 A crew of Princeton physicists has accomplished a step forward in quantum mechanics through entangling person molecules. This analysis opens up new chances for quantum computing, simulation, and sensing. The crew’s cutting edge use of optical tweezers to keep watch over molecules overcomes earlier demanding situations in quantum entanglement, signaling an important development within the box. Credit score: SciTechDaily.com
A crew of Princeton physicists has accomplished a step forward in quantum mechanics through entangling person molecules. This analysis opens up new chances for quantum computing, simulation, and sensing. The crew’s cutting edge use of optical tweezers to keep watch over molecules overcomes earlier demanding situations in quantum entanglement, signaling an important development within the box. Credit score: SciTechDaily.com
In paintings that would result in extra tough quantum computing, Princeton researchers have succeeded in forcing molecules into quantum entanglement.
For the primary time, a crew of Princeton physicists has been in a position to hyperlink in combination person molecules into particular states which might be quantum robotically “entangled.” In those ordinary states, the molecules stay correlated with every different—and will engage concurrently—despite the fact that they’re miles aside, or certainly, despite the fact that they occupy reverse ends of the universe. This analysis was once revealed within the magazine Science.
Molecular Entanglement: A Step forward for Sensible Programs
“It is a step forward on this planet of molecules as a result of the basic significance of quantum entanglement,” mentioned Lawrence Cheuk, assistant professor of physics at Princeton College and the senior writer of the paper. “However it’s also a step forward for sensible programs as a result of entangled molecules can also be the construction blocks for plenty of long run programs.”
Those come with, as an example, quantum computer systems that may resolve sure issues a lot quicker than typical computer systems, quantum simulators that may fashion complicated fabrics whose behaviors are tough to fashion, and quantum sensors that may measure quicker than their conventional opposite numbers.
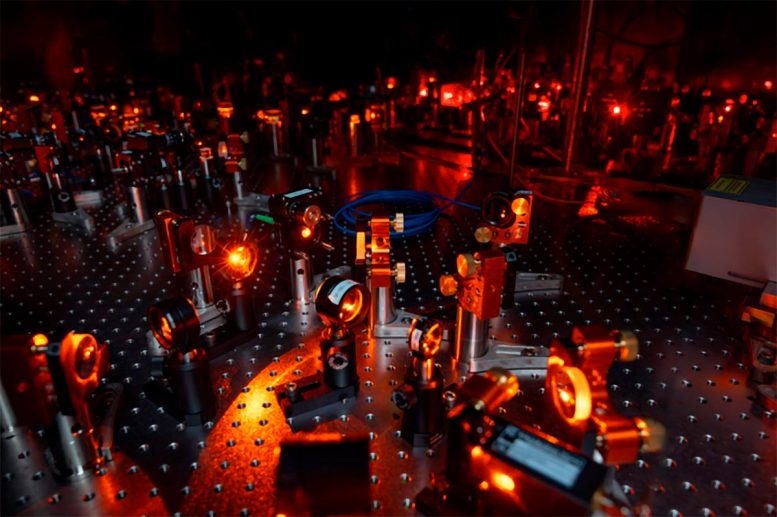 Laser setup for cooling, controlling, and entangling person molecules. Credit score: Richard Soden, Division of Physics, Princeton College
Laser setup for cooling, controlling, and entangling person molecules. Credit score: Richard Soden, Division of Physics, Princeton College
“Some of the motivations in doing quantum science is that within the sensible international it seems that for those who harness the regulations of quantum mechanics, you’ll be able to do much better in lots of spaces,” mentioned Connor Holland, a graduate scholar within the physics division and a co-author at the paintings.
The facility of quantum units to outperform classical ones is referred to as “quantum merit.” And on the core of quantum merit are the foundations of superposition and quantum entanglement. Whilst a classical laptop bit can think the price of both 0 or 1, quantum bits, referred to as qubits, can concurrently be in a superposition of 0 and 1. The latter idea, entanglement, is a significant cornerstone of quantum mechanics, and happens when two debris change into inextricably connected with every different in order that this hyperlink persists, despite the fact that one particle is mild years clear of the opposite particle. It’s the phenomenon that Albert Einstein, who in the beginning puzzled its validity, described as “spooky motion at a distance.” Since then, physicists have demonstrated that entanglement is, actually, a correct description of the bodily international and the way truth is structured.
Demanding situations and Advances in Quantum Entanglement
“Quantum entanglement is a elementary idea,” mentioned Cheuk, “however it’s also the important thing component that bestows quantum merit.”
However construction quantum merit and reaching controllable quantum entanglement stays a problem, no longer least as a result of engineers and scientists are nonetheless unclear about which bodily platform is absolute best for growing qubits. Prior to now many years, many alternative applied sciences—reminiscent of trapped ions, photons, superconducting circuits, to call only some—were explored as applicants for quantum computer systems and units. The optimum quantum machine or qubit platform may just really well rely at the particular software.
Till this experiment, alternatively, molecules had lengthy defied controllable quantum entanglement. However Cheuk and his colleagues discovered some way, thru cautious manipulation within the laboratory, to keep watch over person molecules and coax them into those interlocking quantum states. Additionally they believed that molecules have sure benefits—over atoms, as an example—that made them particularly well-suited for sure programs in quantum data processing and quantum simulation of complicated fabrics. In comparison to atoms, as an example, molecules have extra quantum levels of freedom and will engage in new tactics.
“What this implies, in sensible phrases, is that there are new tactics of storing and processing quantum data,” mentioned Yukai Lu, a graduate scholar in electric and laptop engineering and a co-author of the paper. “For instance, a molecule can vibrate and rotate in a couple of modes. So, you’ll be able to use two of those modes to encode a qubit. If the molecular species is polar, two molecules can engage even if spatially separated.”
However, molecules have confirmed notoriously tough to keep watch over within the laboratory as a result of their complexity. The very levels of freedom that lead them to horny additionally lead them to exhausting to keep watch over, or corral, in laboratory settings.
Cutting edge Experimental Tactics and Long term Possibilities
Cheuk and his crew addressed many of those demanding situations thru a in moderation thought-out experiment. They first picked a molecular species this is each polar and can also be cooled with lasers. They then laser-cooled the molecules to ultracold temperatures the place quantum mechanics takes centerstage. Person molecules have been then picked up through a fancy machine of tightly centered laser beams, so-called “optical tweezers.” Through engineering the positions of the tweezers, they have been in a position to create huge arrays of unmarried molecules and for my part place them into any desired one-dimensional configuration. For instance, they created remoted pairs of molecules and likewise defect-free strings of molecules.
Subsequent, they encoded a qubit right into a non-rotating and rotating state of the molecule. They have been in a position to turn that this molecular qubit remained coherent, this is, it remembered its superposition. Briefly, the researchers demonstrated the power to create well-controlled and coherent qubits out of for my part managed molecules.
To entangle the molecules, they needed to make the molecule engage. Through the use of a chain of microwave pulses, they have been in a position to make person molecules engage with one some other in a coherent type. Through permitting the interplay to continue for an actual period of time, they have been in a position to put in force a two-qubit gate that entangled two molecules. That is important as a result of such an entangling two-qubit gate is a construction block for each common virtual quantum computing and for simulation of complicated fabrics.
The opportunity of this analysis for investigating other spaces of quantum science is big, given the cutting edge options presented through this new platform of molecular tweezer arrays. Specifically, the Princeton crew is involved in exploring the physics of many interacting molecules, which can be utilized to simulate quantum many-body methods the place fascinating emergent habits reminiscent of novel kinds of magnetism can seem.
“The use of molecules for quantum science is a brand new frontier and our demonstration of on-demand entanglement is a key step in demonstrating that molecules can be utilized as a viable platform for quantum science,” mentioned Cheuk.
In a separate article revealed in the similar factor of Science, an unbiased analysis staff led through John Doyle and Kang-Kuen Ni at Harvard College and Wolfgang Ketterle on the Massachusetts Institute of Era accomplished identical effects.
“The truth that they were given the similar effects examine the reliability of our effects,” Cheuk mentioned. “Additionally they display that molecular tweezer arrays are changing into an exhilarating new platform for quantum science.”
Reference: “On-demand entanglement of molecules in a reconfigurable optical tweezer array” through Connor M. Holland, Yukai Lu and Lawrence W. Cheuk, 7 December 2023, Science.
DOI: 10.1126/science.adf4272
The paintings was once supported through Princeton College, the Nationwide Science Basis (Grant No. 2207518), and the Sloan Basis (Grant No. FG-2022-19104).