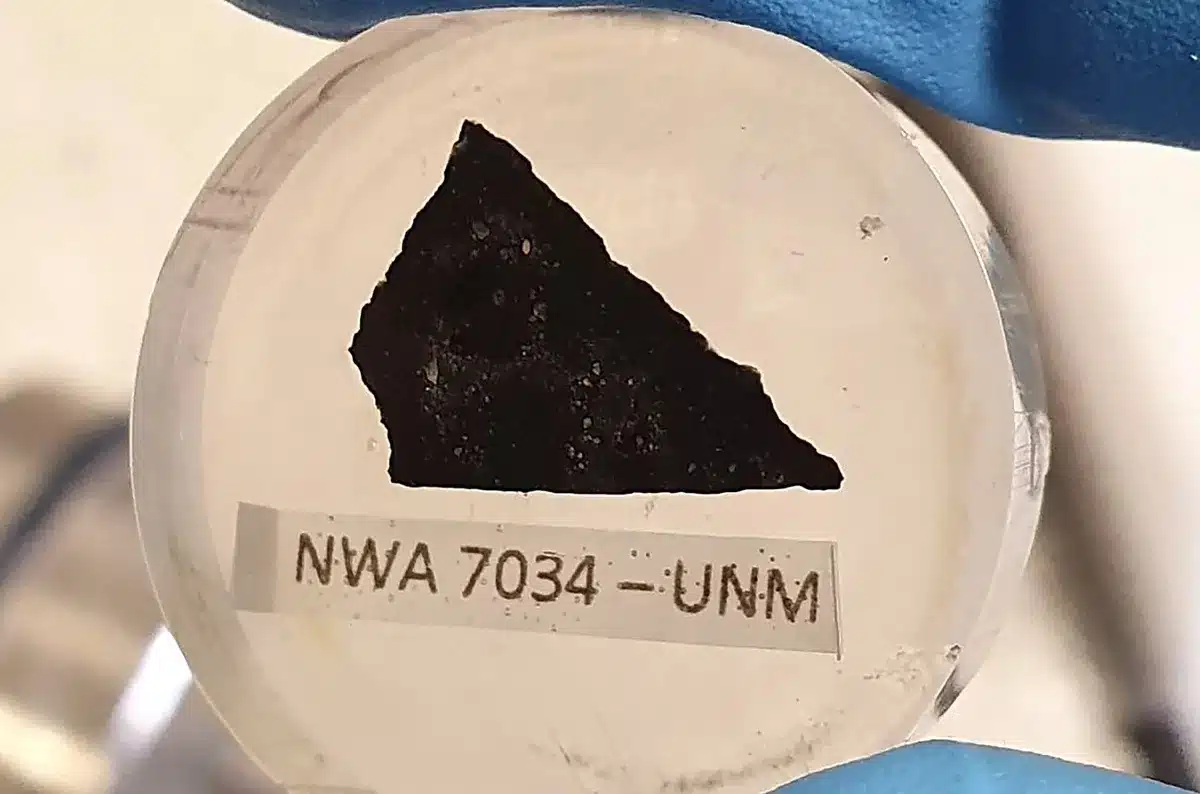
Locals watched in awe as a fireball exploded and masses of meteorite fragments rained down at the town of Tatahouine, Tunisia, on June 27, 1931.Fittingly, town later turned into a big filming location of the Famous person Wars film sequence. The desolate tract local weather and conventional villages turned into an enormous inspiration to the director, George Lucas, who proceeded to call the fictitious house planet of Luke Skywalker and Darth Vader “Tatooine”.The mysterious 1931 meteorite, an extraordinary form of achondrite (a meteorite that has skilled melting) referred to as a diogenite, is clearly no longer a fraction of Skywalker’s house planet. Nevertheless it used to be in a similar fashion named after town of Tatahouine.Now, a up to date find out about has gleaned essential insights into the the starting place of the meteorite – and the early Sun Device. The asteroid 4 vesta, left, and Tatooine, as noticed in Famous person Wars, at the proper. (NASA/Wikipedia)Lucas filmed more than a few scenes for Famous person Wars in Tatahouine. Those come with Episode IV – A New Hope (1977), Famous person Wars: Episode I – The Phantom Threat (1999) and Famous person Wars: Episode 2 – Assault of the Clones (2002). More than a few well-known scenes had been filmed there, together with scenes of “Mos Espa” and “Mos Eisley Cantina”.Mark Hamill, the actor who performed Luke Skywalker, reminisced about filming in Tunisia and mentioned it with Empire Mag: “If it’s essential to get into your personal thoughts, close out the staff and have a look at the horizon, you actually felt such as you had been transported to any other global”.
The asteroid 4 vesta, left, and Tatooine, as noticed in Famous person Wars, at the proper. (NASA/Wikipedia)Lucas filmed more than a few scenes for Famous person Wars in Tatahouine. Those come with Episode IV – A New Hope (1977), Famous person Wars: Episode I – The Phantom Threat (1999) and Famous person Wars: Episode 2 – Assault of the Clones (2002). More than a few well-known scenes had been filmed there, together with scenes of “Mos Espa” and “Mos Eisley Cantina”.Mark Hamill, the actor who performed Luke Skywalker, reminisced about filming in Tunisia and mentioned it with Empire Mag: “If it’s essential to get into your personal thoughts, close out the staff and have a look at the horizon, you actually felt such as you had been transported to any other global”. Tatahouine, Tunisia. (Wikipedia, CC BY-SA)Composition and originDiogenites, named after the Greek thinker Diogenes, are igneous meteorites (rocks that experience solidified from lava or magma). They shaped at intensity inside an asteroid and cooled slowly, ensuing within the formation of quite huge crystals.Tatahouine isn’t any exception, containing crystals as large as 5mm with black veins reducing move the pattern right through. The black veins are known as shock-induced have an effect on soften veins, and are a results of prime temperatures and pressures led to by means of a projectile smashing into the skin of the meteorite’s guardian frame.The presence of those veins and the construction of the grains of pyroxene (minerals containing calcium, magnesium, iron, and aluminum) recommend the pattern has skilled pressures of as much as 25 gigapascals (GPa) of drive.To position that into point of view, the drive on the backside of the Mariana Trench, the inner most a part of our ocean, is simplest 0.1 GPa. So it’s secure to mention this pattern has skilled a beautiful hefty have an effect on.Via comparing the spectrum (mild reflecting off their floor, damaged down by means of wavelength) of meteorites and evaluating it to asteroids and planets in our Sun Device, it’s been advised that diogenites, together with Tatahouine, originate from the second one greatest asteroid in our asteroid belt, referred to as 4 Vesta.This asteroid possesses attention-grabbing and thrilling details about the early Sun Device. Most of the meteorites from 4 Vesta are historic, round ~4 billion years. Subsequently, they provide a window to the previous occasions of the early Sun Device that we’re not able to judge right here on Earth.Violent pastThe contemporary find out about investigated 18 diogenites, together with Tatahouine, all from 4 Vesta. The authors undertook “radiometric argon-argon age courting” tactics to resolve the ages of the meteorites.That is in response to having a look at two other isotopes (variations of components whose nuclei have extra or fewer debris known as neutrons). We all know {that a} sure argon isotope in samples will increase with age at a recognized price, serving to scientists estimate an age of a pattern by means of evaluating the ratio between two other isotopes.The group additionally evaluated deformation led to by means of collisions, known as have an effect on occasions, the use of one of those electron microscope methodology known as electron backscatter diffraction.
Tatahouine, Tunisia. (Wikipedia, CC BY-SA)Composition and originDiogenites, named after the Greek thinker Diogenes, are igneous meteorites (rocks that experience solidified from lava or magma). They shaped at intensity inside an asteroid and cooled slowly, ensuing within the formation of quite huge crystals.Tatahouine isn’t any exception, containing crystals as large as 5mm with black veins reducing move the pattern right through. The black veins are known as shock-induced have an effect on soften veins, and are a results of prime temperatures and pressures led to by means of a projectile smashing into the skin of the meteorite’s guardian frame.The presence of those veins and the construction of the grains of pyroxene (minerals containing calcium, magnesium, iron, and aluminum) recommend the pattern has skilled pressures of as much as 25 gigapascals (GPa) of drive.To position that into point of view, the drive on the backside of the Mariana Trench, the inner most a part of our ocean, is simplest 0.1 GPa. So it’s secure to mention this pattern has skilled a beautiful hefty have an effect on.Via comparing the spectrum (mild reflecting off their floor, damaged down by means of wavelength) of meteorites and evaluating it to asteroids and planets in our Sun Device, it’s been advised that diogenites, together with Tatahouine, originate from the second one greatest asteroid in our asteroid belt, referred to as 4 Vesta.This asteroid possesses attention-grabbing and thrilling details about the early Sun Device. Most of the meteorites from 4 Vesta are historic, round ~4 billion years. Subsequently, they provide a window to the previous occasions of the early Sun Device that we’re not able to judge right here on Earth.Violent pastThe contemporary find out about investigated 18 diogenites, together with Tatahouine, all from 4 Vesta. The authors undertook “radiometric argon-argon age courting” tactics to resolve the ages of the meteorites.That is in response to having a look at two other isotopes (variations of components whose nuclei have extra or fewer debris known as neutrons). We all know {that a} sure argon isotope in samples will increase with age at a recognized price, serving to scientists estimate an age of a pattern by means of evaluating the ratio between two other isotopes.The group additionally evaluated deformation led to by means of collisions, known as have an effect on occasions, the use of one of those electron microscope methodology known as electron backscatter diffraction.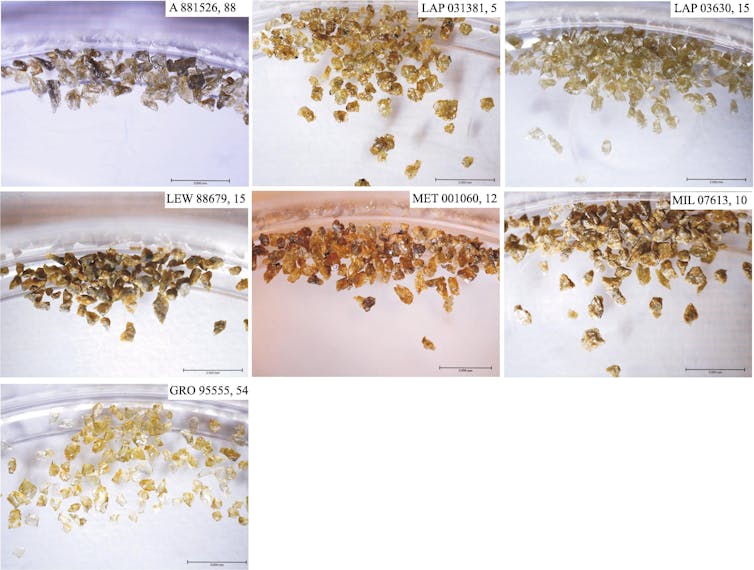 Seven of the diogenites analysed. (F. Jourdan et al, CC BY-SA)Via combining the age courting tactics and the microscope methodology, the authors controlled to map the timing of have an effect on occasions on 4 Vesta and the early Sun Device. The find out about means that 4 Vesta skilled ongoing have an effect on occasions till 3.4 billion years in the past when a catastrophic one befell.This catastrophic tournament, perhaps any other colliding asteroid, ended in more than one smaller rubble pile asteroids being produced referred to as “vestoids”. Unravelling huge scale have an effect on occasions reminiscent of this, finds the adverse nature of the early Sun Device.Those smaller our bodies skilled additional collisions that led to subject matter to hurtle to Earth during the last 50 to 60 million years – together with the fireball in Tunisia.In the end, this paintings demonstrates the significance of investigating meteorites – affects have performed a big function within the evolution of asteroids in our Sun Device.
Seven of the diogenites analysed. (F. Jourdan et al, CC BY-SA)Via combining the age courting tactics and the microscope methodology, the authors controlled to map the timing of have an effect on occasions on 4 Vesta and the early Sun Device. The find out about means that 4 Vesta skilled ongoing have an effect on occasions till 3.4 billion years in the past when a catastrophic one befell.This catastrophic tournament, perhaps any other colliding asteroid, ended in more than one smaller rubble pile asteroids being produced referred to as “vestoids”. Unravelling huge scale have an effect on occasions reminiscent of this, finds the adverse nature of the early Sun Device.Those smaller our bodies skilled additional collisions that led to subject matter to hurtle to Earth during the last 50 to 60 million years – together with the fireball in Tunisia.In the end, this paintings demonstrates the significance of investigating meteorites – affects have performed a big function within the evolution of asteroids in our Sun Device.![]()
Ben Rider-Stokes, Publish Doctoral Researcher in Achondrite Meteorites, The Open UniversityThis article is republished from The Dialog underneath a Inventive Commons license. Learn the unique article.
The Actual-Lifestyles 'Tatahouine' Meteorite At the back of Famous person Wars Unearths Its Secrets and techniques