The possible discovery means that Mars as soon as regarded very other from how it seems that these days and may as soon as have sustained existence.
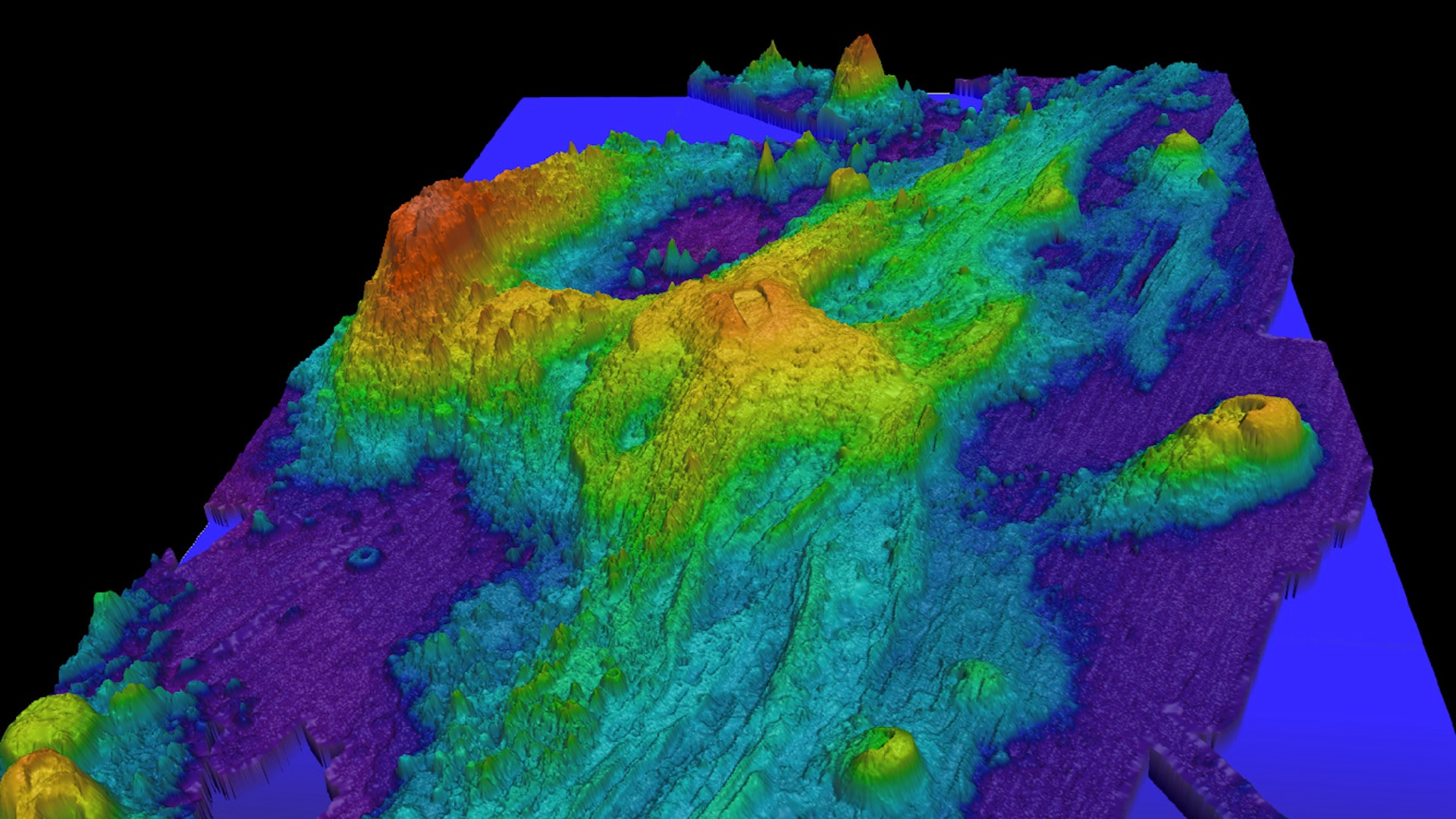
ADVERTISEMENTScientists working Europe’s Mars Categorical orbiter say it is going to have noticed large ice water deposits underneath the skin of Mars.It’s estimated that the deposits are round 3.7 kilometres thick, that means that they may fill Earth’s Purple Sea if melted or quilt everything of Mars in a layer of water about two metres deep.
The brand new findings recommend that Mars as soon as regarded very other to how it seems that these days, with glaciers, lakes, and river channels, consistent with scientists.”Now we have observed proof of glaciers, extinct glaciers that are now not there, but in addition some glaciers coated with mud. Many of the water ice we’ve got observed on Mars these days is at upper latitudes, the place the temperatures are chillier and so the ice can also be strong,” stated Colin Wilson, a mission scientist at ESA.”It is a testomony to how a lot water there would were on Mars up to now to accumulate piles of water ice a number of kilometres thick. That is an unlimited quantity of water. So, we’ve got observed the proof of quite a lot of water at the Martian floor somewhere else,” Wilson added.ESA’s Mars Categorical orbiter first showed the presence of ice at the Purple Planet in 2004.It came upon the deposits in 2007, but it surely wasn’t transparent what they have been made from — possibly large accumulations of mud, volcanic ash or sediment.In 2015, NASA additionally stated Mars seems to have flowing streams of salty water.”Nowadays, we are revolutionising our working out of this planet. Our rovers are discovering that there is a lot extra humidity within the air than we ever imagined,” stated Jim Inexperienced, NASA’s Director of Planetary Science, at a press convention.Now, 15 years later, Mars Categorical’ new knowledge suggests the deposits are in fact layers of mud and ice.Attainable for long run manned Mars missionsThe ice water is situated at its equator, no longer at its poles, which stunned scientists.”We do not be expecting to look a polar ice cap on the equator,” stated Wilson.”It is as ludicrous on Mars as it might be on Earth, however that is what the knowledge are telling us, pronouncing it does seem like that”.This excited scientists about the potential for human exploration missions.For the reason that Mars is a chilly planet, between 20C and -153C, consistent with NASA, discovering water ice in low latitudes as a substitute of polar areas would have made human exploration missions more straightforward.”Probably the most causes we have been fascinated by discovering water ice at low latitudes is that this is the place long run exploration missions, particularly human exploration missions, are going to must land for causes of orbital mechanics and in addition energy availability,” stated Wilson. The layers of mud and ice are crowned with a protecting layer of mud or ash a number of hundred metres thick.”On the other hand, if it is 300 metres down, that isn’t very useful for exploration targets. Sadly, this most certainly may not be the solution to our human exploration wishes,” Wilson added.
ADVERTISEMENTEurope’s Mars Categorical probe departed Earth in June 2003 and arrived at Mars in December 2003. It not too long ago marked 20 years learning the Purple Planet.For extra in this tale, watch the video within the media participant above.Video editor • Roselyne Min
Ecu orbiter will have came upon large water deposits on Mars