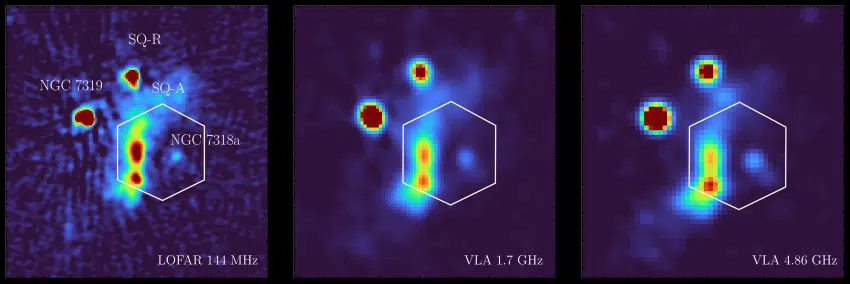
This symbol of a galaxy from the early universe is infrequently what you would name dazzling. You’re looking at an excessively blurry, extremely dust-obscured resident of the cosmos whose title is just a string of numbers and letters. It even sits at a distance to this point from Earth that it slips out and in of the watchful eyes of quite a lot of telescopes. The picture, captured by means of the robust James Webb Area Telescope, spotlights galaxy AzTECC71 — however what is hanging here’s that we are seeing AzTECC71the method it used to be simply 900 million years after the Giant Bang. That is when the universe used to be turning on its first actual stars, absolute eons prior to our sun machine used to be born.The James Webb Area Telescope’s view of this galaxy as a hazy speck of sunshine is a some distance cry from many different superb photographs of galaxies and galaxy clusters in its repertoire. On the other hand, even this smudge holds vital courses for our figuring out of the early universe.”The truth that even one thing that excessive is only visual in probably the most delicate imaging from our latest telescope is so thrilling to me,” learn about creator Jed McKinney of the College of Texas at Austin stated in a commentary. “It is doubtlessly telling us there is a complete inhabitants of galaxies which have been hiding from us.”Similar: James Webb Area Telescope unearths 2 of probably the most far away galaxies ever seenThis may just imply the early universe used to be a lot dustier than up to now concept, scientists say, dropping slightly extra gentle on the way it advanced because the Giant Bang came about more or less 13.8 billion years in the past.AzTECC71 used to be first noticed as an incomprehensible blob of sunshine by means of the James Clerk Maxwell Telescope in Hawaii. Later, it used to be additionally noticed by means of the ALMA radio telescope in Chile. Then, then again, it appeared to vanish in photographs taken by means of the Hubble Area Telescope.”This factor is an actual monster,” stated McKinney. “Despite the fact that it looks as if slightly blob, it is in truth forming masses of recent stars once a year.”As a part of a global effort to map the earliest buildings of the universe (in a piece of the sky the scale of 3 complete moons as noticed from Earth), McKinney and his colleagues seemed for the galaxy in information accumulated by means of the JWST. This observatory’s robust, extraordinary infrared eye is in a position to peering into dust-thick clouds prevalent within the early universe. Sooner than the JWST, those galaxies have been with reference to not possible to hunt out. The sunshine from birthing stars, sitting deep inside dust-shrouded galaxies, used to be absorbed in optical wavelengths by means of the grime itself and re-emitted at faint, longer wavelengths that the JWST can select up. One in 5 such galaxies had remained invisible to Hubble, forming a bunch of what astronomers name “Hubble-dark galaxies.” “That implies our figuring out of the historical past of galaxy evolution is biased as a result of we are best seeing the unobscured, much less dusty galaxies,” stated McKinney.Within the close to long term, McKinney and his crew plans to discover extra faint, hidden galaxies with JWST information, which can’t best “stare again into the farthest reaches of the universe, however it might additionally pierce the thickest of dusty veils.”This analysis is described in a paper revealed in October in The Astrophysical Magazine.
James Webb Area Telescope pierces thru grime to search out an historical ghostly galaxy