98.57%, p < 0.001). Additionally, L’Abbé and Galbraith plots, as proven in Determine S6 and Determine S7, visually point out the discrepancies amongst those research. Opposite to expectancies, the meta-regression effects, as proven in Determine S8, recommend that covariates comparable to observational periods (3, 6, 12, 24 months), varieties of keep watch over teams (non-COVID cohorts another way unspecified vs. non-COVID cohorts with different varieties of respiration infections), and dementia varieties assessed (all-cause dementia vs. AD) didn’t give a contribution to the range a few of the 11 research. The sensitivity evaluation, as proven in Determine S9, means that the whole effects remained constant in spite of the elimination of every particular person learn about (with applicable adjustments in impact dimension starting from 0.09 to 0.12), indicating that the findings of our primary meta-analysis in Fig. 2 had been powerful and now not overly depending on any unmarried learn about.E-newsletter biasThe contour-enhanced funnel plot, illustrated in Determine S10, visually signifies possible asymmetry, hinting at newsletter bias. Two imputed research had been strategically positioned to reflect the asymmetrical gaps. On the other hand, the regression-based Egger’s check (p = 0.052) and the nonparametric rank correlation Begg’s check (p = 0.978) don’t supply sturdy proof of important newsletter bias in our primary total pooled meta-analysis. In the meantime, incorporating the 2 imputed research into the evaluation yields a revised pooled impact dimension for a complete of 13 research (RR = 1.48, 95% CI 1.12–1.96), which nonetheless does now not markedly vary from the preliminary evaluation (RR = 1.58, 95% CI 1.21–2.08). As well as, the common high quality appraisal (NOS) rating of 8.1 [standard deviation (SD) = 0.79] is suggestive of a excellent methodological high quality of the 11 incorporated research. All incorporated research correctly constitute the objective inhabitants, investigating the have an effect on of COVID-19 at the NOD possibility in older adults, with sufficient pattern sizes all over.
Affiliation between COVID-19 an infection and new-onset dementia in older adults: a scientific evaluation and meta-analysis – BMC Geriatrics













