Tiny fossils that experience spent just about 2 billion years locked up in chunks of historical rock are giving us the earliest proof but for photosynthesis on Earth.Within the McDermott Formation within the wilderness of northern Australia, tiny constructions referred to as thylakoids were found out in what are considered fossilized cyanobacteria courting again to one.75 billion years in the past.Those constructions are discovered within the cells of photosynthetic organisms lately that comprise the pigment chlorophyll, used to take in the sunshine for photosynthesis.Which means the microfossils constitute the oldest direct proof for photosynthesis, giving us a brand new minimal age for the emergence of thylakoid-bearing cyanobacteria, and a brand new instrument for figuring out early Earth ecosystems, and the way lifestyles emerged on our planet.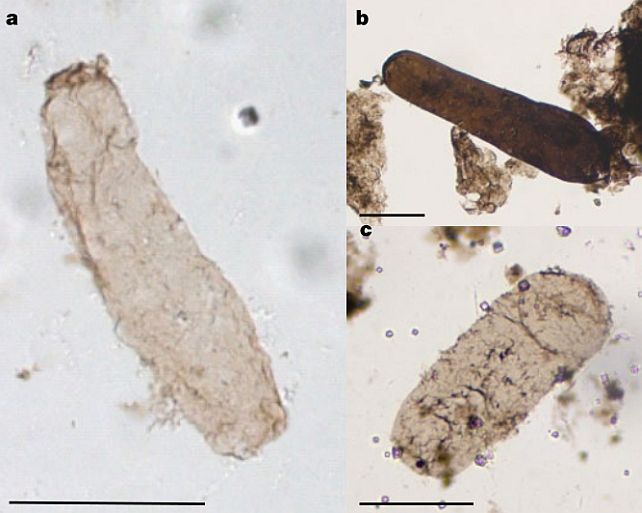 Photographs of microfossil specimens of Navifusa majensis. (Demoulin et al., Nature, 2024)”Our learn about supplies direct proof for the presence of metabolically lively cyanobacteria appearing oxygenic photosynthesis,” writes a crew led through paleomicrobiologist Catherine Demoulin of the College of Liège.The findings suggest {that a} detailed research of alternative fossils may just establish extra constructions find it irresistible, pinpointing the instant photosynthesizing constructions have been wolfed up and put to paintings through the earliest types of advanced algal cells.Photosynthesis, which harnesses daylight to transform water and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen, may look like one thing vegetation and algae are simply doing quietly to themselves over there, however it’s the foundation for the survival of just about all dwelling issues.Now not best do photosynthetic organisms shape the basis of maximum meals webs, their metabolic processes fill the ambience with the breathable oxygen maximum people wish to live to tell the tale.We all know that, early in Earth’s historical past, there wasn’t numerous oxygen floating freely within the environment and oceans. On the other hand, other strains of geochemical proof expose that oxygen ranges abruptly skyrocketed some 2.4 billion years in the past in what’s referred to as the Nice Oxidation Tournament. It is unclear what brought about it, however one risk is the emergence of photosynthetic organisms.The earliest undisputed microfossil proof of cyanobacteria is an organism referred to as Eoentophysalis belcherensis, dated to as much as 2.018 billion years in the past. However fossils are ceaselessly tough to interpret, and their inside constructions do not at all times live to tell the tale intact. And now not all cyanobacteria species have thylakoids.
Photographs of microfossil specimens of Navifusa majensis. (Demoulin et al., Nature, 2024)”Our learn about supplies direct proof for the presence of metabolically lively cyanobacteria appearing oxygenic photosynthesis,” writes a crew led through paleomicrobiologist Catherine Demoulin of the College of Liège.The findings suggest {that a} detailed research of alternative fossils may just establish extra constructions find it irresistible, pinpointing the instant photosynthesizing constructions have been wolfed up and put to paintings through the earliest types of advanced algal cells.Photosynthesis, which harnesses daylight to transform water and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen, may look like one thing vegetation and algae are simply doing quietly to themselves over there, however it’s the foundation for the survival of just about all dwelling issues.Now not best do photosynthetic organisms shape the basis of maximum meals webs, their metabolic processes fill the ambience with the breathable oxygen maximum people wish to live to tell the tale.We all know that, early in Earth’s historical past, there wasn’t numerous oxygen floating freely within the environment and oceans. On the other hand, other strains of geochemical proof expose that oxygen ranges abruptly skyrocketed some 2.4 billion years in the past in what’s referred to as the Nice Oxidation Tournament. It is unclear what brought about it, however one risk is the emergence of photosynthetic organisms.The earliest undisputed microfossil proof of cyanobacteria is an organism referred to as Eoentophysalis belcherensis, dated to as much as 2.018 billion years in the past. However fossils are ceaselessly tough to interpret, and their inside constructions do not at all times live to tell the tale intact. And now not all cyanobacteria species have thylakoids.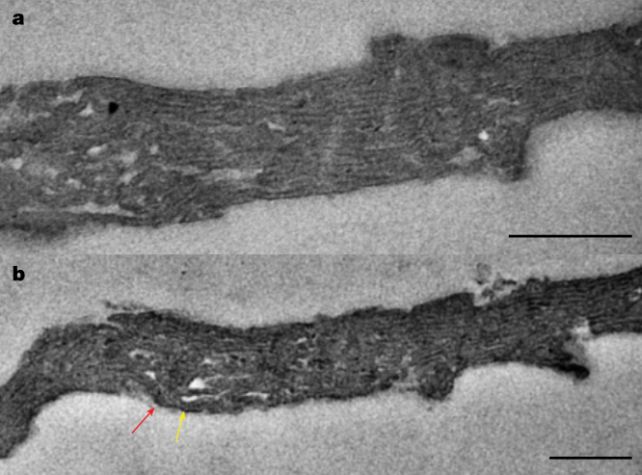 Transmission electron microscopy photographs of specimens of Navifusa majensis from the McDermott Formation. (Demoulin et al., Nature, 2024)Demoulin and her colleagues used other high-resolution microscopy tactics to probe the exterior and inside constructions of microfossils of a species referred to as Navifusa majensis, considered cyanobacteria. And, inside the our bodies of the single-celled organisms from two fossil beds, they discovered thylakoid membranes.Those fossils have been from the Grassy Bay Formation in Canada, dated to as much as 1.01 billion years in the past; and the McDermott Formation, stretching way back to 1.75 billion years in the past. This extends the fossil document of thylakoids again through a whopping 1.2 billion years – and implies that oxygenic photosynthesis will have to have developed ahead of that point.However what we nonetheless do not know is whether or not it developed in time to give a contribution to the Nice Oxidation Tournament. Simplest discovering, and moderately finding out, even older fossils may just give us a solution to this burning query.”The invention of preserved thylakoids inside of N. majensis reported right here supplies direct proof for a minimal age of about 1.75 billion years in the past for the divergence between thylakoid-bearing and thylakoid-less cyanobacteria,” the researchers write.”We expect that equivalent ultrastructural analyses of well-preserved microfossils may enlarge the geological document of oxygenic photosynthesizers, and of early, weakly oxygenated ecosystems during which advanced cells advanced.”The analysis has been printed in Nature.
Transmission electron microscopy photographs of specimens of Navifusa majensis from the McDermott Formation. (Demoulin et al., Nature, 2024)Demoulin and her colleagues used other high-resolution microscopy tactics to probe the exterior and inside constructions of microfossils of a species referred to as Navifusa majensis, considered cyanobacteria. And, inside the our bodies of the single-celled organisms from two fossil beds, they discovered thylakoid membranes.Those fossils have been from the Grassy Bay Formation in Canada, dated to as much as 1.01 billion years in the past; and the McDermott Formation, stretching way back to 1.75 billion years in the past. This extends the fossil document of thylakoids again through a whopping 1.2 billion years – and implies that oxygenic photosynthesis will have to have developed ahead of that point.However what we nonetheless do not know is whether or not it developed in time to give a contribution to the Nice Oxidation Tournament. Simplest discovering, and moderately finding out, even older fossils may just give us a solution to this burning query.”The invention of preserved thylakoids inside of N. majensis reported right here supplies direct proof for a minimal age of about 1.75 billion years in the past for the divergence between thylakoid-bearing and thylakoid-less cyanobacteria,” the researchers write.”We expect that equivalent ultrastructural analyses of well-preserved microfossils may enlarge the geological document of oxygenic photosynthesizers, and of early, weakly oxygenated ecosystems during which advanced cells advanced.”The analysis has been printed in Nature.
Scientists Simply Came upon a 1.75 Billion-Yr-Outdated Secret About The Starting place of Lifestyles














