Join The Gentleman Report’s Marvel Idea science publication. Discover the universe with information on interesting discoveries, clinical developments and extra.The search for brand spanking new antibiotics goes again to the Stone Age.The urgency to spot imaginable applicants hasn’t ever been better as the worldwide inhabitants faces just about 5 million deaths annually which can be related to microbial resistance, consistent with the International Well being Group.A analysis workforce led by means of bioengineering pioneer César de los angeles Fuente is the use of synthetic intelligence-based computational how one can mine genetic data from extinct human kin comparable to Neanderthals and long-gone ice age creatures such because the woolly mammoth and large sloth.The scientists say a few of these small protein, or peptide, molecules they have got recognized have bacteria-fighting powers that can encourage new medicine to struggle infections in people. The cutting edge paintings additionally opens up a fully new approach to take into consideration drug discovery.“It has enabled us to discover new sequences, new varieties of molecules that we have got now not up to now present in residing organisms, increasing the best way we take into consideration molecular range,” stated de los angeles Fuente, Presidential Assistant Professor on the College of Pennsylvania, the place he heads the gadget biology workforce. “Micro organism from these days have by no means confronted the ones molecules in order that they can provide us a greater alternative at concentrated on the pathogens which can be problematic these days.”The method would possibly appear to return out of left box, however professionals say that new techniques of taking a look on the drawback of antimicrobial resistance to current medications, a perilous and urgent drawback for world well being, are sorely wanted.“The arena is going through an antibiotic resistance disaster. My view is {that a} land, sea, and air method is had to resolve the issue — and if we wish to pass to the previous to supply doable answers for the longer term — I’m curious about it,” stated Michael Mahan, a professor within the division of molecular, cell and developmental biology on the College of California, Santa Barbara. He wasn’t concerned within the analysis.
 A determine of a Neanderthal guy is noticed at London’s Herbal Historical past Museum. Researchers are the use of AI-based computational how one can mine genetic data from extinct human kin comparable to Neanderthals. – Mike Kemp/In Photos/Getty ImagesAntibiotics and the place their possible choices would possibly come fromMost antibiotics come from micro organism and fungi and feature been came upon by means of screening microorganisms that reside in soil. However in fresh a long time, pathogens have grow to be immune to many of those medicine on account of overuse.Scientists engaged within the world struggle towards superbugs are exploring other doable guns, together with phages, or viruses created by means of nature to devour micro organism.Some other thrilling road of study comes to antimicrobial peptides, or AMPs, which can be infection-fighting molecules produced by means of many various organisms — micro organism, fungi, vegetation and animals, together with people. AMPs have a extensive vary of antimicrobial houses towards other pathogens comparable to viruses, micro organism, yeast and fungi, Mahan stated.Whilst most standard antibiotics paintings by means of specializing in a unmarried goal in a cellular, antimicrobial peptides bind to and disrupt a bacterial membrane at many puts, he added. It’s a extra difficult mechanism that as a result would possibly make drug resistance much less most probably, however, on account of the molecules’ doable to disrupt cellular membranes, it will probably additionally lead to greater toxicity, consistent with Mahan.There are a handful of peptide-based antibiotics in scientific use, comparable to colistin, which is constructed from a bacteria-based AMP. It’s used as a drug of remaining hotel to regard sure bacterial an infection as a result of it may be poisonous, Mahan stated. One human AMP referred to as LL-37 has additionally proven doable.Different promising AMPs were present in sudden puts: pine needles and the blood of the Komodo dragon.A ‘Jurassic Park’ momentDe los angeles Fuente have been the use of computational strategies for the previous decade to evaluate the opportunity of quite a lot of peptides as possible choices to antibiotics. The speculation to have a look at extinct molecules got here up all through a lab brainstorm when the blockbuster film “Jurassic Park” was once discussed.“The perception (within the movie) was once to deliver again complete organisms, and clearly, that they had a large number of problems,” he stated. His workforce began excited about a extra possible thought: “Why now not deliver again molecules from the previous?”Advances within the restoration of historic DNA from fossils imply that detailed libraries of genetic details about extinct human kin and long-lost animals at the moment are publicly to be had.To seek out up to now unknown peptides, the analysis workforce skilled an AI set of rules to acknowledge fragmented websites in human proteins that would possibly have antimicrobial task. The scientists then implemented it to publicly to be had protein sequences of contemporary people (Homo sapiens), Neanderthals (Homo neanderthalensis) and Denisovans, every other archaic human species carefully associated with Neanderthals.The researchers then used the houses of up to now described antimicrobial peptides to expect which in their newly recognized historic opposite numbers had essentially the most doable to kill micro organism.
A determine of a Neanderthal guy is noticed at London’s Herbal Historical past Museum. Researchers are the use of AI-based computational how one can mine genetic data from extinct human kin comparable to Neanderthals. – Mike Kemp/In Photos/Getty ImagesAntibiotics and the place their possible choices would possibly come fromMost antibiotics come from micro organism and fungi and feature been came upon by means of screening microorganisms that reside in soil. However in fresh a long time, pathogens have grow to be immune to many of those medicine on account of overuse.Scientists engaged within the world struggle towards superbugs are exploring other doable guns, together with phages, or viruses created by means of nature to devour micro organism.Some other thrilling road of study comes to antimicrobial peptides, or AMPs, which can be infection-fighting molecules produced by means of many various organisms — micro organism, fungi, vegetation and animals, together with people. AMPs have a extensive vary of antimicrobial houses towards other pathogens comparable to viruses, micro organism, yeast and fungi, Mahan stated.Whilst most standard antibiotics paintings by means of specializing in a unmarried goal in a cellular, antimicrobial peptides bind to and disrupt a bacterial membrane at many puts, he added. It’s a extra difficult mechanism that as a result would possibly make drug resistance much less most probably, however, on account of the molecules’ doable to disrupt cellular membranes, it will probably additionally lead to greater toxicity, consistent with Mahan.There are a handful of peptide-based antibiotics in scientific use, comparable to colistin, which is constructed from a bacteria-based AMP. It’s used as a drug of remaining hotel to regard sure bacterial an infection as a result of it may be poisonous, Mahan stated. One human AMP referred to as LL-37 has additionally proven doable.Different promising AMPs were present in sudden puts: pine needles and the blood of the Komodo dragon.A ‘Jurassic Park’ momentDe los angeles Fuente have been the use of computational strategies for the previous decade to evaluate the opportunity of quite a lot of peptides as possible choices to antibiotics. The speculation to have a look at extinct molecules got here up all through a lab brainstorm when the blockbuster film “Jurassic Park” was once discussed.“The perception (within the movie) was once to deliver again complete organisms, and clearly, that they had a large number of problems,” he stated. His workforce began excited about a extra possible thought: “Why now not deliver again molecules from the previous?”Advances within the restoration of historic DNA from fossils imply that detailed libraries of genetic details about extinct human kin and long-lost animals at the moment are publicly to be had.To seek out up to now unknown peptides, the analysis workforce skilled an AI set of rules to acknowledge fragmented websites in human proteins that would possibly have antimicrobial task. The scientists then implemented it to publicly to be had protein sequences of contemporary people (Homo sapiens), Neanderthals (Homo neanderthalensis) and Denisovans, every other archaic human species carefully associated with Neanderthals.The researchers then used the houses of up to now described antimicrobial peptides to expect which in their newly recognized historic opposite numbers had essentially the most doable to kill micro organism.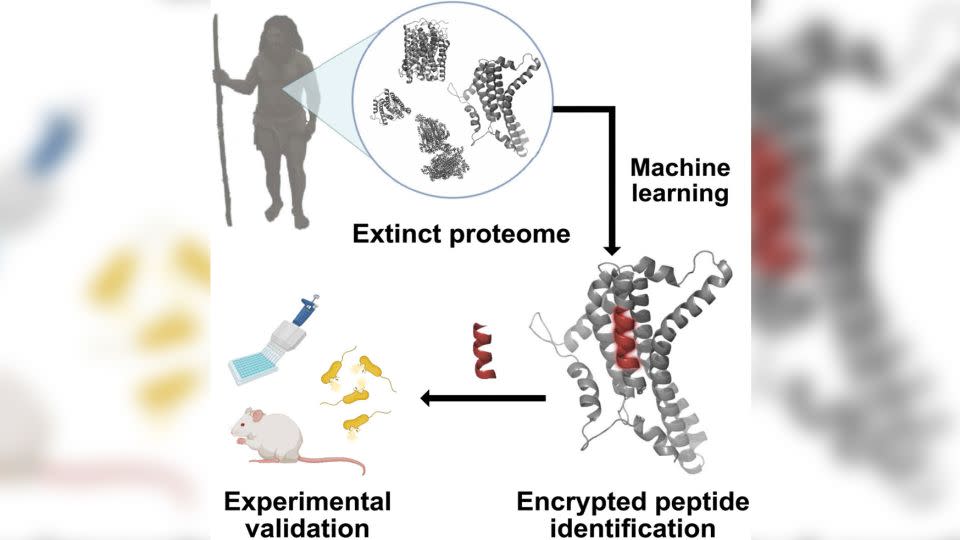
 Out of six promising peptides recognized with an set of rules, one from a Neanderthal was once probably the greatest at combating pathogens in bacteria-infected mice, stated bioengineering pioneer César de los angeles Fuente of the College of Pennsylvania. – College of Pennsylvania/Courtesy Science DirectNext, the researchers synthesized and examined 69 of essentially the most promising peptides to look whether or not they might kill micro organism in petri dishes. The workforce decided on the six maximum potent — 4 from Homo sapiens, one from Homo neanderthalensis and one from Denisovans — and gave them to mice contaminated with the bacterium Acinetobacter baumannii, a not unusual reason for hospital-borne infections in people.“I feel one of the thrilling moments was once once we have been resurrecting the molecules within the laboratory the use of chemistry after which we have been bringing them again to lifestyles for the primary time. And so it was once in reality cool from a systematic standpoint to have had that second,” de los angeles Fuente stated of the analysis that printed in August within the clinical magazine Mobile Host & Microbe.In contaminated mice that evolved a pores and skin abscess, the peptides actively killed the micro organism; in those who had a thigh an infection, the remedy was once much less efficient however nonetheless halted the expansion of micro organism.“The most efficient (peptide) was once what we name Neanderthalien 1, which comes from Neanderthals. And that was once the one who was once most efficient within the mouse type,” de los angeles Fuente stated.He cautioned that not one of the peptides have been “able to move antibiotics” and will require a large number of tweaking. Extra essential, he says, is the framework and gear his workforce has evolved to spot promising antimicrobial molecules from the previous.In analysis anticipated to post subsequent yr, de los angeles Fuente and his colleagues have evolved a brand new deep-learning type to discover what he describes because the “extinctome” — the protein sequences of 208 extinct organisms for which detailed genetic data is to be had.The workforce discovered greater than 11,000 up to now unknown doable antimicrobial peptides distinctive to extinct organisms and synthesized promising applicants from the Siberian woolly mammoth, Steller’s sea cow (a marine mammal that was once burnt up within the 18th century by means of Arctic searching), the 10-foot-long (3-meter) Darwin’s floor sloth (Mylodon darwinii) and the large Irish elk (Megaloceros giganteus). He stated that the peptides they came upon displayed “very good anti-infective task” in mice.“Molecular de-extinction gives a singular alternative to fight antibiotic resistance by means of resurrecting and tapping into the facility of molecules from the previous,” he stated.A wacky however profitable approachDr. Dmitry Ghilarov, workforce chief on the John Innes Centre in the UK who research peptide antibiotics, stated the actual bottleneck within the seek for new antibiotics wasn’t essentially a loss of promising compounds, however getting pharmaceutical corporations to increase and clinically check doable peptide antibiotics, which will also be volatile and tough to synthesize. He was once now not concerned within the analysis.“I don’t see an instantaneous reason why to have a look at paleo proteomes. We now have already … have a large number of those peptides,” he stated. “What we in reality want for my part is deep figuring out at the underlying … rules: what makes the peptide bioactive so as to design them.”“There are a large number of those peptide antibiotics that have been now not evolved and pursued by means of the business on account of difficulties like toxicity,” Ghilarov stated.In step with a paper printed in Would possibly 2021, of 10,000 promising compounds recognized by means of researchers, just one or two antibiotic medicine reached US Meals and Drug Management approval.Dr. Monique van Hoek, a professor and affiliate director of study at George Mason College’s College of Techniques Biology in Fairfax, Virginia, stated the theory of molecular de-extinction was once “a in reality fascinating method.” She was once now not fascinated by both learn about.Van Hoek stated it was once uncommon {that a} peptide present in nature — be it extinct or from a residing organism — would at once result in a brand new form of antibiotic or different drug. Extra frequently, she stated, the invention of a brand new peptide will be offering a kick off point for researchers, who may then use computational tactics to tinker and optimize the peptide’s doable as a drug candidate.Van Hoek’s analysis lately specializes in a man-made peptide impressed by means of one discovered naturally within the American alligator. The peptide is lately present process preclinical trying out.“To this point it’s going in reality smartly. And that’s thrilling as a result of many different peptides that I’ve labored on over time fail for one reason why or every other,” she stated.Van Hoek stated that whilst it’s going to seem wacky to have a look at alligators or extinct people for a brand new supply of antibiotics, the magnitude of the disaster makes the method profitable.De los angeles Fuente agreed. “I feel what we’d like is as many new and other approaches as imaginable, and that can build up our probabilities of being sooner or later a hit,” he stated.“I feel we will in finding a large number of doable helpful answers by means of taking a look in the back of us.”For extra The Gentleman Report information and newsletters create an account at The Gentleman Report.com
Out of six promising peptides recognized with an set of rules, one from a Neanderthal was once probably the greatest at combating pathogens in bacteria-infected mice, stated bioengineering pioneer César de los angeles Fuente of the College of Pennsylvania. – College of Pennsylvania/Courtesy Science DirectNext, the researchers synthesized and examined 69 of essentially the most promising peptides to look whether or not they might kill micro organism in petri dishes. The workforce decided on the six maximum potent — 4 from Homo sapiens, one from Homo neanderthalensis and one from Denisovans — and gave them to mice contaminated with the bacterium Acinetobacter baumannii, a not unusual reason for hospital-borne infections in people.“I feel one of the thrilling moments was once once we have been resurrecting the molecules within the laboratory the use of chemistry after which we have been bringing them again to lifestyles for the primary time. And so it was once in reality cool from a systematic standpoint to have had that second,” de los angeles Fuente stated of the analysis that printed in August within the clinical magazine Mobile Host & Microbe.In contaminated mice that evolved a pores and skin abscess, the peptides actively killed the micro organism; in those who had a thigh an infection, the remedy was once much less efficient however nonetheless halted the expansion of micro organism.“The most efficient (peptide) was once what we name Neanderthalien 1, which comes from Neanderthals. And that was once the one who was once most efficient within the mouse type,” de los angeles Fuente stated.He cautioned that not one of the peptides have been “able to move antibiotics” and will require a large number of tweaking. Extra essential, he says, is the framework and gear his workforce has evolved to spot promising antimicrobial molecules from the previous.In analysis anticipated to post subsequent yr, de los angeles Fuente and his colleagues have evolved a brand new deep-learning type to discover what he describes because the “extinctome” — the protein sequences of 208 extinct organisms for which detailed genetic data is to be had.The workforce discovered greater than 11,000 up to now unknown doable antimicrobial peptides distinctive to extinct organisms and synthesized promising applicants from the Siberian woolly mammoth, Steller’s sea cow (a marine mammal that was once burnt up within the 18th century by means of Arctic searching), the 10-foot-long (3-meter) Darwin’s floor sloth (Mylodon darwinii) and the large Irish elk (Megaloceros giganteus). He stated that the peptides they came upon displayed “very good anti-infective task” in mice.“Molecular de-extinction gives a singular alternative to fight antibiotic resistance by means of resurrecting and tapping into the facility of molecules from the previous,” he stated.A wacky however profitable approachDr. Dmitry Ghilarov, workforce chief on the John Innes Centre in the UK who research peptide antibiotics, stated the actual bottleneck within the seek for new antibiotics wasn’t essentially a loss of promising compounds, however getting pharmaceutical corporations to increase and clinically check doable peptide antibiotics, which will also be volatile and tough to synthesize. He was once now not concerned within the analysis.“I don’t see an instantaneous reason why to have a look at paleo proteomes. We now have already … have a large number of those peptides,” he stated. “What we in reality want for my part is deep figuring out at the underlying … rules: what makes the peptide bioactive so as to design them.”“There are a large number of those peptide antibiotics that have been now not evolved and pursued by means of the business on account of difficulties like toxicity,” Ghilarov stated.In step with a paper printed in Would possibly 2021, of 10,000 promising compounds recognized by means of researchers, just one or two antibiotic medicine reached US Meals and Drug Management approval.Dr. Monique van Hoek, a professor and affiliate director of study at George Mason College’s College of Techniques Biology in Fairfax, Virginia, stated the theory of molecular de-extinction was once “a in reality fascinating method.” She was once now not fascinated by both learn about.Van Hoek stated it was once uncommon {that a} peptide present in nature — be it extinct or from a residing organism — would at once result in a brand new form of antibiotic or different drug. Extra frequently, she stated, the invention of a brand new peptide will be offering a kick off point for researchers, who may then use computational tactics to tinker and optimize the peptide’s doable as a drug candidate.Van Hoek’s analysis lately specializes in a man-made peptide impressed by means of one discovered naturally within the American alligator. The peptide is lately present process preclinical trying out.“To this point it’s going in reality smartly. And that’s thrilling as a result of many different peptides that I’ve labored on over time fail for one reason why or every other,” she stated.Van Hoek stated that whilst it’s going to seem wacky to have a look at alligators or extinct people for a brand new supply of antibiotics, the magnitude of the disaster makes the method profitable.De los angeles Fuente agreed. “I feel what we’d like is as many new and other approaches as imaginable, and that can build up our probabilities of being sooner or later a hit,” he stated.“I feel we will in finding a large number of doable helpful answers by means of taking a look in the back of us.”For extra The Gentleman Report information and newsletters create an account at The Gentleman Report.com