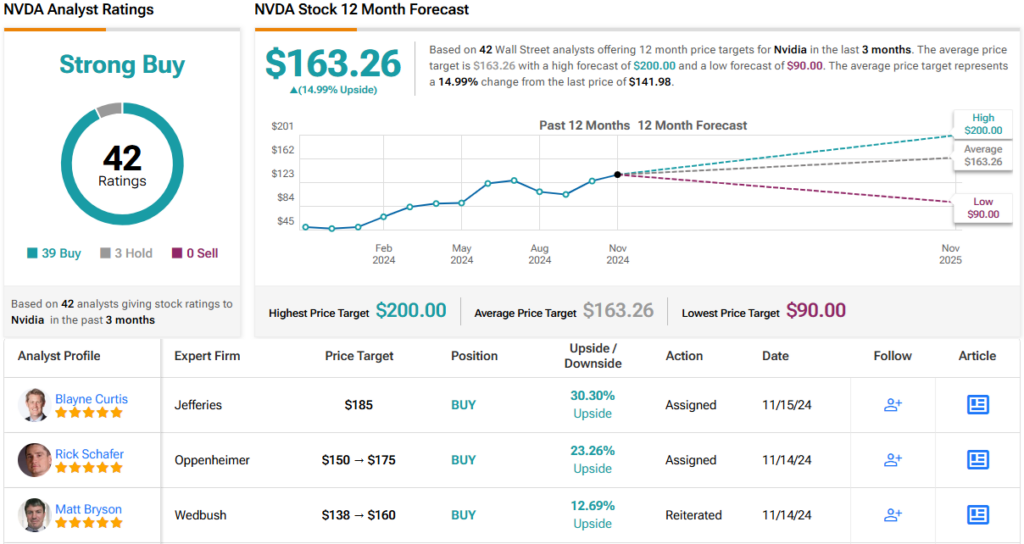
One thing close to the supermassive black hollow on the center of the Milky Means has been firing common blasts of high-energy gamma-rays towards Earth, and scientists might in any case know what it’s.In new non-peer-reviewed analysis posted to the preprint server arXiv, a duo of astrophysicists on the Nationwide Independent College of Mexico conclude that the bursts of radiation are emanating from a blob of fuel spinning across the black hollow at virtually one-third the velocity of sunshine. The crew’s findings might resolve a thriller in regards to the Milky Means’s central black hollow — officially named Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*) and positioned round 26,700 light-years from Earth — that has confused astronomers for 2 years .Comparable: Supermassive black hollow on the center of the Milky Means is drawing near the cosmic velocity restrict, dragging space-time along side it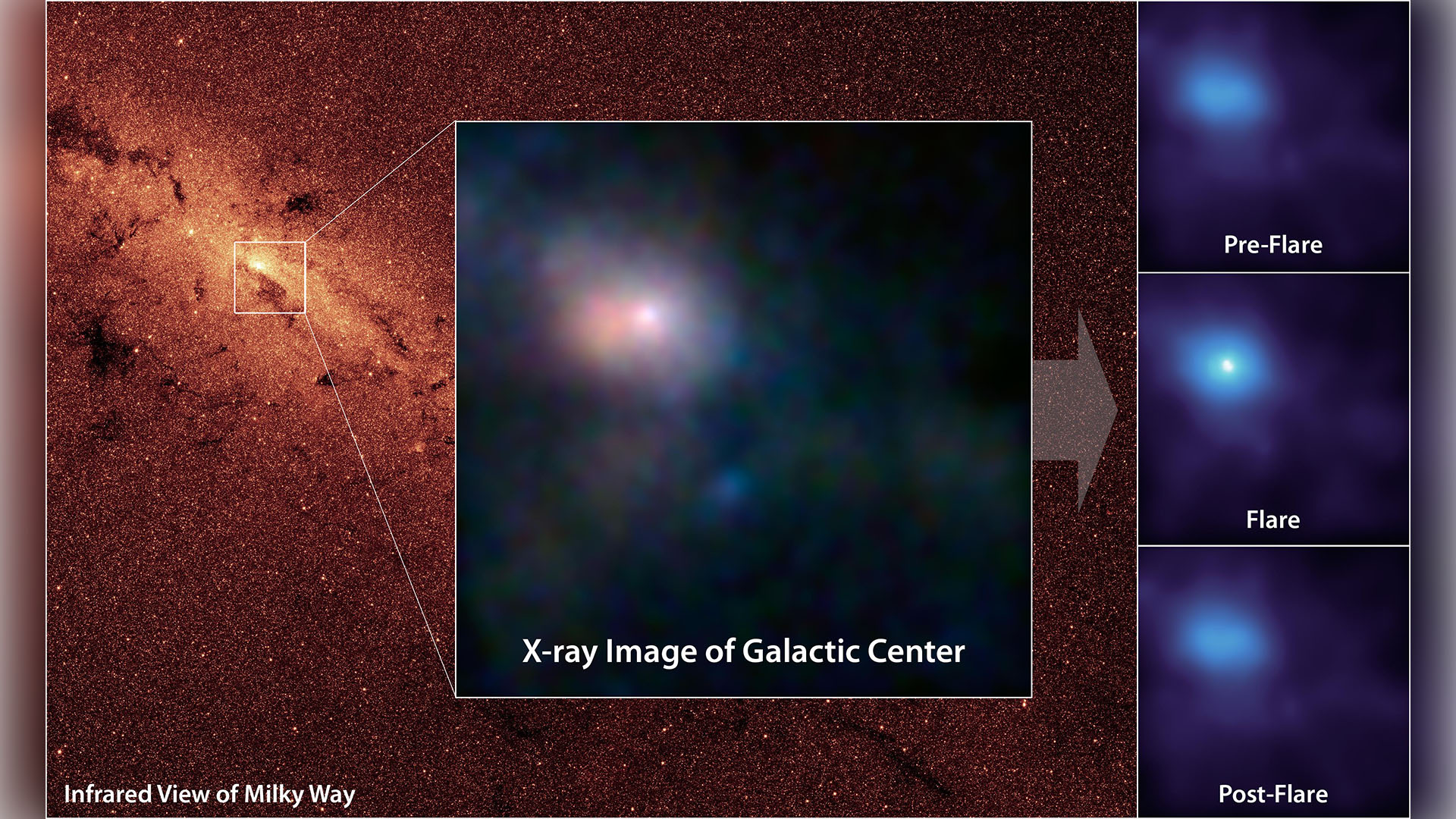 A view of the mysterious X-ray emissions noticed close to the Milky Means’s central black hollow. Those could also be associated with new gamma-ray detections from the similar area. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech)The gamma-ray radiation pulses from round Sgr A* had been first detected belting Earth in 2021. The crew at the back of the commentary knew that the radiation could not be coming from inside the supermassive black hollow itself, alternatively.That is as a result of all black holes are certain by means of a area known as an tournament horizon, which marks the purpose past which not anything, no longer even mild, has the speed had to get away the black hollow’s immense gravity. This implies black holes do not emit radiation themselves, so the gamma-rays will have to be coming from the surroundings of Sgr A*.Different supermassive black holes are recognized to emit tough radiation from their quick environment when their gravitational affect generates turbulent stipulations in surrounding fuel and mud, forming a construction known as an accretion disk. As black holes feed in this subject, the accretion disk emits mild that spans the electromagnetic spectrum, from low-energy radio waves to high-energy gamma-rays.This can not account for the gamma-rays from Sgr A*, alternatively, because the Milky Means’s black hollow is surrounded by means of little or no subject and is feeding so slowly that it will be an identical to a human residing on a nutrition of 1 grain of rice each and every million years, in keeping with College of Arizona astronomer Chris Impey, who used to be no longer concerned within the analysis.The use of knowledge from the Fermi Gamma-ray House Telescope accumulated between June and December 2022, the researchers aimed to find the beginning of those gamma-rays.The duo searched the publicly to be had Fermi knowledge for patterns of periodicity within the gamma-ray emissions. They discovered that the pulses emerge from with reference to Sgr A* kind of as soon as each and every 76.32 mins. This era of emission is part the time between pulses of X-ray radiation additionally noticed coming from the neighborhood of the Milky Means’s supermassive black hollow, suggesting the 2 emissions are in solidarity and are most probably similar.”The accident of the multiwavelength periodicity in X-ray and gamma-ray issues in opposition to a unmarried bodily mechanism that produces it,” the crew wrote within the paper.This revelation of what the researchers name a “distinctive oscillatory bodily mechanism” led them to conclude that each the gamma-rays and the X-rays are being emitted by means of a “blob” of fuel this is swirling round Sgr A* at round 30% the velocity of sunshine — or round 200 million mph (320 million km/h). They suspect this dashing lump of subject is emitting mild throughout a number of wavelengths of radiation because it swirls round Sgr A*, flaring periodically as its orbit proceeds.The invention may give scientists a greater figuring out of the environments round supermassive black holes, specifically less-ravenous examples, corresponding to the only on the center of the Milky Means.
A view of the mysterious X-ray emissions noticed close to the Milky Means’s central black hollow. Those could also be associated with new gamma-ray detections from the similar area. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech)The gamma-ray radiation pulses from round Sgr A* had been first detected belting Earth in 2021. The crew at the back of the commentary knew that the radiation could not be coming from inside the supermassive black hollow itself, alternatively.That is as a result of all black holes are certain by means of a area known as an tournament horizon, which marks the purpose past which not anything, no longer even mild, has the speed had to get away the black hollow’s immense gravity. This implies black holes do not emit radiation themselves, so the gamma-rays will have to be coming from the surroundings of Sgr A*.Different supermassive black holes are recognized to emit tough radiation from their quick environment when their gravitational affect generates turbulent stipulations in surrounding fuel and mud, forming a construction known as an accretion disk. As black holes feed in this subject, the accretion disk emits mild that spans the electromagnetic spectrum, from low-energy radio waves to high-energy gamma-rays.This can not account for the gamma-rays from Sgr A*, alternatively, because the Milky Means’s black hollow is surrounded by means of little or no subject and is feeding so slowly that it will be an identical to a human residing on a nutrition of 1 grain of rice each and every million years, in keeping with College of Arizona astronomer Chris Impey, who used to be no longer concerned within the analysis.The use of knowledge from the Fermi Gamma-ray House Telescope accumulated between June and December 2022, the researchers aimed to find the beginning of those gamma-rays.The duo searched the publicly to be had Fermi knowledge for patterns of periodicity within the gamma-ray emissions. They discovered that the pulses emerge from with reference to Sgr A* kind of as soon as each and every 76.32 mins. This era of emission is part the time between pulses of X-ray radiation additionally noticed coming from the neighborhood of the Milky Means’s supermassive black hollow, suggesting the 2 emissions are in solidarity and are most probably similar.”The accident of the multiwavelength periodicity in X-ray and gamma-ray issues in opposition to a unmarried bodily mechanism that produces it,” the crew wrote within the paper.This revelation of what the researchers name a “distinctive oscillatory bodily mechanism” led them to conclude that each the gamma-rays and the X-rays are being emitted by means of a “blob” of fuel this is swirling round Sgr A* at round 30% the velocity of sunshine — or round 200 million mph (320 million km/h). They suspect this dashing lump of subject is emitting mild throughout a number of wavelengths of radiation because it swirls round Sgr A*, flaring periodically as its orbit proceeds.The invention may give scientists a greater figuring out of the environments round supermassive black holes, specifically less-ravenous examples, corresponding to the only on the center of the Milky Means.