One among astronomy’s maximum perplexing mysteries has been resolved, in step with scientists concerned with new findings made conceivable via NASA’s James Webb Area Telescope.
Consistent with new findings, tiny faint gadgets had been positioned surrounding galaxies that, previously, have displayed anomalous emissions of hydrogen, a discovery made conceivable via Webb’s tough NIRCam tool.
Astronomers have lengthy questioned why mild from hydrogen atoms will also be detected, for the reason that they must be blocked from view via gasoline shaped within the aftermath of the Giant Bang.
The brand new findings expose mergers between galaxies because the most probably supply of those mysterious hydrogen emissions.
When astronomers view extraordinarily far-off galaxies, they seem as they might have appeared way back because of the time it takes the sunshine they produce to shuttle throughout area. Therefore, observations made via the James Webb Area Telescope aren’t simplest revealing essentially the most far-off areas of the universe in extraordinary element, but additionally how they appeared in a lot previous instances.
Then again, those galaxies are very faint, and therefore tough telescopes are required to make the observations, a role that Webb is definitely provided to perform.
Very lively celebrity formation passed off throughout the universe’s earliest galaxies, giving upward thrust to their different title: stellar nurseries. Those areas of area produced a selected number of mild emitted from hydrogen referred to as Lyman-α emission.
Necessarily, Lyman-α emission is produced via hydrogen atoms when an electron falls from a better power stage to the bottom one it may be in, which will also be likened to the electron’s house base. This mild has an excessively particular colour spectra that may simplest be discerned with the assistance of particular tools, which will also be likened to being a “fingerprint” for this sort of process.
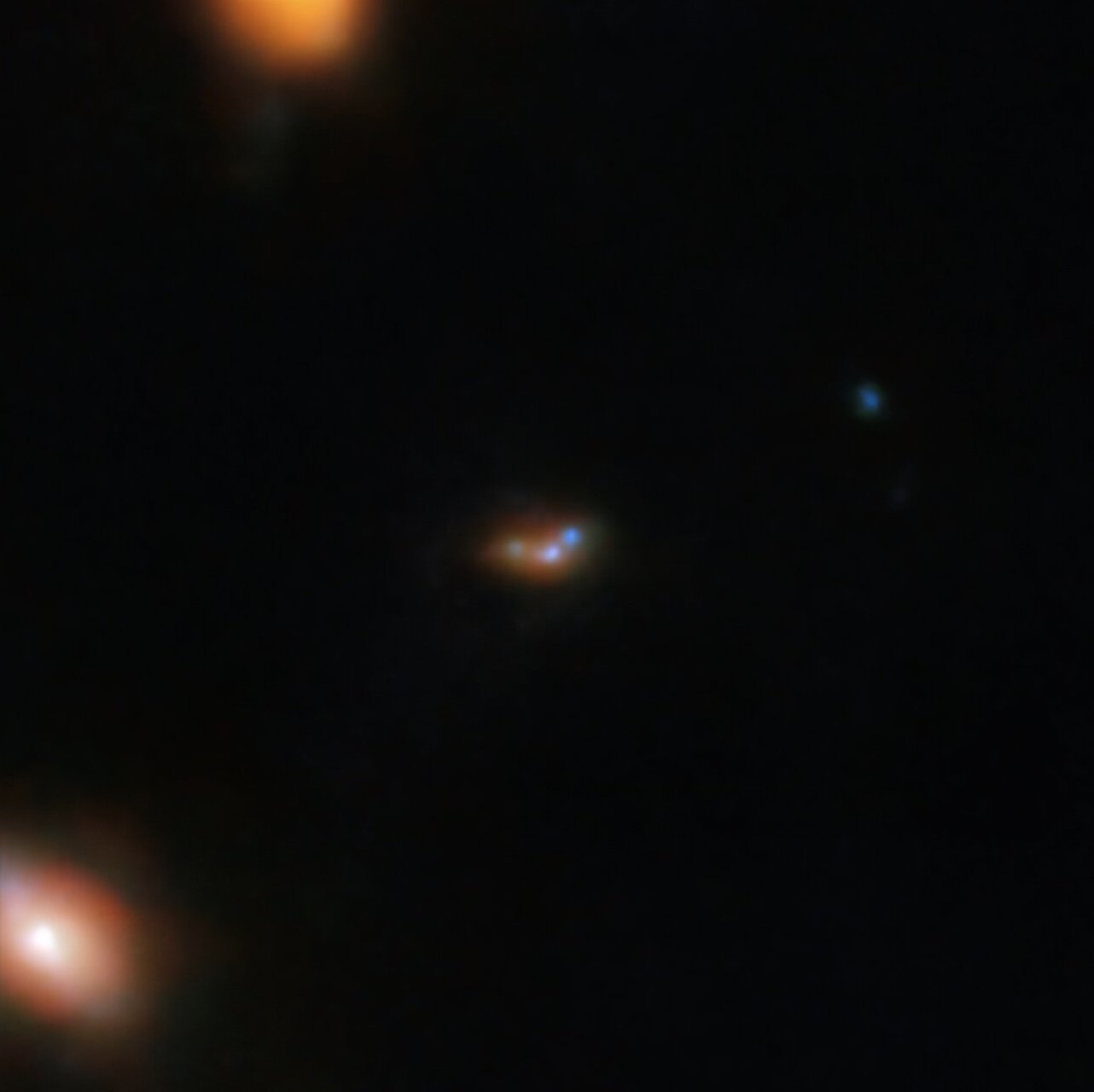

 NIRCam symbol of the Lyman-α emitting galaxy EGSY8p7 (Credit score: NASA/ESA/Ceers survey)
NIRCam symbol of the Lyman-α emitting galaxy EGSY8p7 (Credit score: NASA/ESA/Ceers survey)
Way back, those stellar nurseries have been enveloped in massive quantities of impartial hydrogen gasoline, and the even the areas between galaxies as soon as contained way more gasoline than what’s seen these days. Mild emissions produced via hydrogen are simply absorbed via this gasoline, inflicting astronomers to expect that the Lyman-α emission that populated those areas of the early Universe, regardless of their abundance, would successfully stay invisible to astronomers these days.
But, mysteriously, some early hydrogen emissions had been effectively seen via astronomers, a phenomenon that has till just lately remained unexplained. However how may just hydrogen that are meant to had been scattered all over the universe via now, if no longer absorbed altogether, nonetheless be visual these days?
College of Cambridge astronomer Callum Witten, who makes a speciality of the find out about of galaxies and lively galactic nuclei, calls this query “one of the vital puzzling problems” astronomers have confronted in looking to unravel this cosmic thriller.
“Many hypotheses have up to now been prompt to give an explanation for the nice get away of this ‘inexplicable’ emission,” Witten, the primary investigator on a brand new find out about that explores this phenomenon, mentioned in a up to date observation.
Then again, because of the ability and precision of the James Webb Area Telescope, new insights seem to have make clear this longstanding thriller.


With assist from Webb’s Close to-Infrared Digicam (NIRCam), Witten and his colleagues have been in a position to watch a lot smaller and dimmer galaxies clustered across the brighter ones from which mysterious hydrogen emissions have been up to now famous. Then again, those lesser galaxies aren’t static, however as a substitute seem to be dynamically interacting and mixing.
“The place Hubble was once seeing simplest a big galaxy, Webb sees a cluster of smaller interacting galaxies,” mentioned Sergio Martin-Alvarez, a crew member from Stanford College concerned with the find out about, who provides that Webb’s newest revelations have “had an enormous have an effect on on our figuring out of the surprising hydrogen emission from one of the most first galaxies.”
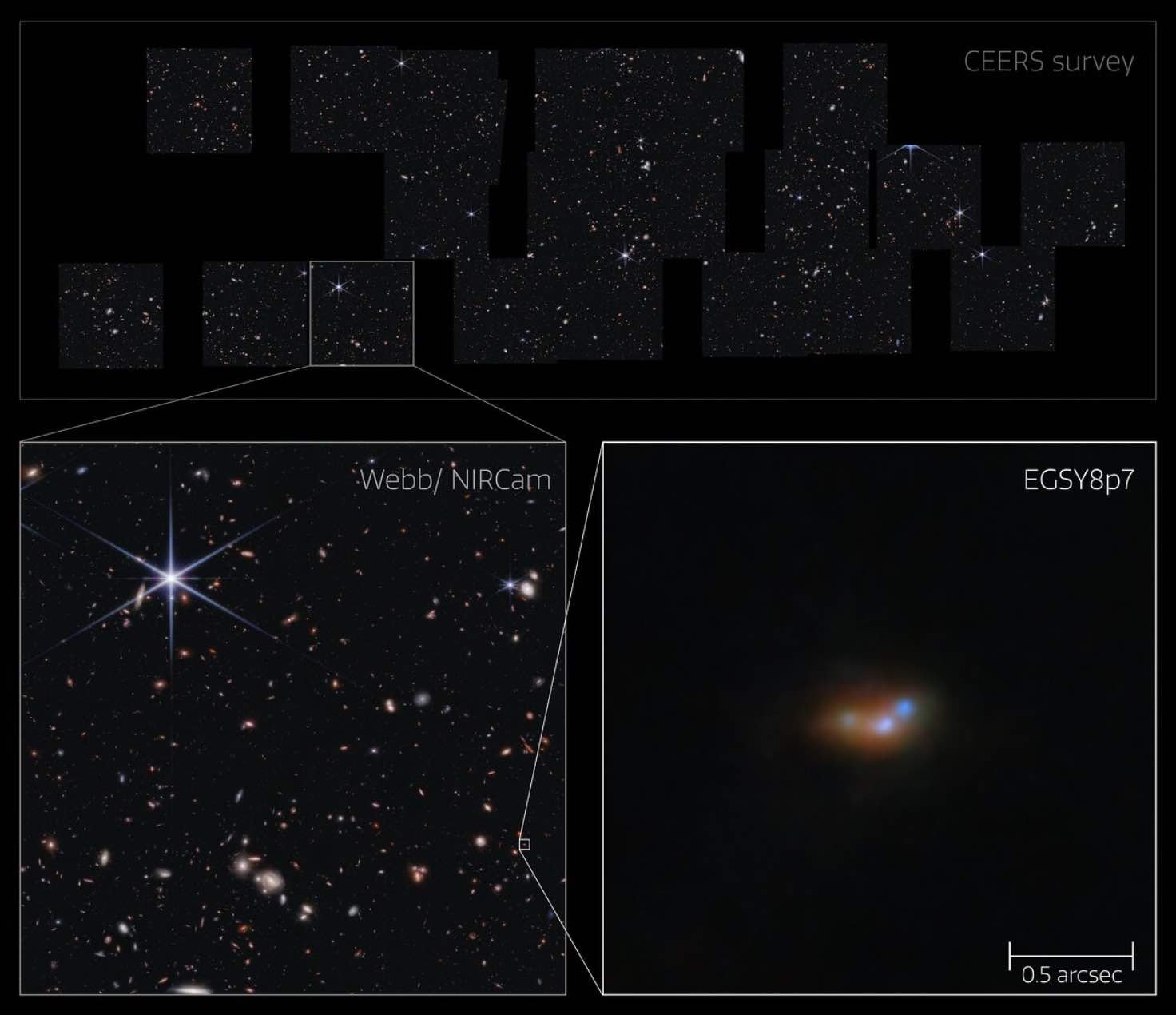

 NIRCam symbol depicting Lyman-α emitting galaxy EGSY8p7 within the CEERS survey box (Credit score: NASA/ESA/CEERS survey).
NIRCam symbol depicting Lyman-α emitting galaxy EGSY8p7 within the CEERS survey box (Credit score: NASA/ESA/CEERS survey).
The use of cutting-edge simulations, the crew then explored the physics at the back of what they seen, studying that the quick accumulation of stellar mass that effects from galaxy mergers had most probably pushed the sturdy hydrogen emissions being seen. In accordance with the brand new observations, this perceived to have passed off via channels that have been cleared of impartial gasses that had at the beginning been prevalent.
The crew believes that the merging of those smaller, up to now unobserved galaxies could be very prone to be the strategy to the lasting riddle of inexplicable early hydrogen emissions, and now targets to observe up their contemporary observations via taking a look at galaxies in different phases of merging, which they imagine is not going to simplest assist them to raised know how hydrogen emission is ejected, but additionally to expose new clues to the evolution of galaxies.
The crew’s analysis was once the topic of a brand new paper, “Decoding Lyman-α emission deep into the epoch of reionization, that was once just lately printed within the magazine Nature Astronomy.
Micah Hanks is the Editor-in-Leader and Co-Founding father of The Debrief. He will also be reached via e mail at micah@thedebrief.org. Practice his paintings at micahhanks.com and on X: @MicahHanks.




.webp)








