The Porsmose Guy from the Neolithic Duration, discovered in1947 in Porsmose, Denmark. Credit score: The Danish Nationwide Museum
4 analysis articles printed in Nature practice the genetic strains and geographical origins of human sicknesses some distance again in time. The analyses supply detailed footage of prehistoric human range and migration, whilst proposing an reason behind a upward thrust within the genetic chance for a couple of sclerosis (MS).
By way of inspecting information from the arena’s biggest information set so far on 5,000 historical human genomes from Europe and Western Asia (Eurasia), new analysis has exposed the prehistoric human gene swimming pools of western Eurasia in extraordinary element.
The consequences are introduced in 4 articles printed in the similar factor of Nature by way of a global crew of researchers led by way of professionals from the College of Copenhagen and contributions from round 175 researchers from universities and museums within the U.Ok., the U.S., Germany, Australia, Sweden, Denmark, Norway, France, Poland, Switzerland, Armenia, Ukraine, Russia, Kazakhstan, and Italy. The various researchers constitute quite a lot of medical disciplines, together with archaeology, evolutionary biology, medication, historical DNA analysis, infectious illness analysis, and epidemiology.
The analysis discoveries introduced within the Nature articles are in line with analyses of a subset of the 5,000 genomes and come with:
The huge genetic implications of a culturally made up our minds barrier, which till about 4,000 years in the past prolonged up thru Europe from the Black Sea within the south to the Baltic Sea within the north.
Mapping of the way chance genes for a number of sicknesses, together with sort 2 diabetes and Alzheimer’s illness, had been dispersed in Eurasia within the wake of huge migration occasions greater than 5,000 years in the past.
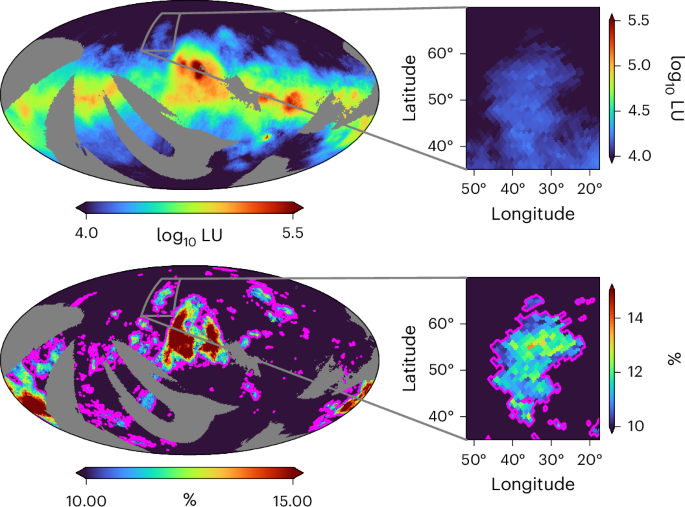
New medical proof of historical migrations explaining why the superiority of a couple of sclerosis is two times as top in Scandinavia than in Southern Europe.
Mapping of 2 virtually entire inhabitants turnovers in Denmark, inside of a unmarried millennium.
The 5,000 historical human genomes challenge
The extraordinary information set of five,000 historical human genomes used to be reconstructed by the use of research of bones and enamel made to be had thru a systematic partnership with museums and universities throughout Europe and western Asia. The sequencing effort used to be completed the usage of the ability of Illumina generation.
The age of specimens levels from the Mesolithic and Neolithic during the Bronze Age, Iron Age and Viking duration into the Heart Ages. The oldest genome within the information set is from a person who lived roughly 34,000 years in the past.
“The unique intention of the traditional human genomes challenge used to be to reconstruct 1,000 historical human genomes from Eurasia as a singular precision instrument for analysis in mind problems,” say the 3 College of Copenhagen professors, who in 2018 got here up with the theory for the DNA information set, and initially defined the challenge thought: Eske Willerslev, a professional in research of historical DNA, collectively on the College of Cambridge, and the director of the challenge; Thomas Werge, a professional in genetic components underlying psychological problems, and head of the Institute of Organic Psychiatry serving Psychological Well being Services and products within the Capital Area of Denmark; and Rasmus Nielsen, skilled in statistical and computational analyses of historical DNA, collectively at College of California, Berkeley, within the U.S.
The target used to be to supply a singular historical genomic information set for finding out the strains and genetic evolutionary historical past of mind problems as some distance again in time as conceivable to achieve new clinical and organic figuring out of those problems. This used to be to be achieved by way of evaluating data from the traditional DNA profiles with information from a number of different medical disciplines.
A few of the mind problems the 3 professors initially recognized as applicants for this investigation had been neurological prerequisites similar to Parkinson’s illness, Alzheimer’s illness, and a couple of sclerosis, along with psychological problems similar to ADHD and schizophrenia.
In 2018, the 3 professors then approached the Lundbeck Basis—a significant Danish analysis basis—for investment to assemble the particular DNA information set. They had been awarded a five-year analysis grant totaling DKK 60 million (app. EUR 8m) for the challenge, which used to be to be coordinated on the College of Copenhagen by the use of a newly established middle, therefore named the Lundbeck Basis GeoGenetics Heart.
“The reason for awarding this kind of huge analysis grant to this challenge, because the Lundbeck Basis did again in 2018, used to be that if all of it labored out, it will constitute a trail-blazing approach of gaining a deeper figuring out of the way the genetic structure underlying mind problems advanced over the years. And mind problems are our particular center of attention space,” says Jan Egebjerg, Director of Analysis, Lundbeck Basis.
The Lundbeck Basis could also be supporting iPYSCH consortium, one of the most biggest research globally of genetic and environmental reasons of psychological problems similar to autism, ADHD, schizophrenia, bipolar dysfunction, and despair, the place the point of interest could also be on making genetic chance profiles for those problems as actual as conceivable.
The consequences reported in Nature, had been substantiated by way of evaluating the traditional genomic information set with de-identified genetic information from the huge Danish iPYSCH consortium and DNA profiles from 400,000 present-day people registered in UK Biobank.
Many demanding situations
The idea for the challenge used to be experimental, recounts Professor Werge. “We needed to gather historical human specimens to peer what lets get out of them, like seeking to perceive one of the crucial environmental background to how sicknesses and problems advanced. As I see it, the truth that the challenge took on such huge, complicated proportions that Nature sought after it described in 4 articles is moderately distinctive.”
Professor Willerslev feedback that compiling the DNA information set posed primary logistical demanding situations. “We would have liked get entry to to archaeological specimens of human enamel and bones that we knew had been scattered round in museums and different establishments within the Eurasian area, and that referred to as for lots of collaboration agreements. However after they had been in position, issues truly took off—the knowledge set used to be booming, and it now exceeds 5,000 historical human genomes. The dimensions of the knowledge set has vastly enhanced each the usability and precision of the effects.”
Professor Nielsen used to be accountable for making plans the statistical and bioinformatics analyses of the ideas gleaned from the traditional enamel and bones in laboratories on the College of Copenhagen. And he used to be coping with an amazing quantity of information, wherein the DNA used to be incessantly critically degraded.
“Nobody had in the past analyzed such a lot of historical genomes. Now we needed to learn how to take care of such huge information volumes. The issue used to be that the uncooked information could be very tricky to paintings with as a result of you find yourself with many brief DNA sequences with many mistakes, after which the ones sequences need to be appropriately mapped to the appropriate place within the human genome. Plus, there’s the problem of contamination from all of the microorganisms gift at the historical enamel and bones.
“Consider having a jigsaw puzzle consisting of thousands and thousands of items combined up with 4 different incomplete puzzle units, after which operating all that within the dishwasher for an hour. Piecing all of it in combination afterwards isn’t any simple activity. One of the crucial keys to our good fortune after all used to be that we teamed up with Dr. Olivier Delanau from the College of Lausanne who advanced algorithms to triumph over that very drawback,” says Professor Nielsen.
Global hobby
Rumors that an enormous historical human genome information set used to be being compiled had been quickly circulating in medical circles. And because 2022 hobby has been operating very top, say Professors Werge, Willerslev and Nielsen. “We’re continuously taking inquiries from researchers all over the place the globe—particularly the ones investigating sicknesses—who most often request get entry to to discover the traditional DNA information set.”
The 4 Nature articles display that the huge information set of five,000 genomes serves as a precision instrument able to offering new insights into sicknesses when mixed with analyses of present-day human DNA information and inputs from a number of different analysis fields.
That during itself is immensely wonderful, in line with Professor Willerslev. “There is not any doubt that an historical genomic information set of this dimension can have packages in many alternative contexts inside of illness analysis. As new medical discoveries derived from the 5,000-genome information set turn into printed, extra information will regularly be made freely to be had to all researchers. In the end, all the information set will likely be open get entry to for everybody.”
Additional info:
Morten E. Allentoft et al, Inhabitants genomics of post-glacial western Eurasia, Nature (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06865-0
Evan Ok. Irving-Pease et al, The choice panorama and genetic legacy of historical Eurasians, Nature (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06705-1
William Barrie et al, Increased genetic chance for a couple of sclerosis emerged in steppe pastoralist populations, Nature (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06618-z
Morten E. Allentoft et al, 100 historical genomes display repeated inhabitants turnovers in Neolithic Denmark, Nature (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06862-3
Supplied by way of
College of Copenhagen
Quotation:
Discoveries gleaned from historical human DNA (2024, January 13)
retrieved 14 January 2024
from
This report is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal learn about or analysis, no
phase could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is equipped for info functions best.