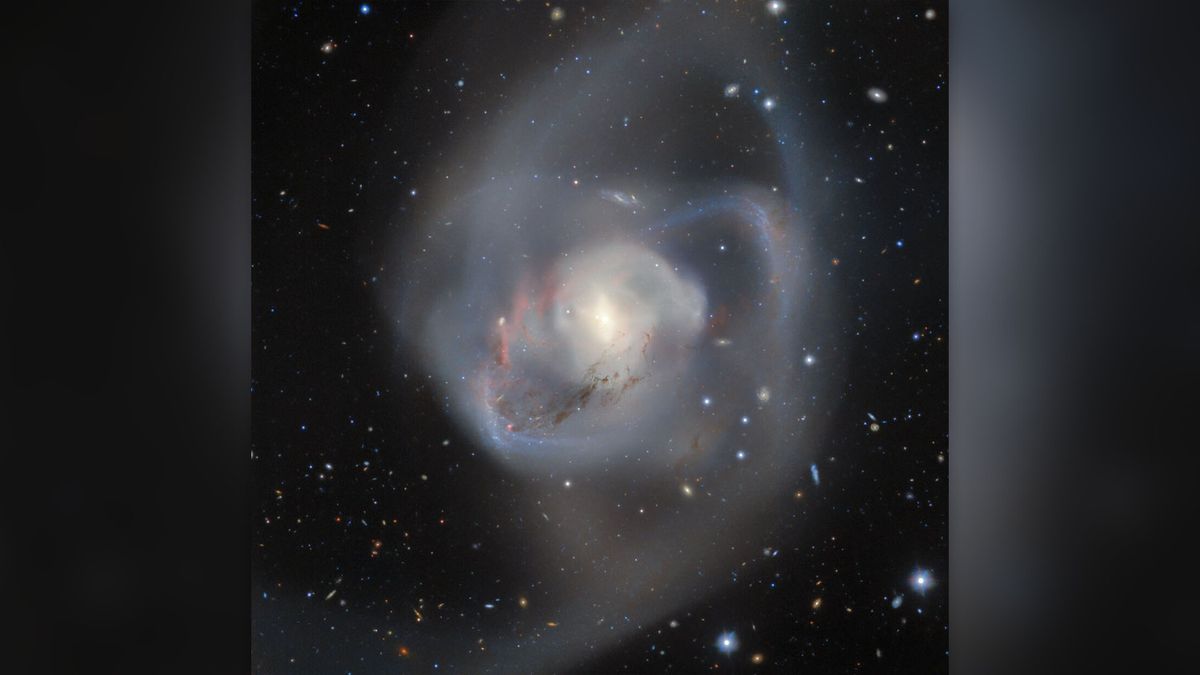
What it’s: NGC 7727, the tangled aftermath of 2 spiral galaxies colliding.When it was once taken: Oct. 25, 2023.The place it’s: Between 73 million and 90 million light-years away within the constellation Aquarius.The place it was once taken: Cerro Pachón mountain in ChileWhy it is so particular: The picture no longer most effective presentations without equal destiny of our Milky Manner galaxy but additionally hides the nearest pair of supermassive black holes to Earth ever recorded.The picture, which was once captured through the World Gemini Observatory and could also be to be had as a zoomable model, presentations bands of interstellar mud and fuel. It is the messy aftermath of 2 spiral galaxies colliding a few billion years in the past.Spiral galaxies have twisted hands filled with stars that lead them to seem like large rotating pinwheels. Once they merge, they shape chaotic elliptical galaxies, which astronomers expect is going on now to NGC 7727. All elliptical galaxies are idea to originate from collisions and mergers with spirals, consistent with NASA.Similar: Supermassive black hollow on the middle of the Milky Manner is drawing near the cosmic pace restrict, dragging space-time in conjunction with itWhat makes NGC 7727 in particular attention-grabbing is what is going down to the nuclei of the 2 previously separate galaxies. Inside of each and every is a supermassive black hollow, consistent with analysis revealed in 2021. At simply 1,600 light-years aside, their gravitational tug-of-war is the reason for the chaotic mess of stars and nebulas scattered throughout NGC 7727.Alternatively, those supermassive black holes don’t seem to be similarly matched. One is 6.3 million occasions the mass of the solar, and the opposite is as large as 154 million suns. Scientists suppose the 2 monsters will merge in about 250 million years, generating gravitational waves, or ripples throughout space-time first detected in 2015.NGC 7727 is a snapshot of the longer term for our Milky Manner galaxy, which is able to regularly merge with the Andromeda galaxy (M31) in about 4 billion years. The picture of NGC 7727 was once taken through Gemini South, a 26-foot-wide (8.1 meters) optical/infrared telescope within the foothills of the Andes this is operated through the Nationwide Science Basis’s NOIRLab. It has an equivalent dual, Gemini North, atop Mauna Kea in Hawaii. In combination, they quilt all the night time sky from their respective hemispheres.