A workforce of researchers has exposed a unique approach that molecules can engage non-reciprocally with out exterior forces, via a mechanism involving kinetic asymmetry. This discovery demanding situations conventional perspectives on molecular interactions and may have profound implications for working out existence’s evolution and designing molecular machines. Credit score: SciTechDaily.comScientists have discovered that molecules can engage in a non-reciprocal method with out exterior forces, a discovery that might trade our working out of molecular interactions and the evolution of existence.Researchers from the College of Maine and Penn State found out that molecules enjoy non-reciprocal interactions with out exterior forces.Elementary forces equivalent to gravity and electromagnetism are reciprocal, the place two gadgets are attracted to one another or are repelled by means of each and every different. In our on a regular basis enjoy, then again, interactions don’t appear to apply this reciprocal regulation. For instance, a predator is interested in prey, however the prey has a tendency to escape from the predator. Such non-reciprocal interactions are crucial for complicated conduct related to dwelling organisms.For microscopic methods equivalent to micro organism, the mechanism of non-reciprocal interactions has been defined by means of hydrodynamic or different exterior forces, and it used to be up to now idea that equivalent forms of forces may provide an explanation for interactions between unmarried molecules.In paintings printed within the prestigious Mobile Press magazine Chem, UMaine theoretical physicist R. Dean Astumian and collaborators Ayusman Sen and Niladri Sekhar Mandal at Penn State have printed a special mechanism during which unmarried molecules can engage non-reciprocally with out hydrodynamic results.This mechanism invokes the native gradients of reactants and merchandise because of the reactions facilitated by means of each and every chemical catalyst, a organic instance of which is an enzyme. Since the reaction of a catalyst to the gradient will depend on the catalyst’s homes, it’s conceivable to have a state of affairs through which one molecule is repelled by means of, however draws, every other molecule.Kinetic Asymmetry: A Key FactorThe authors’ “Eureka second” befell when, of their dialogue, they discovered {that a} assets of each and every catalyst referred to as the kinetic asymmetry controls the course of reaction to a focus gradient. As a result of kinetic asymmetry is a assets of the enzyme itself, it could actually go through evolution and adaptation. The non-reciprocal interactions allowed by means of kinetic asymmetry additionally play a a very powerful function in permitting molecules to engage with each and every different, and can have performed a vital function within the processes during which easy topic turns into complicated.
A workforce of researchers has exposed a unique approach that molecules can engage non-reciprocally with out exterior forces, via a mechanism involving kinetic asymmetry. This discovery demanding situations conventional perspectives on molecular interactions and may have profound implications for working out existence’s evolution and designing molecular machines. Credit score: SciTechDaily.comScientists have discovered that molecules can engage in a non-reciprocal method with out exterior forces, a discovery that might trade our working out of molecular interactions and the evolution of existence.Researchers from the College of Maine and Penn State found out that molecules enjoy non-reciprocal interactions with out exterior forces.Elementary forces equivalent to gravity and electromagnetism are reciprocal, the place two gadgets are attracted to one another or are repelled by means of each and every different. In our on a regular basis enjoy, then again, interactions don’t appear to apply this reciprocal regulation. For instance, a predator is interested in prey, however the prey has a tendency to escape from the predator. Such non-reciprocal interactions are crucial for complicated conduct related to dwelling organisms.For microscopic methods equivalent to micro organism, the mechanism of non-reciprocal interactions has been defined by means of hydrodynamic or different exterior forces, and it used to be up to now idea that equivalent forms of forces may provide an explanation for interactions between unmarried molecules.In paintings printed within the prestigious Mobile Press magazine Chem, UMaine theoretical physicist R. Dean Astumian and collaborators Ayusman Sen and Niladri Sekhar Mandal at Penn State have printed a special mechanism during which unmarried molecules can engage non-reciprocally with out hydrodynamic results.This mechanism invokes the native gradients of reactants and merchandise because of the reactions facilitated by means of each and every chemical catalyst, a organic instance of which is an enzyme. Since the reaction of a catalyst to the gradient will depend on the catalyst’s homes, it’s conceivable to have a state of affairs through which one molecule is repelled by means of, however draws, every other molecule.Kinetic Asymmetry: A Key FactorThe authors’ “Eureka second” befell when, of their dialogue, they discovered {that a} assets of each and every catalyst referred to as the kinetic asymmetry controls the course of reaction to a focus gradient. As a result of kinetic asymmetry is a assets of the enzyme itself, it could actually go through evolution and adaptation. The non-reciprocal interactions allowed by means of kinetic asymmetry additionally play a a very powerful function in permitting molecules to engage with each and every different, and can have performed a vital function within the processes during which easy topic turns into complicated.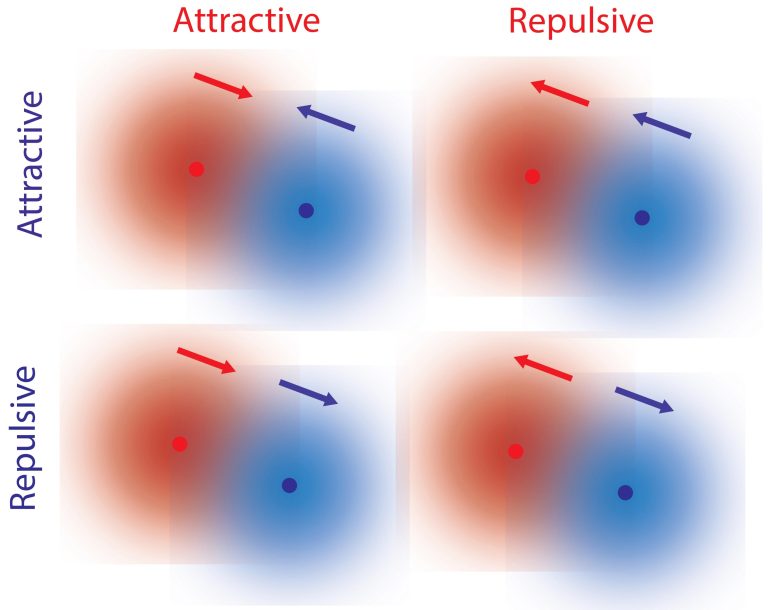 A graphic illustrating the 4 conceivable interactions between two debris, the place the arrows point out the drive skilled by means of the particle of that colour because of the gradient surrounding the particle of the opposite colour. The interactions proven within the higher left-hand and decrease right-hand corners illustrate reciprocal interactions the place the 2 debris draw in each and every different, or the place they repel each and every different, respectively. The higher right-hand graphic illustrates a state of affairs the place the crimson particle draws the blue particle, however the blue particle repels the crimson particle. The decrease left-hand graphic illustrates a state of affairs the place the crimson particle repels, however is interested in, the blue particle. Graphic courtesy of R. Dean Astumian. Credit score: R. Dean AstumianMuch earlier paintings has been carried out by means of different researchers on what occurs when non-reciprocal interactions happen. Those efforts have performed a central function within the building of a box referred to as “energetic topic.” On this previous paintings, the non-reciprocal interactions have been offered by means of incorporation of advert hoc forces.The analysis described by means of Mandal, Sen, and Astumian, then again, describes a fundamental molecular mechanism during which such interactions can rise up between unmarried molecules. This analysis builds on previous paintings through which the similar authors confirmed how a unmarried catalyst molecule may use power from the response it catalyzed to go through directional movement in a focus gradient.Affect on Biomolecular Machines and Early LifeThe kinetic asymmetry that includes in figuring out the non-reciprocal interactions between other catalysts has additionally been proven to be vital for the directionality of biomolecular machines, and has been integrated within the design of man-made molecular motors and pumps.The collaboration between Astumian, Sen, and Mandal objectives to show the organizational rules at the back of free associations of various catalysts that can have shaped the earliest metabolic buildings that finally resulted in the evolution of existence.“We’re on the very starting levels of this paintings, however I see working out kinetic asymmetry as a conceivable alternative for working out how existence advanced from easy molecules,” Astumian says. “No longer simplest can it supply perception into complexification of topic, kinetic asymmetry will also be used within the design of molecular machines and related applied sciences.”Reference: “A molecular beginning of non-reciprocal interactions between interacting energetic catalysts” by means of Niladri Sekhar Mandal, Ayusman Sen and R. Dean Astumian, 29 December 2023, Chem.
A graphic illustrating the 4 conceivable interactions between two debris, the place the arrows point out the drive skilled by means of the particle of that colour because of the gradient surrounding the particle of the opposite colour. The interactions proven within the higher left-hand and decrease right-hand corners illustrate reciprocal interactions the place the 2 debris draw in each and every different, or the place they repel each and every different, respectively. The higher right-hand graphic illustrates a state of affairs the place the crimson particle draws the blue particle, however the blue particle repels the crimson particle. The decrease left-hand graphic illustrates a state of affairs the place the crimson particle repels, however is interested in, the blue particle. Graphic courtesy of R. Dean Astumian. Credit score: R. Dean AstumianMuch earlier paintings has been carried out by means of different researchers on what occurs when non-reciprocal interactions happen. Those efforts have performed a central function within the building of a box referred to as “energetic topic.” On this previous paintings, the non-reciprocal interactions have been offered by means of incorporation of advert hoc forces.The analysis described by means of Mandal, Sen, and Astumian, then again, describes a fundamental molecular mechanism during which such interactions can rise up between unmarried molecules. This analysis builds on previous paintings through which the similar authors confirmed how a unmarried catalyst molecule may use power from the response it catalyzed to go through directional movement in a focus gradient.Affect on Biomolecular Machines and Early LifeThe kinetic asymmetry that includes in figuring out the non-reciprocal interactions between other catalysts has additionally been proven to be vital for the directionality of biomolecular machines, and has been integrated within the design of man-made molecular motors and pumps.The collaboration between Astumian, Sen, and Mandal objectives to show the organizational rules at the back of free associations of various catalysts that can have shaped the earliest metabolic buildings that finally resulted in the evolution of existence.“We’re on the very starting levels of this paintings, however I see working out kinetic asymmetry as a conceivable alternative for working out how existence advanced from easy molecules,” Astumian says. “No longer simplest can it supply perception into complexification of topic, kinetic asymmetry will also be used within the design of molecular machines and related applied sciences.”Reference: “A molecular beginning of non-reciprocal interactions between interacting energetic catalysts” by means of Niladri Sekhar Mandal, Ayusman Sen and R. Dean Astumian, 29 December 2023, Chem.
DOI: 10.1016/j.chempr.2023.11.017Astumian joined UMaine’s Division of Physics and Astronomy in 2001. His analysis specializes in biophysics, condensed topic physics, and chemically pushed molecular machines.He used to be named a fellow of the American Affiliation for the Development of Science (AAAS) In 2016. His different honors come with the Galvani Prize of the Bio-electrochemical Society, the Humboldt Prize, the Feynman Prize, and the Royal Society of Chemistry Horizon Prize, the Perkin Prize in bodily natural chemistry.
Redefining Molecular Physics: The Sudden Phenomenon of Kinetic Asymmetry