Photographs created by means of NASA’s drawing close Nancy Grace Roman Area Telescope might permit scientists to seek for darkish subject between stars.A world staff of researchers believes that gaps found in strings of stars striking from tightly packed balls of historical stellar our bodies, referred to as globular clusters, might be influenced by means of darkish subject clumps. To this point, astronomers have simplest been in a position to review those dangling stellar streams inside the Milky Means, which means our working out of them is restricted. Roman, set to release in 2027, will have to be delicate sufficient to peer those buildings in our neighboring galaxy Andromeda — and with such element it might be conceivable to peer disruptions led to by means of darkish subject, giving astronomers clues about this elusive substance.”There are stellar streams in our personal galaxy, the place we see gaps that could be because of darkish subject,” Tjitske Starkenburg, staff member and a scientist at Northwestern College, stated in a remark. “However those gaps additionally will also be shaped by means of different manner.”Comparable: ‘Darkish pressure’ principle may remedy 2 open cosmic mysteriesThe staff makes the case that, as Roman observes gaps in galaxies instead of the Milky Means, it’s going to supply scientists with a greater image of those gaps as a complete. This is able to in the long run assist resolve the life and homes of darkish subject clumps.Studying between the traces (or the celebs, somewhat)Darkish subject is troubling for scientists as a result of, in spite of the reality it accounts for an estimated 85% of the subject within the universe, they’ve little or no thought what it’s.Darkish subject does not have interaction with mild, because of this it is successfully invisible to our eyes and cannot be made up of atoms created from the electrons, protons and neutrons that make up “on a regular basis” subject we are used to. Assume, stars, planets, plants, books. The whole thing we see with the unaided eye — together with our our bodies — is made up of such “standard” subject. Darkish subject does have interaction with gravity, then again, and that implies the one means that scientists can infer its presence is by means of having a look at how its affect on gravity due to this fact influences all that on a regular basis subject and light-weight. The truth that darkish subject interacts gravitationally is in truth lucky for the evolution of the universe. Some galaxies, as an example, are rotating so speedy that the gravity in their visual subject — stars, gasoline, mud and planets — would not be enough to stop them from just about flying aside.”We see darkish subject’s impact on galaxies,” Christian Aganze, staff member and a postdoctoral fellow at Stanford College, stated within the remark. “For instance, after we fashion how galaxies rotate, we’d like further mass to provide an explanation for their rotation. Darkish subject might supply that lacking mass.”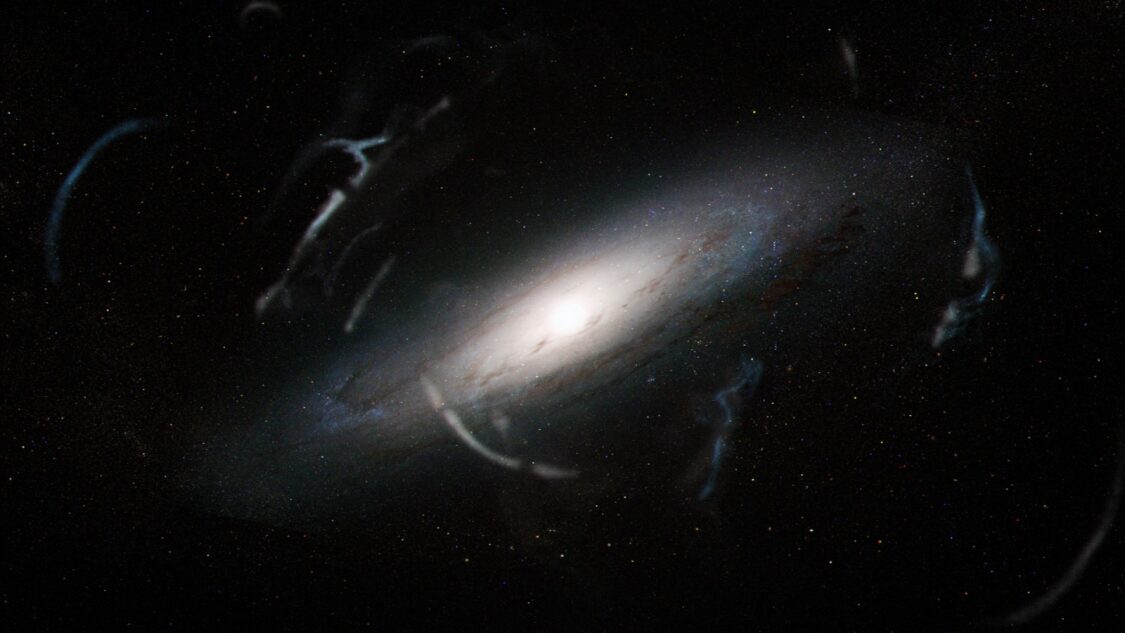 Representation displays streams of stars observed across the Andromeda galaxy (Symbol credit score: NASA, Joseph Olmsted (STScI))Clues about darkish subject could be dangling from globular clusters, which frequently comprise thousands and thousands of stars, along side free stellar streams. This is as a result of scientists suppose darkish subject can “punch holes” in those stellar streams, developing gaps that can be utilized to evaluate the character of this mysterious type of subject. “The explanation those streams are maximum attention-grabbing to peer the consequences of those darkish subject clumps is twofold,” Starkenburg stated. “First, those streams ‘reside’ within the excessive outer areas of a galaxy, the place there in a different way could be very little construction. “And 2nd, those streams are intrinsically very skinny as a result of they shaped from dense clusters of stars, because of this that you’ll see gaps or any disturbance a lot more simply.”This is not a brand new thought, however it’s person who hasn’t been totally exploited to resolve the darkish subject downside. Present area telescopes and ground-based tools are restricted to looking for dark-matter-punched holes in a small choice of stellar streams striking from globular clusters inside the Milky Means.From its place round 1 million miles (1.6 million kilometers) from Earth, Roman will be capable of examine such options in neighboring galaxies, specifically Andromeda, for the primary time. Its wide-field device will produce pictures 200 instances the scale of the ones created by means of the Hubble Area Telescope.To check this, this staff simulated streams of stars and allowed them to have interaction with darkish subject clumps, producing gaps as predicted. The scientists then created mock Roman observations of those darkish matter-punched areas in stellar streams. They concluded that Roman will certainly be able to detecting those gaps when it opens its eyes to the cosmos eventually.Roman will shed extra mild on darkish matterThe learn about of stellar streams striking from globular clusters would possibly not be the one darkish subject hunt that Roman engages in because it research the universe.Scientists suppose that the majority, if no longer all, galaxies are enveloped in haloes of this mysterious subject. And those haloes are believed to increase some distance past the galaxies’ visual subject contents. The latter can also be studied by means of the gap telescope, named after NASA’s first Leader of Astronomy Nancy Grace Roman, who’s affectionately referred to as the “mom of Hubble.”No longer simplest will Roman be used to analyze the darkish subject halo round Andromeda, however it’s going to additionally examine the conceivable life of smaller “sub-haloes” of darkish subject across the within reach galaxy.”We predict smaller darkish subject sub-halos to have interaction with globular cluster streams,” Starkenburg stated. “If those sub-halos are found in different galaxies, we think that we can see gaps in globular cluster streams which might be most probably led to by means of those sub-halos. “That may give us new details about darkish subject, together with which sorts of darkish subject halos are provide and what their lots are.”In addition to being concerned with this learn about, Starkenburg is already serving to to put the groundwork for Roman’s darkish subject detective paintings with the help of investment via NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Area Telescope Analysis and Fortify Participation Alternatives program.“That staff plans to fashion how globular clusters shape into stellar streams by means of growing a a lot more detailed theoretical framework,” she stated. “We will be able to pass directly to expect the origins of stream-forming globular clusters and whether or not those streams can be observable with Roman.”The staff’s analysis is detailed in a preprint paper featured at the paper repository arXiv and has been accredited for e-newsletter in The Astrophysical Magazine.
Representation displays streams of stars observed across the Andromeda galaxy (Symbol credit score: NASA, Joseph Olmsted (STScI))Clues about darkish subject could be dangling from globular clusters, which frequently comprise thousands and thousands of stars, along side free stellar streams. This is as a result of scientists suppose darkish subject can “punch holes” in those stellar streams, developing gaps that can be utilized to evaluate the character of this mysterious type of subject. “The explanation those streams are maximum attention-grabbing to peer the consequences of those darkish subject clumps is twofold,” Starkenburg stated. “First, those streams ‘reside’ within the excessive outer areas of a galaxy, the place there in a different way could be very little construction. “And 2nd, those streams are intrinsically very skinny as a result of they shaped from dense clusters of stars, because of this that you’ll see gaps or any disturbance a lot more simply.”This is not a brand new thought, however it’s person who hasn’t been totally exploited to resolve the darkish subject downside. Present area telescopes and ground-based tools are restricted to looking for dark-matter-punched holes in a small choice of stellar streams striking from globular clusters inside the Milky Means.From its place round 1 million miles (1.6 million kilometers) from Earth, Roman will be capable of examine such options in neighboring galaxies, specifically Andromeda, for the primary time. Its wide-field device will produce pictures 200 instances the scale of the ones created by means of the Hubble Area Telescope.To check this, this staff simulated streams of stars and allowed them to have interaction with darkish subject clumps, producing gaps as predicted. The scientists then created mock Roman observations of those darkish matter-punched areas in stellar streams. They concluded that Roman will certainly be able to detecting those gaps when it opens its eyes to the cosmos eventually.Roman will shed extra mild on darkish matterThe learn about of stellar streams striking from globular clusters would possibly not be the one darkish subject hunt that Roman engages in because it research the universe.Scientists suppose that the majority, if no longer all, galaxies are enveloped in haloes of this mysterious subject. And those haloes are believed to increase some distance past the galaxies’ visual subject contents. The latter can also be studied by means of the gap telescope, named after NASA’s first Leader of Astronomy Nancy Grace Roman, who’s affectionately referred to as the “mom of Hubble.”No longer simplest will Roman be used to analyze the darkish subject halo round Andromeda, however it’s going to additionally examine the conceivable life of smaller “sub-haloes” of darkish subject across the within reach galaxy.”We predict smaller darkish subject sub-halos to have interaction with globular cluster streams,” Starkenburg stated. “If those sub-halos are found in different galaxies, we think that we can see gaps in globular cluster streams which might be most probably led to by means of those sub-halos. “That may give us new details about darkish subject, together with which sorts of darkish subject halos are provide and what their lots are.”In addition to being concerned with this learn about, Starkenburg is already serving to to put the groundwork for Roman’s darkish subject detective paintings with the help of investment via NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Area Telescope Analysis and Fortify Participation Alternatives program.“That staff plans to fashion how globular clusters shape into stellar streams by means of growing a a lot more detailed theoretical framework,” she stated. “We will be able to pass directly to expect the origins of stream-forming globular clusters and whether or not those streams can be observable with Roman.”The staff’s analysis is detailed in a preprint paper featured at the paper repository arXiv and has been accredited for e-newsletter in The Astrophysical Magazine.
Are gaps within the Andromeda galaxy stuffed with darkish subject? This NASA telescope may in finding out













/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25735437/HT057_BLUESKY_CVirginia_A.jpg)
