Astronomers the usage of the James Webb House Telescope have seen water and molecules crucial for rocky planet formation in a extremely irradiated space of the Lobster Nebula. This discovery, a part of the XUE program, expands the recognized environments the place rocky planets can shape, difficult earlier ideals and offering new insights into exoplanet variety.
Astronomers the usage of the James Webb House Telescope have seen water and molecules crucial for rocky planet formation in a extremely irradiated space of the Lobster Nebula. This discovery, a part of the XUE program, expands the recognized environments the place rocky planets can shape, difficult earlier ideals and offering new insights into exoplanet variety.
Astronomers discover a vary of molecules which can be a few of the construction blocks for rocky planets.
House is a harsh surroundings, however some spaces are even harsher than others. A celeb-forming area, referred to as the Lobster Nebula, is host to probably the most maximum large stars in our galaxy. Huge stars are warmer, and due to this fact emit extra ultraviolet (UV) mild. That UV mild bathes planet-forming disks round within reach stars. Astronomers would be expecting the UV to damage aside many chemical molecules. On the other hand, the James Webb House Telescope has detected quite a lot of molecules in a single such disk, together with water, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, hydrogen cyanide, and acetylene. Such molecules are a few of the construction blocks of rocky planets.
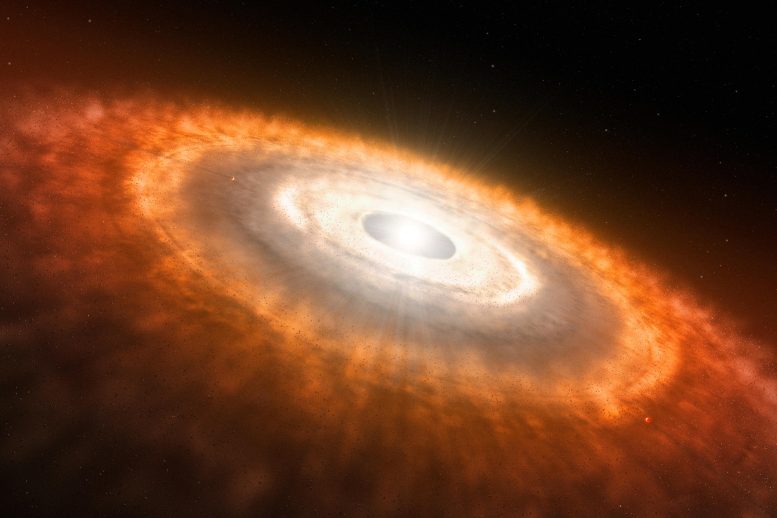 That is an artist’s influence of a tender superstar surrounded by means of a protoplanetary disk through which planets are forming. Credit score: ESO
That is an artist’s influence of a tender superstar surrounded by means of a protoplanetary disk through which planets are forming. Credit score: ESO
Webb House Telescope Unearths Rocky Planets Can Shape in Excessive Environments
A world crew of astronomers has used NASA’s James Webb House Telescope to give you the first remark of water and different molecules within the extremely irradiated internal, rocky-planet-forming areas of a disk in one of the vital excessive environments in our galaxy. Those effects recommend that the prerequisites for rocky planet formation can happen in a imaginable broader vary of environments than in the past idea.
First Effects From XUE Program
Those are the primary effects from the eXtreme Ultraviolet Environments (XUE) James Webb House Telescope program, which makes a speciality of the characterization of planet-forming disks (huge, spinning clouds of gasoline, mud, and chunks of rock the place planets shape and evolve) in large star-forming areas. Those areas are most likely consultant of our environment through which maximum planetary techniques shaped. Working out the affect of surroundings on planet formation is vital for scientists to realize insights into the variety of the various kinds of exoplanets.
Learn about of the Lobster Nebula
The XUE program goals a complete of 15 disks in 3 spaces of the Lobster Nebula (sometimes called NGC 6357), a big emission nebula kind of 5,500 light-years clear of Earth within the constellation Scorpius. The Lobster Nebula is among the youngest and closest large star-formation complexes, and is host to probably the most maximum large stars in our galaxy. Huge stars are warmer, and due to this fact emit extra ultraviolet (UV) radiation. It will disperse the gasoline, making the predicted life of the disk as quick as one million years. Due to Webb, astronomers can now learn about the impact of UV radiation at the internal terrestrial-planet forming areas of protoplanetary disks round stars like our Solar.
Webb’s Distinctive Functions
“Webb is the one telescope with the spatial answer and sensitivity to review planet-forming disks in large star-forming areas,” mentioned crew lead María Claudia Ramírez-Tannus of the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy in Germany.
Astronomers intention to symbolize the bodily homes and chemical composition of the rocky-planet-forming areas of disks within the Lobster Nebula the usage of the Medium Answer Spectrometer on Webb’s Mid-Infrared Software (MIRI). This primary outcome makes a speciality of the protoplanetary disk termed XUE 1, which is positioned within the superstar cluster Pismis 24.
“Handiest the MIRI wavelength vary and spectral answer let us probe the molecular stock and bodily prerequisites of the nice and cozy gasoline and dirt the place rocky planets shape,” added crew member Arjan Bik of Stockholm College in Sweden.
Because of its location close to a number of large stars in NGC 6357, scientists be expecting XUE 1 to were continuously uncovered to top quantities of ultraviolet radiation all the way through its existence. On the other hand, on this excessive surroundings the crew nonetheless detected a spread of molecules which can be the construction blocks for terrestrial planets.
“We discover that the interior disk round XUE 1 is remarkably very similar to the ones in within reach star-forming areas,” mentioned crew member Rens Waters of Radboud College within the Netherlands. “We’ve detected water and different molecules like carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, hydrogen cyanide, and acetylene. On the other hand, the emission discovered used to be weaker than some fashions predicted. This may indicate a small outer disk radius.”
“We have been stunned and excited as a result of that is the primary time that those molecules were detected below those excessive prerequisites,” added Lars Cuijpers of Radboud College. The crew additionally discovered small, in part crystalline silicate mud on the disk’s floor. This is thought of as to be the construction blocks of rocky planets.
Implications for Rocky Planet Formation
Those effects are just right information for rocky planet formation, because the science crew reveals that the prerequisites within the internal disk resemble the ones discovered within the well-studied disks positioned in within reach star-forming areas, the place handiest low-mass stars shape. This implies that rocky planets can shape in a wider vary of environments than in the past believed.
The crew notes that the remainder observations from the XUE program are an important to setting up the commonality of those prerequisites.
“XUE 1 presentations us that the prerequisites to shape rocky planets are there, so your next step is to test how commonplace this is,” says Ramírez-Tannus. “We will be able to practice different disks in the similar area to decide the frequency with which those prerequisites will also be seen.”
Those effects were revealed in The Astrophysical Magazine.
Reference: “XUE: Molecular Stock within the Inside Area of an Extraordinarily Irradiated Protoplanetary Disk” by means of María Claudia Ramírez-Tannus, Arjan Bik, Lars Cuijpers, Rens Waters, Christiane Göppl, Thomas Henning, Inga Kamp, Thomas Preibisch, Konstantin V. Getman, Germán Chaparro, Pablo Cuartas-Restrepo, Alex de Koter, Eric D. Feigelson, Sierra L. Grant, Thomas J. Haworth, Sebastián Hernández, Michael A. Kuhn, Giulia Perotti, Matthew S. Povich, Megan Reiter, Veronica Roccatagliata, Elena Sabbi, Benoît Tabone, Andrew J. Wintry weather, Anna F. McLeod, Roy van Boekel and Sierk E. van Terwisga, 30 November 2023, The Astrophysical Magazine Letters.
DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/ad03f8
The James Webb House Telescope is the sector’s premier area science observatory. Webb is fixing mysteries in our sun machine, having a look past to far away worlds round different stars, and probing the mysterious buildings and origins of our universe and our position in it. Webb is a global program led by means of NASA with its companions, ESA (Eu House Company) and the Canadian House Company.