Within the twilight of the Cretaceous, 86 million years in the past, a volcanic fissure in what’s now South Africa rumbled to existence. Under the outside, magma from loads of miles down shot upward as speedy as a automotive at the autobahn — if that automotive had been barreling via forged rock — chewing up rocks and minerals and sporting them towards the outside in a opposite avalanche.What this appeared like at the floor is misplaced to historical past, however it’s going to were as dramatic because the eruption of Mount Vesuvius. What it left in the back of was once a chain of carrot-shaped, igneous-rock-filled tubes underneath low, weathered white hills.In 1869, a shepherd’s discovery of an enormous, sparkly rock on a close-by riverbank would catapult this unassuming panorama into infamy. The rock was once a huge diamond that may sooner or later be referred to as the Celebrity of Africa, and the white hills concealed what would change into the Kimberley Mine, the epicenter of South Africa’s diamond rush and fairly perhaps the biggest hollow on Earth ever dug out by way of hand.Because of the Kimberley Mine, frequently referred to as “The Large Hollow,” the formations the place diamonds are discovered at the moment are referred to as kimberlites. The formations are sprinkled around the globe, from Ukraine to Siberia to Western Australia, however they are reasonably small and uncommon. What makes them particular is that their magmas come from very deep down. There are nonetheless questions on exactly how deep, however they’re identified to stand up from underneath the bases of continents on the border of the new, convecting mantle. Some would possibly originate even deeper, on the transition between the higher and decrease mantle.Comparable: What is inside of Earth?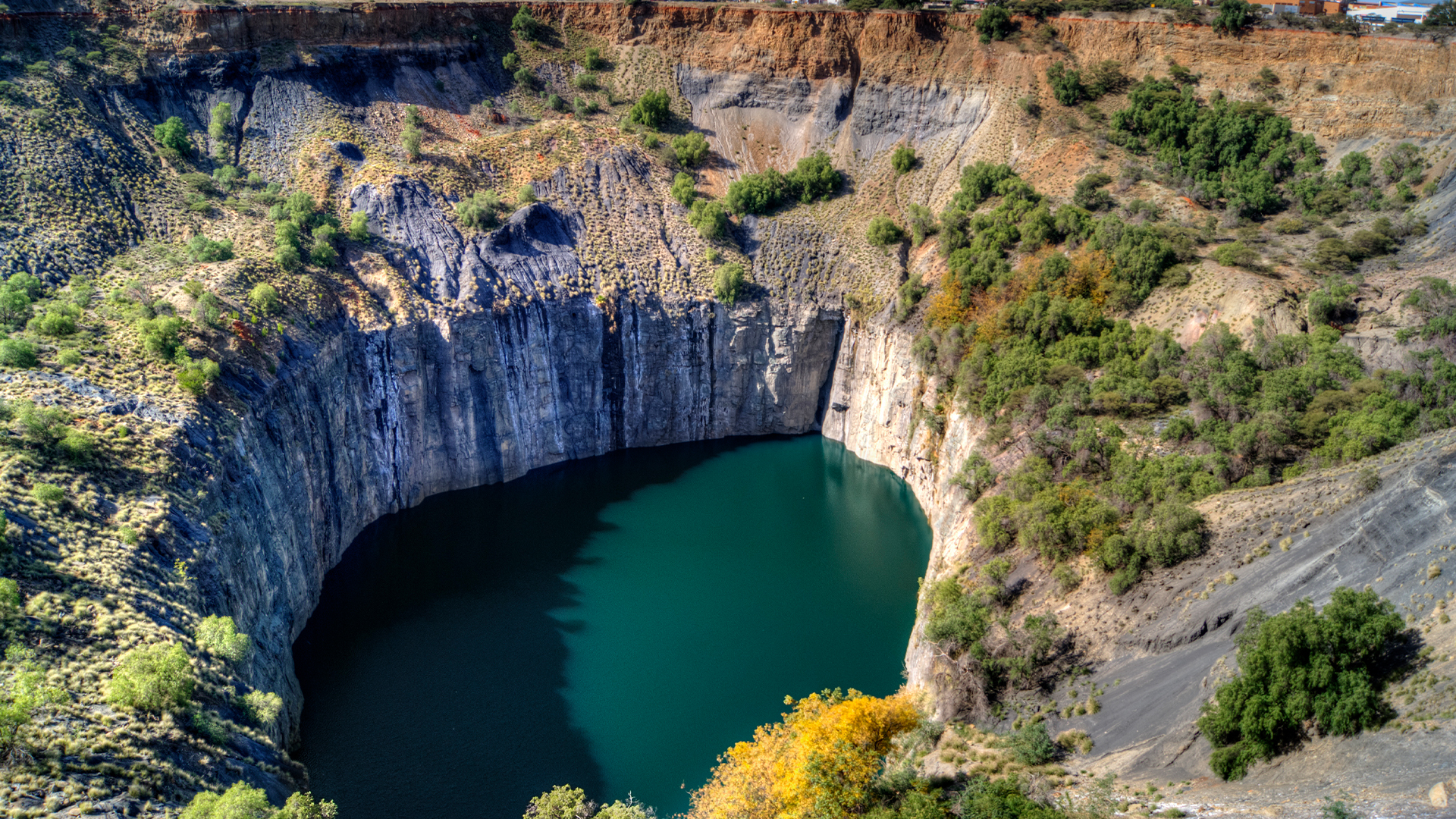 In 1869, a shepherd in South Africa found out a large diamond within the hills, and the Kimberley Mine was once born. The mine has since closed and the “large hollow,” perhaps the biggest hollow ever dug by way of hand, is full of water. (Symbol credit score: Hans Zúñiga Rojas by means of Getty Pictures)As such, those magmas faucet into very deep, very historic rock, and they have interaction with different processes that happen simplest within the deep Earth — specifically, the formation of diamonds. To crystallize plain-old carbon into laborious, sparkly diamond calls for nice drive, so those gem stones shape a minimum of 93 miles (150 kilometers) down, within the private layers of the lithosphere, the medical time period for the crust and reasonably inflexible higher mantle. Some, referred to as sub-lithospheric diamonds, shape even deeper, all the way down to round 435 miles (700 km). Kimberlites, on their eruptive trips to the outside, catch diamonds and drag them into the higher crust, handing over them reasonably unscathed and from time to time even containing wallet of fluid from the mantle itself.Researchers have lengthy identified that as tectonic plates grind underneath one any other, they drag down carbon from the outside to depths the place it will probably crystallize into diamond. Now, they are beginning to see that what is going down should (from time to time) arise, and that this reappearance of carbon — now pressed into glittering gem stones — may be tied to the actions of tectonic plates. Specifically, diamonds appear to erupt when supercontinents damage aside.”Whilst those are other processes, in combination the diamonds and kimberlite can tell us concerning the existence cycle of supercontinent occasions,” stated Suzette Timmerman, a geologist on the College of Bern in Switzerland who research diamonds.Coming to the surfaceNo one has ever observed a kimberlite eruption firsthand. There were only a few up to now 50 million years, and the latest conceivable eruption, within the Igwisi Hills of Tanzania, took place over 10,000 years in the past. Now not simplest that, however the principle subject material in kimberlite, the mineral olivine, weathers away temporarily at the floor, stated Hugo Olierook, a analysis fellow at Curtin College in Australia.This makes finding out kimberlites difficult. Scientists are at a loss for words, for instance, concerning the chemistry of the unique supply of the melted rock within the mantle, in addition to about how kimberlites arrange to punch throughout the strong cores of what geoscientists name “cratons” — the thick internal portions of continents that generally withstand disruption.A handful of latest research are sketching out a brand new reason for why this occurs. The primary clue is timing. It is lengthy been famous that pulses of kimberlite task appear to correspond with the approximate timing of supercontinent break-ups, stated Kelly Russell, a volcanologist on the College of British Columbia in Canada. A 2018 learn about led by way of Sebastian Tappe, a geoscientist at The Arctic College of Norway, took an international take a look at this accident of timing and located that it up: There was once a spike in kimberlite eruptions across the breakup of the supercontinent Nuna some 1.2 billion years in the past to one billion years in the past.Every other pulse took place between 600 million and 500 million years in the past, coinciding with the breakup of the supercontinent Rodinia, in keeping with the 2018 analysis, adopted by way of a smaller pulse between 400 million and 350 million years in the past. However probably the most prolific length, accounting for 62.5% of all identified kimberlites, took place between 250 million and 50 million years in the past. That vary occurs to coincide with the breakup of the supercontinent Pangaea. To a couple researchers, this means that supercontinent cycles are the most important for kimberlite eruptions.”The breakup of those continents are basic to getting those diamonds up from those deep depths,” Olierook informed Are living Science.Olierook and his workforce lately analyzed the ages of bizarre red diamonds from a formation in western Australia and located they most likely got here to the outside about 1.3 billion years in the past, throughout the window of Nuna breaking apart. The brand new discovery hyperlinks diamonds to the stretching of continental crust, Olierook stated.”It is the ones extensional forces that let the ones little wallet of deep-seated magma to upward thrust to the highest,” he stated.The march of the kimberlites
In 1869, a shepherd in South Africa found out a large diamond within the hills, and the Kimberley Mine was once born. The mine has since closed and the “large hollow,” perhaps the biggest hollow ever dug by way of hand, is full of water. (Symbol credit score: Hans Zúñiga Rojas by means of Getty Pictures)As such, those magmas faucet into very deep, very historic rock, and they have interaction with different processes that happen simplest within the deep Earth — specifically, the formation of diamonds. To crystallize plain-old carbon into laborious, sparkly diamond calls for nice drive, so those gem stones shape a minimum of 93 miles (150 kilometers) down, within the private layers of the lithosphere, the medical time period for the crust and reasonably inflexible higher mantle. Some, referred to as sub-lithospheric diamonds, shape even deeper, all the way down to round 435 miles (700 km). Kimberlites, on their eruptive trips to the outside, catch diamonds and drag them into the higher crust, handing over them reasonably unscathed and from time to time even containing wallet of fluid from the mantle itself.Researchers have lengthy identified that as tectonic plates grind underneath one any other, they drag down carbon from the outside to depths the place it will probably crystallize into diamond. Now, they are beginning to see that what is going down should (from time to time) arise, and that this reappearance of carbon — now pressed into glittering gem stones — may be tied to the actions of tectonic plates. Specifically, diamonds appear to erupt when supercontinents damage aside.”Whilst those are other processes, in combination the diamonds and kimberlite can tell us concerning the existence cycle of supercontinent occasions,” stated Suzette Timmerman, a geologist on the College of Bern in Switzerland who research diamonds.Coming to the surfaceNo one has ever observed a kimberlite eruption firsthand. There were only a few up to now 50 million years, and the latest conceivable eruption, within the Igwisi Hills of Tanzania, took place over 10,000 years in the past. Now not simplest that, however the principle subject material in kimberlite, the mineral olivine, weathers away temporarily at the floor, stated Hugo Olierook, a analysis fellow at Curtin College in Australia.This makes finding out kimberlites difficult. Scientists are at a loss for words, for instance, concerning the chemistry of the unique supply of the melted rock within the mantle, in addition to about how kimberlites arrange to punch throughout the strong cores of what geoscientists name “cratons” — the thick internal portions of continents that generally withstand disruption.A handful of latest research are sketching out a brand new reason for why this occurs. The primary clue is timing. It is lengthy been famous that pulses of kimberlite task appear to correspond with the approximate timing of supercontinent break-ups, stated Kelly Russell, a volcanologist on the College of British Columbia in Canada. A 2018 learn about led by way of Sebastian Tappe, a geoscientist at The Arctic College of Norway, took an international take a look at this accident of timing and located that it up: There was once a spike in kimberlite eruptions across the breakup of the supercontinent Nuna some 1.2 billion years in the past to one billion years in the past.Every other pulse took place between 600 million and 500 million years in the past, coinciding with the breakup of the supercontinent Rodinia, in keeping with the 2018 analysis, adopted by way of a smaller pulse between 400 million and 350 million years in the past. However probably the most prolific length, accounting for 62.5% of all identified kimberlites, took place between 250 million and 50 million years in the past. That vary occurs to coincide with the breakup of the supercontinent Pangaea. To a couple researchers, this means that supercontinent cycles are the most important for kimberlite eruptions.”The breakup of those continents are basic to getting those diamonds up from those deep depths,” Olierook informed Are living Science.Olierook and his workforce lately analyzed the ages of bizarre red diamonds from a formation in western Australia and located they most likely got here to the outside about 1.3 billion years in the past, throughout the window of Nuna breaking apart. The brand new discovery hyperlinks diamonds to the stretching of continental crust, Olierook stated.”It is the ones extensional forces that let the ones little wallet of deep-seated magma to upward thrust to the highest,” he stated.The march of the kimberlites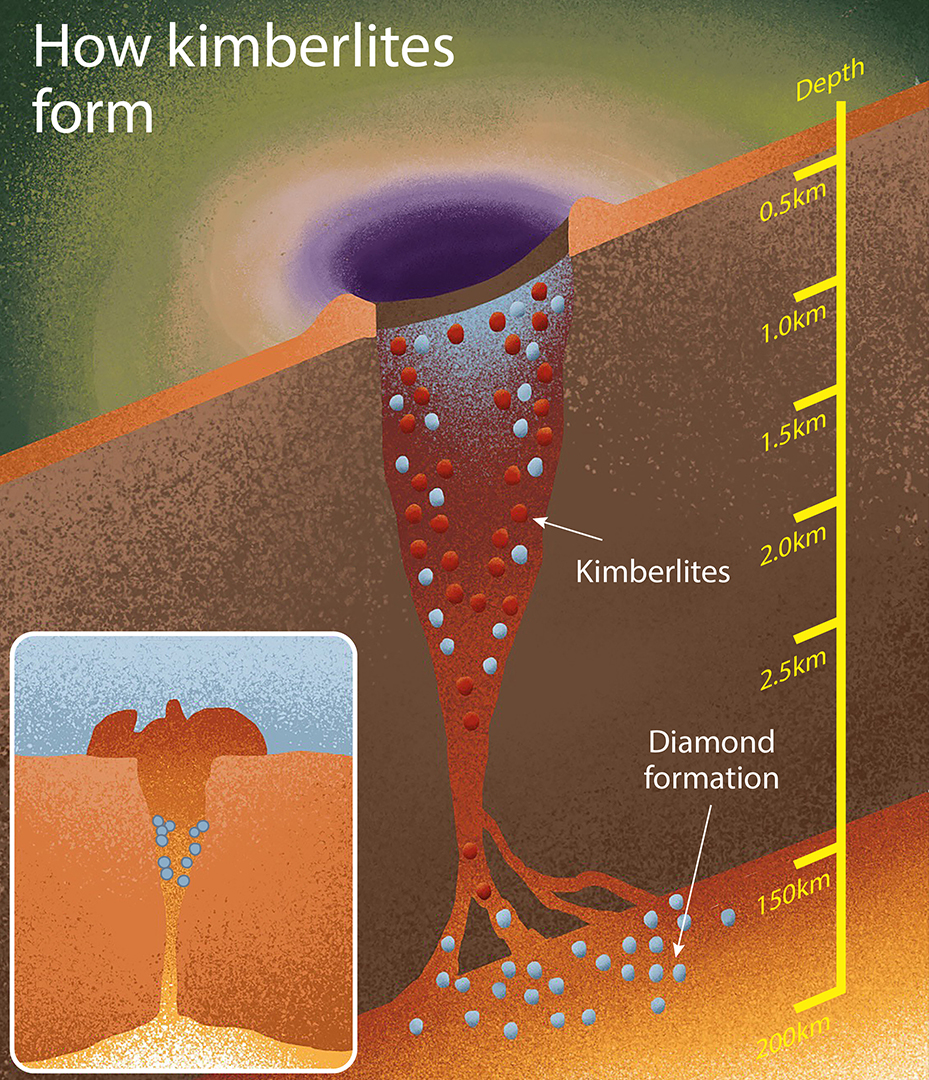 Kimberlites shape on the base of continents and as they upward thrust temporarily, they catch deeper-formed diamonds and drag them to the outside via kimberlite pipes. (Symbol credit score: Rory McNicol for Are living Science)The difficult query, although, is how this occurs. To get a kimberlite, there are two key substances: deep, melted rock wealthy in fluids, and a continental disruption that can deliver that soften to the outside. Nobody is aware of what reasons the formation of the kimberlite soften, however the chemistry of kimberlites may be very other from that of the mantle rock it melts from. Kimberlites also are wealthy in volatiles similar to water and carbon dioxide, which is what makes them so buoyant and high-velocity. They shoot throughout the crust like Champagne speeding via an uncorked bottle, ascending at as much as 83 mph (134 km/h). For comparability, the magmas that go with the flow out of the volcanoes in puts like Hawaii max out at round 13.5 mph (21.7 km/h).An August 2023 learn about used laptop modeling to determine how kimberlites can burst throughout the thick hearts of continents. The researchers discovered that the method of rifting, during which continental crust pulls aside, was once key. The stretching creates peaks and valleys at each the outside and base of the continent. On the base, those jagged edges permit heat mantle fabrics to upward thrust, after which cool and fall, growing eddies. Those eddies combine fabrics from the bottom of the continents, making the frothy, buoyant kimberlites, which will then shoot up towards the outside, sporting any diamonds they may occur to run into on their approach up.This procedure started proper the place the continent was once rifting aside, however modeling confirmed that those jagged areas of eddy formation destabilized neighboring spaces at the craton, growing the similar dynamics nearer and nearer to the continental internal. The end result was once a trend of kimberlite eruptions beginning close to the rift zone however regularly marching into spaces of strong crust. This gradual march explains why kimberlite pulses do not height till a little bit after a large breakup starts, stated Thomas Gernon, a geologist on the College of Southampton within the U.Okay. who led the learn about.”You’ll see those peaks of kimberlites appear to occur after large supercontinents have damaged up,” he stated. “However it is not only a one-hit factor; it is one thing that can ultimate fairly a very long time after supercontinent breakups.”
Kimberlites shape on the base of continents and as they upward thrust temporarily, they catch deeper-formed diamonds and drag them to the outside via kimberlite pipes. (Symbol credit score: Rory McNicol for Are living Science)The difficult query, although, is how this occurs. To get a kimberlite, there are two key substances: deep, melted rock wealthy in fluids, and a continental disruption that can deliver that soften to the outside. Nobody is aware of what reasons the formation of the kimberlite soften, however the chemistry of kimberlites may be very other from that of the mantle rock it melts from. Kimberlites also are wealthy in volatiles similar to water and carbon dioxide, which is what makes them so buoyant and high-velocity. They shoot throughout the crust like Champagne speeding via an uncorked bottle, ascending at as much as 83 mph (134 km/h). For comparability, the magmas that go with the flow out of the volcanoes in puts like Hawaii max out at round 13.5 mph (21.7 km/h).An August 2023 learn about used laptop modeling to determine how kimberlites can burst throughout the thick hearts of continents. The researchers discovered that the method of rifting, during which continental crust pulls aside, was once key. The stretching creates peaks and valleys at each the outside and base of the continent. On the base, those jagged edges permit heat mantle fabrics to upward thrust, after which cool and fall, growing eddies. Those eddies combine fabrics from the bottom of the continents, making the frothy, buoyant kimberlites, which will then shoot up towards the outside, sporting any diamonds they may occur to run into on their approach up.This procedure started proper the place the continent was once rifting aside, however modeling confirmed that those jagged areas of eddy formation destabilized neighboring spaces at the craton, growing the similar dynamics nearer and nearer to the continental internal. The end result was once a trend of kimberlite eruptions beginning close to the rift zone however regularly marching into spaces of strong crust. This gradual march explains why kimberlite pulses do not height till a little bit after a large breakup starts, stated Thomas Gernon, a geologist on the College of Southampton within the U.Okay. who led the learn about.”You’ll see those peaks of kimberlites appear to occur after large supercontinents have damaged up,” he stated. “However it is not only a one-hit factor; it is one thing that can ultimate fairly a very long time after supercontinent breakups.”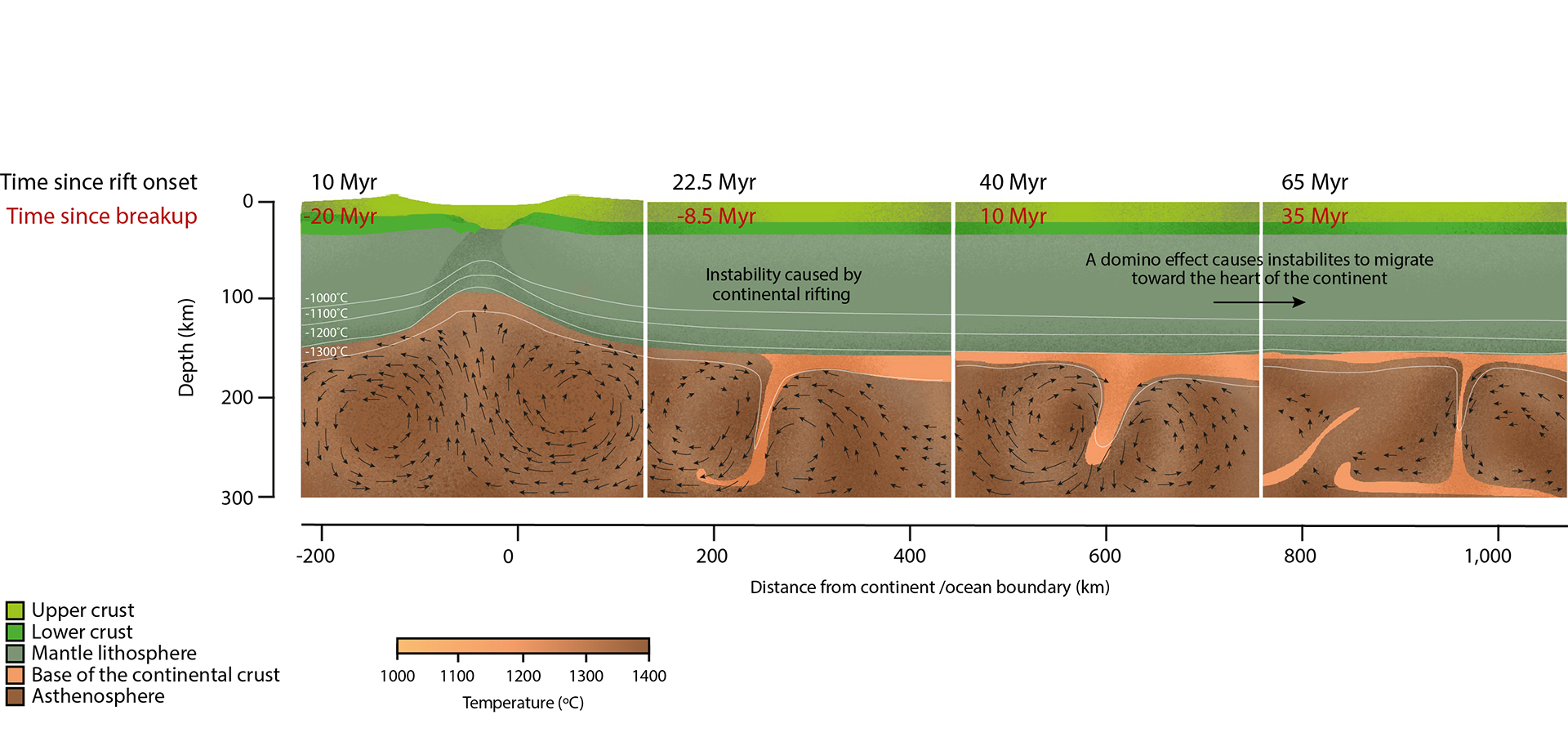 Instabilities shape on the edges of continents however migrate towards the hearts of the “cratons” over tens of millions of years. (Symbol credit score: Rory McNicol for Are living Science, tailored from Gernon et al, 2023.)Kimberlites is also fairly not unusual on the bases of continents, stated Tappe, whose 2018 learn about on kimberlites and supercontinent breakups got here to identical conclusions as Gernon’s. Tappe and his workforce discovered that those melts could have been in particular distinguished all over the breakup of Pangaea, since the mantle, which has been slowly cooling since Earth solidified, reached simply the correct temperature round 250 million years in the past to have kimberlite-type melts dominate. Previous to that length, the rocks in that area could have been too scorching to get that aggregate of soften and risky subject material that makes kimberlites so eruptive. This can be one explanation why maximum kimberlite diamond mines date from the breakup of Pangaea.Messages in a diamondAs the boring, white hills that after coated the Kimberley Mine attest, kimberlites themselves can not say a lot concerning the mantle the place they originated. They climate away inside of a couple of years, shedding a lot of what makes them attention-grabbing on a chemical degree. Alternatively, the diamonds carried inside of kimberlites are a distinct tale. They’ve their very own formation histories that do not coincide with the formation of the kimberlite magma itself. However their likelihood conferences loads of miles underneath the outside imply that bits of the mantle that may by no means differently see sunlight can succeed in human arms.Those bits are microscopic wallet of fluid from the time the diamonds fashioned. Many of those “inclusions” date again loads of tens of millions of years, whilst a couple of specimens depend their ages within the billions. Plus, a few of these diamonds shape very deep within the mantle, so sure stones can lift fabrics from as a long way down because the boundary between the mantle and the core.”Most effective in kimberlites we will be able to see samples coming from 400 kilometers [250 miles], even down to two,000 kilometers [1,200 miles],” stated Maya Kopylova, a professor of diamond exploration on the College of British Columbia. “No different magmas on Earth do this.”Comparable: What is the deepest-forming gemstone on Earth?
Instabilities shape on the edges of continents however migrate towards the hearts of the “cratons” over tens of millions of years. (Symbol credit score: Rory McNicol for Are living Science, tailored from Gernon et al, 2023.)Kimberlites is also fairly not unusual on the bases of continents, stated Tappe, whose 2018 learn about on kimberlites and supercontinent breakups got here to identical conclusions as Gernon’s. Tappe and his workforce discovered that those melts could have been in particular distinguished all over the breakup of Pangaea, since the mantle, which has been slowly cooling since Earth solidified, reached simply the correct temperature round 250 million years in the past to have kimberlite-type melts dominate. Previous to that length, the rocks in that area could have been too scorching to get that aggregate of soften and risky subject material that makes kimberlites so eruptive. This can be one explanation why maximum kimberlite diamond mines date from the breakup of Pangaea.Messages in a diamondAs the boring, white hills that after coated the Kimberley Mine attest, kimberlites themselves can not say a lot concerning the mantle the place they originated. They climate away inside of a couple of years, shedding a lot of what makes them attention-grabbing on a chemical degree. Alternatively, the diamonds carried inside of kimberlites are a distinct tale. They’ve their very own formation histories that do not coincide with the formation of the kimberlite magma itself. However their likelihood conferences loads of miles underneath the outside imply that bits of the mantle that may by no means differently see sunlight can succeed in human arms.Those bits are microscopic wallet of fluid from the time the diamonds fashioned. Many of those “inclusions” date again loads of tens of millions of years, whilst a couple of specimens depend their ages within the billions. Plus, a few of these diamonds shape very deep within the mantle, so sure stones can lift fabrics from as a long way down because the boundary between the mantle and the core.”Most effective in kimberlites we will be able to see samples coming from 400 kilometers [250 miles], even down to two,000 kilometers [1,200 miles],” stated Maya Kopylova, a professor of diamond exploration on the College of British Columbia. “No different magmas on Earth do this.”Comparable: What is the deepest-forming gemstone on Earth?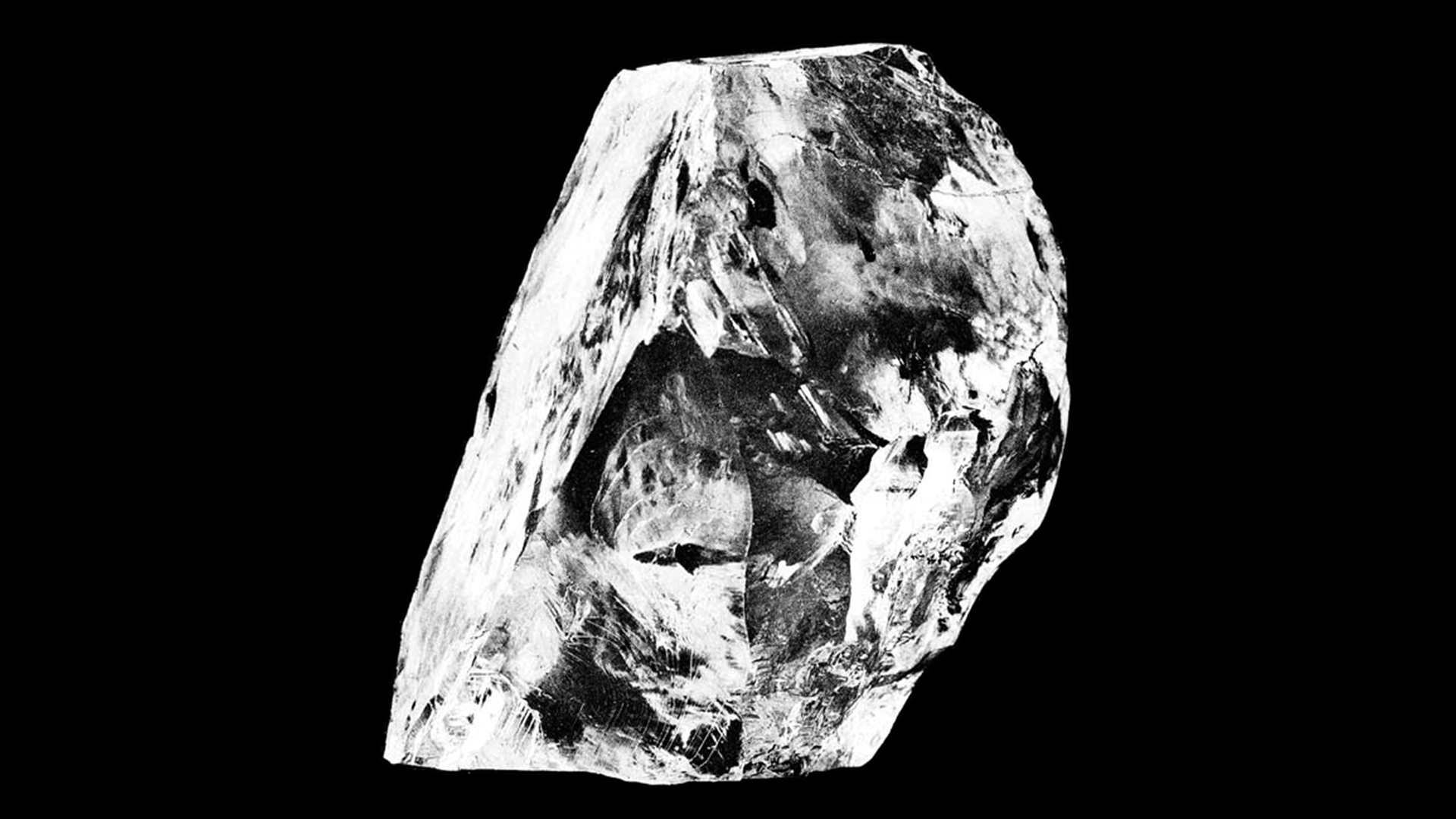 The tough Cullinan diamond, the biggest identified gem-quality tough diamond, was once pulled from the Kimberley Mine in 1905. Diamonds like those can come from deep inside of Earth and disclose billions of years of the planet’s historical past. (Symbol credit score: Public Area)Whilst the eruption of diamonds can hint a tale of supercontinent breakup, their formation may additionally supply a clue to how continents come in combination. In a learn about printed in October 2023 within the magazine Nature, Timmerman studied diamonds from Brazil and Guinea that fashioned between 186 and 434 miles deep (300 to 700 km). Through courting fluid inclusions throughout the diamonds, Timmerman and her colleagues estimated that the diamonds fashioned round 650 million years in the past, when the supercontinent Gondwana was once forming. The diamonds most probably caught to the bottom of the continent and sat there for millennia till Gondwana broke up all over the Cretaceous length and kimberlites introduced them to floor, Timmerman informed Are living Science.What was once necessary about those superdeep diamonds, Timmerman stated, was once that they helped give an explanation for how continents develop. Supercontinents are constructed when oceanic crust pushes underneath continental crust. This procedure, referred to as subduction, tugs two continents on reverse facets of an ocean nearer in combination. This similar subduction brings carbon to the depths, the place it may be compressed into diamond.Down within the mantle, bits of those subducting plates can change into buoyant and upward thrust again up, sporting superdeep diamonds with them, Timmerman defined. This subject material would possibly persist with the bases of continents for millennia, serving to them develop from underneath. It may additionally give an explanation for how superdeep diamonds land in a spot the place a kimberlite can catch them.”Deep diamonds can tell us extra about subduction processes, mantle convection, liquid-rock interactions and different processes taking place underneath the crust all over supercontinent cycles,” Timmerman stated.There are lots of different questions to reply to, she added. As an example, scientists nonetheless do not know the way subducted plates trade the bases of supercontinents and whether or not that has effects on how lengthy a supercontinent lasts sooner than breaking apart. Every other open query is whether or not this recycled crustal subject material influences when and the place kimberlite magmas shape.Historic diamonds may additionally let us know about different milestones in Earth’s chaotic historical past.Some diamonds are solid from carbon that was once included into Earth upon its formation, Olierook stated, whilst others shape from carbon from historic existence, dragged down along side slabs of subducted crust. It is conceivable to inform which procedure fashioned the diamonds by way of examining the molecular construction of the carbon inside of diamond inclusions. Those inclusions can thus grasp secrets and techniques about hazy numbers in Earth historical past, similar to when common subduction started or when existence within the oceans changed into prevalent.However to get at the ones solutions, researchers will want to get well at working out how previous diamonds are. And they are going to want extra diamonds which are each historic and from the private depths.”Going again in time from the latest supercontinent breakup to those sooner than that,” Olierook stated, “I strongly suspect there are nonetheless a lot to be found out.”
The tough Cullinan diamond, the biggest identified gem-quality tough diamond, was once pulled from the Kimberley Mine in 1905. Diamonds like those can come from deep inside of Earth and disclose billions of years of the planet’s historical past. (Symbol credit score: Public Area)Whilst the eruption of diamonds can hint a tale of supercontinent breakup, their formation may additionally supply a clue to how continents come in combination. In a learn about printed in October 2023 within the magazine Nature, Timmerman studied diamonds from Brazil and Guinea that fashioned between 186 and 434 miles deep (300 to 700 km). Through courting fluid inclusions throughout the diamonds, Timmerman and her colleagues estimated that the diamonds fashioned round 650 million years in the past, when the supercontinent Gondwana was once forming. The diamonds most probably caught to the bottom of the continent and sat there for millennia till Gondwana broke up all over the Cretaceous length and kimberlites introduced them to floor, Timmerman informed Are living Science.What was once necessary about those superdeep diamonds, Timmerman stated, was once that they helped give an explanation for how continents develop. Supercontinents are constructed when oceanic crust pushes underneath continental crust. This procedure, referred to as subduction, tugs two continents on reverse facets of an ocean nearer in combination. This similar subduction brings carbon to the depths, the place it may be compressed into diamond.Down within the mantle, bits of those subducting plates can change into buoyant and upward thrust again up, sporting superdeep diamonds with them, Timmerman defined. This subject material would possibly persist with the bases of continents for millennia, serving to them develop from underneath. It may additionally give an explanation for how superdeep diamonds land in a spot the place a kimberlite can catch them.”Deep diamonds can tell us extra about subduction processes, mantle convection, liquid-rock interactions and different processes taking place underneath the crust all over supercontinent cycles,” Timmerman stated.There are lots of different questions to reply to, she added. As an example, scientists nonetheless do not know the way subducted plates trade the bases of supercontinents and whether or not that has effects on how lengthy a supercontinent lasts sooner than breaking apart. Every other open query is whether or not this recycled crustal subject material influences when and the place kimberlite magmas shape.Historic diamonds may additionally let us know about different milestones in Earth’s chaotic historical past.Some diamonds are solid from carbon that was once included into Earth upon its formation, Olierook stated, whilst others shape from carbon from historic existence, dragged down along side slabs of subducted crust. It is conceivable to inform which procedure fashioned the diamonds by way of examining the molecular construction of the carbon inside of diamond inclusions. Those inclusions can thus grasp secrets and techniques about hazy numbers in Earth historical past, similar to when common subduction started or when existence within the oceans changed into prevalent.However to get at the ones solutions, researchers will want to get well at working out how previous diamonds are. And they are going to want extra diamonds which are each historic and from the private depths.”Going again in time from the latest supercontinent breakup to those sooner than that,” Olierook stated, “I strongly suspect there are nonetheless a lot to be found out.”







/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25803039/2190571551.jpg)





