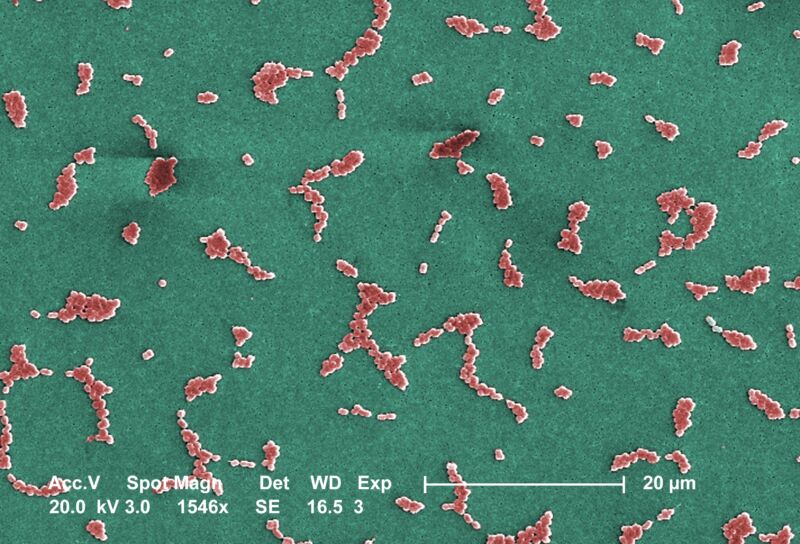
Magnify / This Scanning Electron Microscope symbol depicts a number of clusters of cardio Gram-negative, non-motile Acinetobacter baumannii micro organism underneath a magnification of 24,730x.
Participants of the genus Acinetobacter are nonmotile rods, 1-1.5µm in diameter, and 1.5-2.5µm in period, changing into round in form whilst of their desk bound segment of expansion. This micro organism is oxidase-negative and subsequently does no longer make the most of oxygen for power manufacturing. In addition they happen in pairs underneath magnification. Acinetobacter spp. are extensively allotted in nature, and are commonplace plants at the pores and skin. Some individuals of the genus are essential as a result of they’re an rising reason behind health facility obtained pulmonary, i.e., pneumoniae, hemopathic, and wound infections. For the reason that organism has advanced considerable antimicrobial resistance, remedy of infections attributed to A. baumannii has transform more and more demanding. The one drug that works on multi-resistant lines of A.baumannii is colistin which is an overly poisonous drug.
A brand new experimental antibiotic can handily knock off one of the vital global’s maximum notoriously drug-resistant and fatal micro organism —in lab dishes and mice, no less than. It does so with a never-before-seen way, cracking open a wholly new elegance of gear that might yield extra desperately wanted new treatments for combating drug-resistant infections.
The findings gave the impression this week in a couple of papers revealed in Nature, which lay out the intensive drug construction paintings performed by way of researchers at Harvard College and the Swiss-based pharmaceutical corporate Roche.
In an accompanying observation, chemists Morgan Gugger and Paul Hergenrother of the College of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign mentioned the findings with optimism, noting that it’s been greater than 50 years for the reason that Meals and Drug Management has licensed a brand new elegance of antibiotics towards the class of micro organism the drug objectives: Gram-negative micro organism. This class—which incorporates intestine pathogens akin to E. coli, Salmonella, Shigella, and the micro organism that reason chlamydia, the bubonic plague, gonorrhea, whooping cough, cholera, and typhoid, to call a couple of—is awfully difficult to kill as a result of it is outlined by way of having a posh membrane construction that blocks maximum medicine, and it is excellent at collecting different drug-resistance methods
Weighty discovering
On this case, the brand new drug—dubbed zosurabalpin—fights off the Gram-negative bacterium carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, aka CRAB. Despite the fact that it’s going to sound difficult to understand, it is an opportunistic, invasive micro organism that ceaselessly moves hospitalized and seriously sick sufferers, inflicting fatal infections international. It’s widely drug-resistant, with ongoing emergence of pan-resistant lines around the globe—in different phrases, lines which are proof against each and every present antibiotic to be had. Mortality charges of invasive CRAB infections vary from 40 to 60 p.c. In 2017, the International Well being Group indexed it as a concern 1: essential pathogen, for which new antibiotics are wanted maximum urgently.
Commercial
Zosurabalpin would possibly simply finally end up being that urgently wanted drug, as Gugger and Hergenrother write of their observation: “For the reason that zosurabalpin is already being examined in medical trials, the long run appears promising, with the potential of a brand new antibiotic elegance being in any case at the horizon for invasive CRAB infections.”
A world group of researchers, led by way of Michael Lobritz and Kenneth Bradley at Roche, first known a precursor of zosurabalpin via an strange display screen. Maximum new antibiotics are small molecules—those who have molecular weights of lower than 600 daltons. However on this case, researchers searched via a number of 45,000 larger, heavier compounds, known as tethered macrocyclic peptides (MCPs), that have weights round 800 daltons. The molecules have been screened towards a number of Gram-negative lines, together with an A. baumannii pressure. A gaggle of compounds knocked again the micro organism, and the researchers decided on the highest one—with the to hand care for of RO7036668. The molecule used to be then optimized and fine-tuned, together with fee balancing, to make it simpler, soluble, and secure. This led to zosurabalpin.
Fatal drug
In additional experiments, zosurabalpin proved efficient at killing a number of 129 medical CRAB isolates, lots of that have been difficult-to-treat isolates. The experimental drug used to be additionally efficient at ridding mice of infections with a pan-resistant A. baumannii isolate, that means on the other hand the drug labored, it might circumvent current resistance mechanisms.
Subsequent, the researchers labored to determine how zosurabalpin used to be killing off those pan-resistant, fatal micro organism. They did this the usage of a regular way of subjecting the micro organism to various concentrations of the antibiotic to urge spontaneous mutations. For micro organism that advanced tolerance to zosurabalpin, the researchers used complete genome sequencing to spot the place the mutations have been. They discovered 43 distinct mutations, and maximum have been in genes encoding LPS shipping and biosynthesis equipment.