Possibly counterintuitively, sediment layers are much more likely to stay intact at the seafloor than on land, so they may be able to supply a greater report of the area’s historical past. The seafloor is a extra strong, oxygen-poor surroundings, decreasing erosion and decomposition (two causes scientists in finding way more fossils of marine creatures than land dwellers) and retaining finer main points.
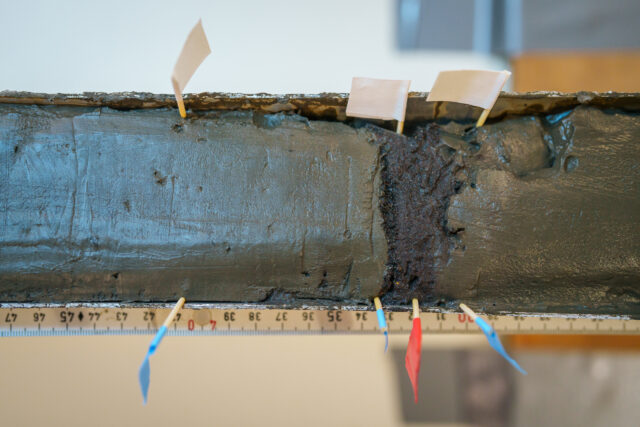

A detailed-up view of a core pattern taken through a vibracorer. Scientists mark puts they plan to check up on extra carefully with little flags.
Credit score:
Alex Ingle / Schmidt Ocean Institute
Samples from other spaces range dramatically in time protection, going again best to 2008 for some and again probably greater than 15,000 years for others because of wildly other sedimentation charges. Scientists will use ways like radiocarbon relationship to decide the ages of sediment layers within the core samples.

ROV SuBastian noticed a helmet jellyfish all through the expedition. Those photophobic (mild avoidant) creatures glow by way of bioluminescence.
Credit score:
Schmidt Ocean Institute
Microscopic research of the sediment cores may even lend a hand the group analyze the way in which the eruption affected marine creatures and the chemistry of the seafloor.
“There’s all kinds of existence and sediment sorts discovered on the other websites we surveyed,” mentioned Alastair Hodgetts, a bodily volcanologist and geologist on the College of Edinburgh, who participated within the expedition. “The oldest position we visited—a space scarred through historic glacier motion—is a fossilized seascape that was once utterly sudden.”
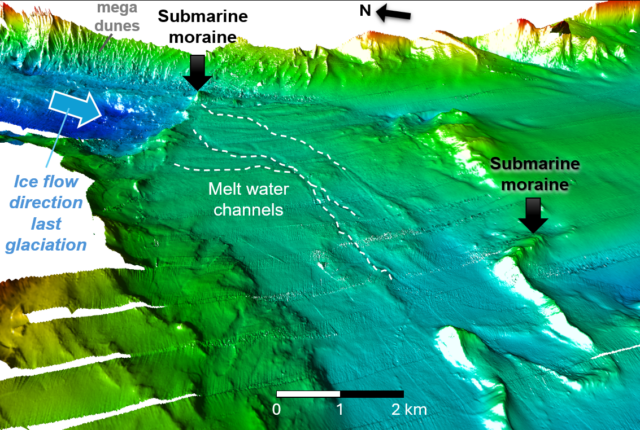
In a area past the dunes, ocean currents have saved the seafloor transparent of sediment. That preserves seabed options left through the retreat of ice sheets on the finish of the ultimate glaciation.
Credit score:
Rodrigo Fernández / CODEX Challenge
This selection, too, tells scientists about the way in which the water strikes. Currents flowing over a space that was once eroded way back through a glacier sweep sediment away, protecting the traditional terrain visual.
“I’m very concerned about inspecting seismic knowledge and correlating it with the layers of sediment within the core samples to create a timeline of geological occasions within the space,” mentioned Giulia Matilde Ferrante, a geophysicist at Italy’s Nationwide Institute of Oceanography and Implemented Geophysics, who co-led the expedition. “Reconstructing the previous on this method will lend a hand us higher perceive the sediment historical past and panorama adjustments within the area.”

On this post-apocalyptic scene, captured June 20, 2008, a thick layer of ash covers the city of Chaitén because the volcano continues to erupt within the background. Round 5,000 folks evacuated, and resettlement efforts didn’t start till the next 12 months.
Credit score:
Javier Rubilar
The group has already amassed measurements of the quantity of sediment the eruption brought to the ocean. Now they’ll paintings to decide whether or not older layers of sediment report previous, unknown occasions very similar to the 2008 eruption.
“Higher figuring out previous volcanic occasions, revealing such things as how a long way away an eruption reached, and the way not unusual, serious, and predictable eruptions are, will lend a hand to plot for long run occasions and cut back the affects they have got on native communities,” Watt mentioned.
Ashley writes about area for a contractor for NASA’s Goddard House Flight Heart through day and freelances as an environmental creator. She holds grasp’s levels in area research from The College of North Dakota and science writing from The Johns Hopkins College. She writes maximum of her articles with a toddler on her lap.














