This text has been reviewed in line with Science X’s editorial procedure
and insurance policies.
Editors have highlighted the next attributes whilst making sure the content material’s credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed newsletter
depended on supply
written via researcher(s)
proofread
Adequate!
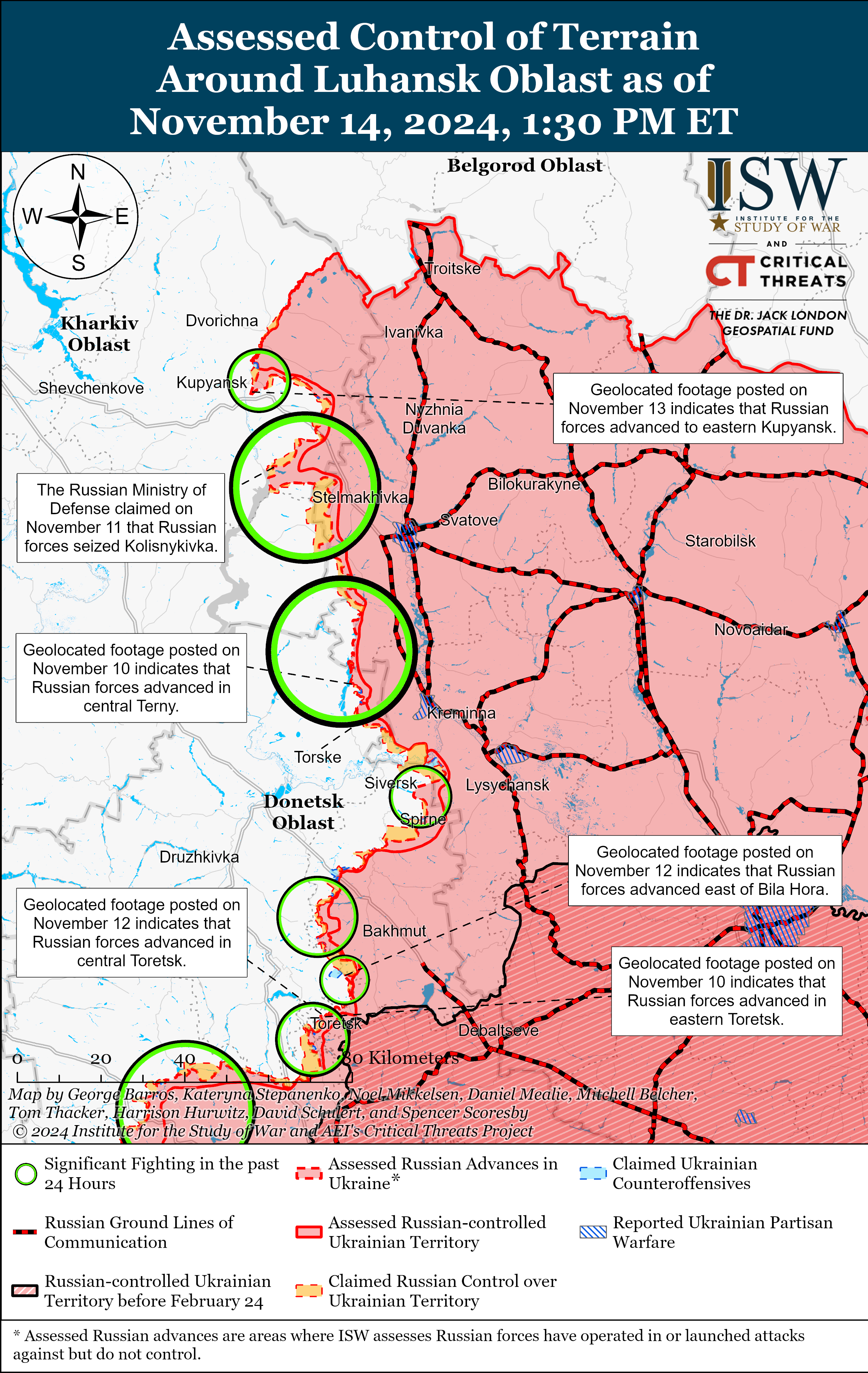
Sediment flux to the oceans and variety of marine animal households over the last 540 million years. The Pearson coefficient of 0.88 signifies a powerful sure correlation between the 2 variables. Credit score: Nature
× shut
Sediment flux to the oceans and variety of marine animal households over the last 540 million years. The Pearson coefficient of 0.88 signifies a powerful sure correlation between the 2 variables. Credit score: Nature
Earth’s floor is the dwelling pores and skin of our planet—it connects the bodily, chemical and organic methods.
Over geological time, this floor evolves. Rivers fragment the panorama into an environmentally numerous vary of habitats. Those rivers additionally switch sediments from the mountains to the continental plains and in the end the oceans.
The concept that landscapes have influenced the trajectory of lifestyles on our planet has an extended historical past, courting again to the early nineteenth century clinical narratives of German polymath Alexander von Humboldt. Whilst we have learnt extra since then, many facets of biodiversity evolution stay enigmatic. As an example, it is nonetheless unclear why there’s a 100-million-year hole between the explosion of marine lifestyles and the advance of crops on continents.
In analysis revealed in Nature lately, we advise a brand new concept that relates the evolution of biodiversity over the last 540 million years to sediment “pulses” managed via previous landscapes.
10 years of computational time
Our simulations are according to an open-source code launched as a part of a Science paper revealed previous this 12 months.
To pressure the evolution of the panorama thru area and time in our pc fashion, we used a chain of reconstructions for what the local weather and tectonics had been like prior to now.
We then when compared the result of our international simulations with reconstructions of marine and continental biodiversity over the last 540 million years.
To accomplish our pc simulations, we took good thing about Australia’s Nationwide Computational Infrastructure operating on a number of masses of processors. The blended simulations introduced in our find out about are similar to 10 years of computational time.
Marine lifestyles and river sediment had been carefully connected
In our fashion, we came upon that the extra sediment rivers carried into the oceans, the extra the ocean lifestyles diverse (a favorable correlation). You’ll be able to see this tracked via the pink line within the chart under.
Because the continents climate, rivers do not simply lift sediment into the oceans, in addition they deliver a big amount of vitamins. Those vitamins, equivalent to carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus, are very important to the organic cycles that transfer essential components thru all dwelling issues.
This is the reason we expect rivers turning in roughly vitamins to the sea—on a geological timescale of thousands and thousands of years—is said to the diversification of marine lifestyles.
Most likely much more strangely, we discovered that episodes of mass extinctions within the oceans took place in a while after vital decreases in sedimentary drift. This implies {that a} lack or deficiency of vitamins can destabilize biodiversity and make it prone to catastrophic occasions (like asteroid affects or volcanic eruptions).
Landscapes additionally drove the variety of crops
At the continents, we designed a variable that integrates sediment duvet and panorama ruggedness to explain the continents’ capability to host numerous species.
Right here we additionally discovered a placing correlation (see under) between our variable and plant diversification for the previous 400 million years. This highlights how adjustments in panorama even have a sturdy affect on species diversifying on land.
We hypothesize that as Earth’s floor used to be progressively lined with thicker soil, richer in vitamins deposited via rivers, crops may just increase and diversify with extra elaborate root methods.
As crops slowly expanded around the land, the planet ended up internet hosting numerous environments and habitats with favorable stipulations for plant evolution, such because the emergence of flowering crops some 100 million years in the past.
A dwelling planet
Total, our findings counsel the variety of lifestyles on our planet is strongly influenced via panorama dynamics. At any given second, Earth’s landscapes resolve the utmost choice of other species continents and oceans can reinforce.
This presentations it is not simply tectonics or climates, however their interactions that resolve the long-term evolution of biodiversity. They do that thru sediment flows and adjustments to the landscapes at huge.
Our findings additionally display that biodiversity has at all times advanced on the tempo of plate tectonics. That is a tempo incomparably slower than the present charge of extinction brought about via human job.
Additional info:
Tristan Salles et al, Panorama dynamics and the Phanerozoic diversification of the biosphere, Nature (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06777-z
Magazine knowledge:
Nature
,
Science