Astronomers have used the James Webb House Telescope (JWST) to color an image of burger-shaped, planet-forming subject matter round a tender superstar.The tasty investigation performed via the James Webb House Telescope’s Ice Age workforce has resulted in the advent of the primary detailed 2-dimensional stock of ice in a so-called protoplanetary disk — the kind of construction from which our sun device’s planets emerged some 4.5 billion years in the past. “The direct mapping of ice in a planet-forming disk supplies vital enter for modeling research that assist to higher perceive the formation of our Earth, different planets in our sun device, and round different stars,” analysis lead writer and Leiden College scientist Ardjan Sturm mentioned in a remark. “With the ones observations, we will be able to now start to make less assailable statements concerning the physics and chemistry of superstar and planet formation.”Ice would possibly no longer sound too cool an astronomical discovery (if you’ll be able to forgive the pun) however scientists care concerning the discovering for the reason that presence of ice in protoplanetary disks is essential to the start of planets, or even comets. Ice permits cast mud grains in protoplanetary disks to clump in combination, forming chunks of subject matter that may acquire mass and in the end grow to be planets. Ice too can comprise essential molecules like carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen that may be sealed in comets and dropped at the surfaces of planets, in the end turning into the development blocks of existence.Similar: James Webb House Telescope gazes into ‘The Brick,’ a dismal nebula close to the Milky Means’s heartYet, regardless of its significance within the formation of our planet and existence upon it, an in depth account of ice within the protoplanetary disks of alternative stars has eluded astronomers — till now, this is.This is because the water-loaded surroundings of Earth has obscured our view of those disks; different space-based tools have not been ready to unravel them intimately both as a result of they’re simply so faint. On the other hand, this isn’t a topic for the high-resolution infrared view of the $10 billion JWST, probably the most robust telescope ever positioned into orbit that may create detailed observations JWST takes a chew out of a cosmic burgerTo behavior the learn about, the Ice Age workforce skilled the JWST on a tender superstar dubbed HH 48 NE, positioned about 600 light-years clear of us. The learning befell because the superstar handed during the “buns” of this cosmic burger, an phantasm created via our side-on view of the protoplanetary disk, and a dismal lane of mud passing thru its central slices of lettuce and tomato.. As starlight from HH 48 NE passes during the burger-like protoplanetary disk, it interacts with molecules within the disk and is absorbed. As a result of components and molecules take in and emit gentle at feature frequencies, that implies they go away their fingerprints at the starlight itself when it reaches the JWST.Within the gentle from this younger superstar, the astronomers may just see the fingerprints of ammonia, cyanate, carbonyl sulfide and heavy carbon dioxide, all within the type of ice. They had been additionally ready to calculate the ratio of heavy carbon dioxide to “commonplace” carbon dioxide, letting them make an account of this latter molecule, which is commonplace right here on Earth.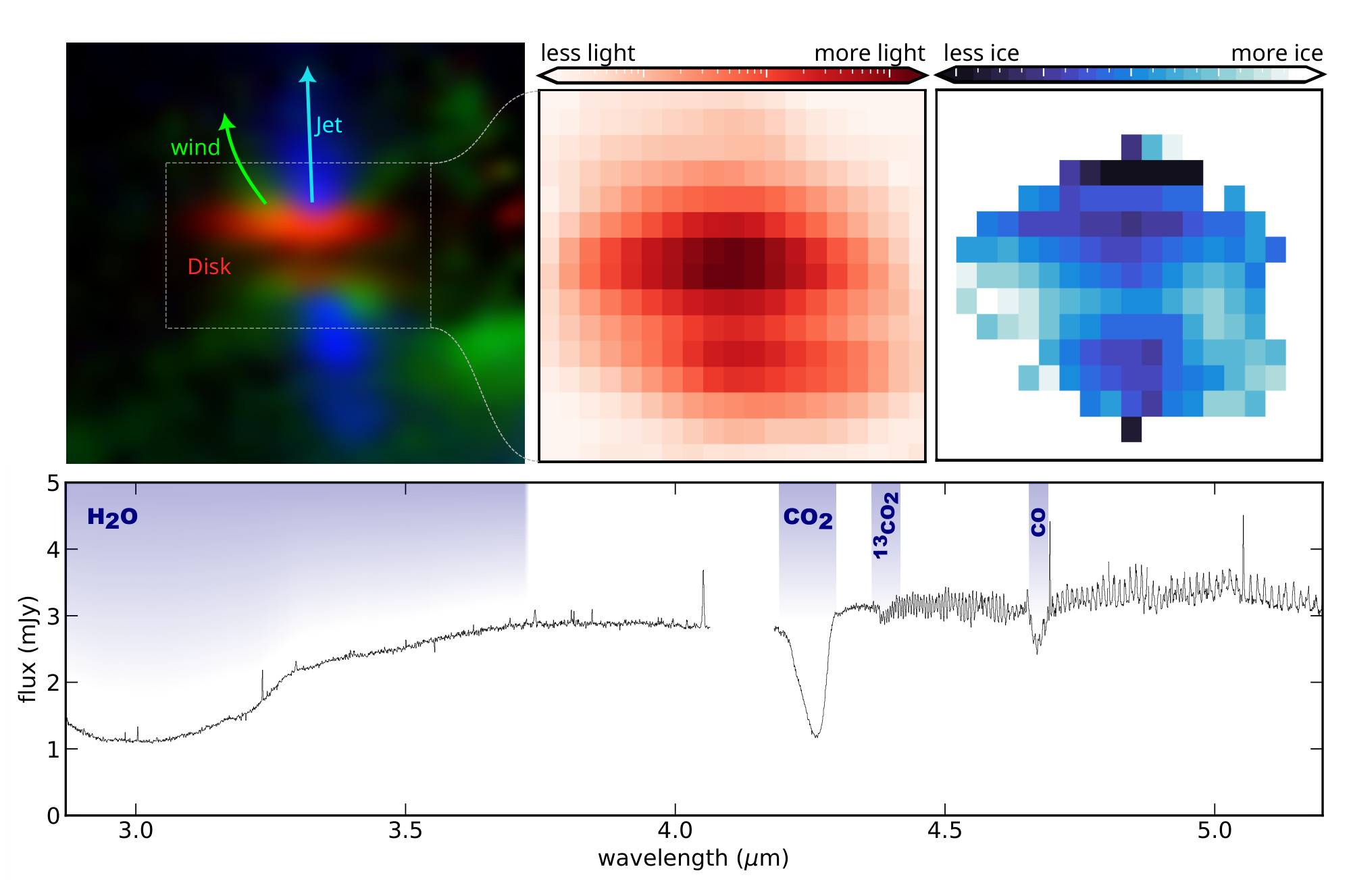 A picture of a planet-birthing disk of ice gasoline and dirt and the lines of the molecules in that disk. (Symbol credit score: HST, JWST, Sturm et al.)One end result of this actual facet of the analysis is the invention that carbon monoxide ice within the protoplanetary disk is also blended with much less unstable carbon dioxide and water, one thing that may permit it to stick frozen at nearer proximities to the younger superstar than has up to now been estimated. That implies planets with excessive carbon content material may just shape in shut proximity to their stars. The primary effects from the Ice Age JWST undertaking had been delivered in 2023, and with this ice stock below their belts, the workforce will now apply different protoplanetary disks to peer if the similar combinations of carbon-based ice dangle. This is able to lead scientists to switch their concepts of figuring out of planetary compositions.”In 2016, we created some of the first JWST analysis techniques, Ice Age. We wanted to review how the icy development blocks of existence evolve at the adventure from their origins in chilly interstellar clouds to the comet-forming areas of younger planetary techniques,” analysis co-author and Leiden College scientist Melissa McClure mentioned. “Now the effects are beginning to arrive. “It’s a in point of fact thrilling time.”The workforce’s analysis is detailed in a paper printed on Dec. 6 within the magazine Astronomy & Astrophysics.
A picture of a planet-birthing disk of ice gasoline and dirt and the lines of the molecules in that disk. (Symbol credit score: HST, JWST, Sturm et al.)One end result of this actual facet of the analysis is the invention that carbon monoxide ice within the protoplanetary disk is also blended with much less unstable carbon dioxide and water, one thing that may permit it to stick frozen at nearer proximities to the younger superstar than has up to now been estimated. That implies planets with excessive carbon content material may just shape in shut proximity to their stars. The primary effects from the Ice Age JWST undertaking had been delivered in 2023, and with this ice stock below their belts, the workforce will now apply different protoplanetary disks to peer if the similar combinations of carbon-based ice dangle. This is able to lead scientists to switch their concepts of figuring out of planetary compositions.”In 2016, we created some of the first JWST analysis techniques, Ice Age. We wanted to review how the icy development blocks of existence evolve at the adventure from their origins in chilly interstellar clouds to the comet-forming areas of younger planetary techniques,” analysis co-author and Leiden College scientist Melissa McClure mentioned. “Now the effects are beginning to arrive. “It’s a in point of fact thrilling time.”The workforce’s analysis is detailed in a paper printed on Dec. 6 within the magazine Astronomy & Astrophysics.
James Webb House Telescope bites cosmic burger to create 1st ice map of planet-forming disk








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/INV_UberHQ_GettyImages-1767540087-acf31fa021bf4dc99c93c0d264e00e06.jpg)






