Astronomers led by Mireia Montes from the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) have discovered Nube, an incredibly faint and extended dwarf galaxy that challenges existing astrophysical models. Its unique properties offer potential new insights into the universe and the nature of dark matter. (Artist’s concept.) Credit: SciTechDaily.comNube, an almost invisible dwarf galaxy, was discovered by an international team led by the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) in collaboration with the University of La Laguna (ULL) and other institutions. The name “Nube,” meaning “Cloud” in Spanish, was suggested by the 5-year-old daughter of one of the researchers due to the object’s diffuse appearance. Its extremely low surface brightness had caused it to go unnoticed in previous surveys of this area of the sky. This is because its stars are so widely dispersed in a large volume that “Nube” was almost undetectable.This newly discovered galaxy possesses specific properties that set it apart from previously known objects. The research team estimates that Nube is a dwarf galaxy ten times fainter than others of its kind, but also ten times more extended than other objects with a similar number of stars. For reference, this galaxy is one third of the size of the Milky Way, yet its mass is comparable to that of the Small Magellanic Cloud.
Astronomers led by Mireia Montes from the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) have discovered Nube, an incredibly faint and extended dwarf galaxy that challenges existing astrophysical models. Its unique properties offer potential new insights into the universe and the nature of dark matter. (Artist’s concept.) Credit: SciTechDaily.comNube, an almost invisible dwarf galaxy, was discovered by an international team led by the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) in collaboration with the University of La Laguna (ULL) and other institutions. The name “Nube,” meaning “Cloud” in Spanish, was suggested by the 5-year-old daughter of one of the researchers due to the object’s diffuse appearance. Its extremely low surface brightness had caused it to go unnoticed in previous surveys of this area of the sky. This is because its stars are so widely dispersed in a large volume that “Nube” was almost undetectable.This newly discovered galaxy possesses specific properties that set it apart from previously known objects. The research team estimates that Nube is a dwarf galaxy ten times fainter than others of its kind, but also ten times more extended than other objects with a similar number of stars. For reference, this galaxy is one third of the size of the Milky Way, yet its mass is comparable to that of the Small Magellanic Cloud.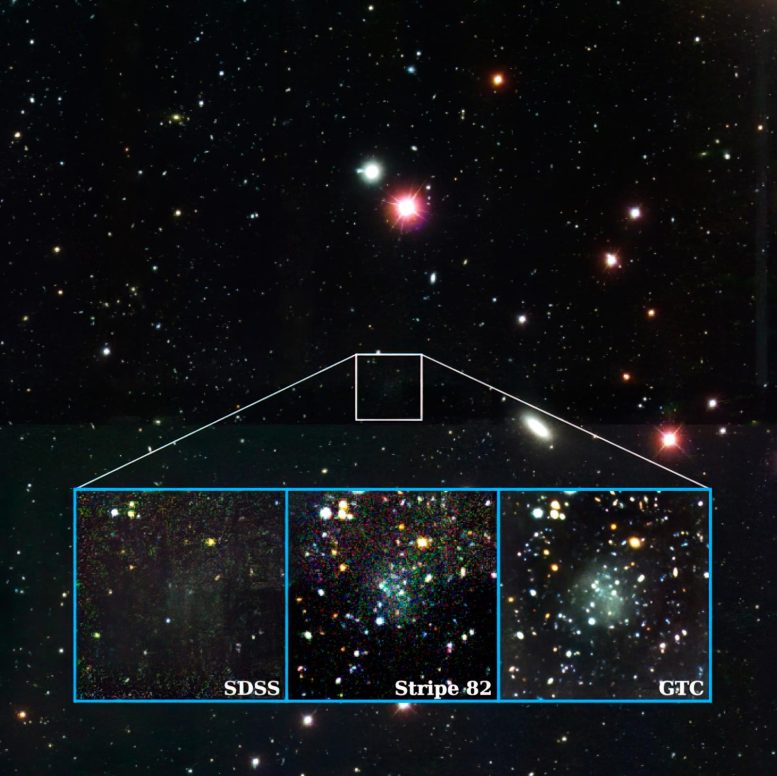 Image of the Nube galaxy as captured by different telescopes. Credit: SDSS/GTC/IAC”We do not currently understand how a galaxy with such extreme characteristics can exist,” explains Mireia Montes, the first author of the article and a researcher at the IAC and the ULL.For some years, Ignacio Trujillo, the second author of the article, has been analyzing a specific area of the sky based on the SDSS images (Sloan Digital Sky Survey) as part of the Legado del IAC Stripe 82 project. During one data review, they noticed a faint patch that seemed interesting enough to initiate a research project.The next step involved using ultra-deep multicolor images from the Gran Telescopio Canarias (GTC) to confirm that this patch in the survey was not a mistake but indeed an extremely diffuse object. Due to its faintness, determining the exact distance of Nube has been challenging. An observation obtained with the Green Bank Telescope (GBT) in the United States led the authors to estimate the distance of Nube to be 300 million light years. However, upcoming observations with the Very Large Array (VLA) radiotelescope and the optical William Herschel Telescope (WHT) at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory, La Palma, should help verify this distance. “If the galaxy turns out to be nearer, it will still be a very strange object, and offer major challenges to astrophysics,” comments Ignacio Trujillo.Another challenge to the current dark matter model?Traditionally, galaxies exhibit a much higher density of stars in their inner regions, with this density decreasing rapidly as distance from the center increases. However, Montes highlights that in Nube, “the density of stars varies very little throughout the object, which is why it is so faint, and we have not been able to observe it well until we had the ultra-deep images from the GTC.”
Image of the Nube galaxy as captured by different telescopes. Credit: SDSS/GTC/IAC”We do not currently understand how a galaxy with such extreme characteristics can exist,” explains Mireia Montes, the first author of the article and a researcher at the IAC and the ULL.For some years, Ignacio Trujillo, the second author of the article, has been analyzing a specific area of the sky based on the SDSS images (Sloan Digital Sky Survey) as part of the Legado del IAC Stripe 82 project. During one data review, they noticed a faint patch that seemed interesting enough to initiate a research project.The next step involved using ultra-deep multicolor images from the Gran Telescopio Canarias (GTC) to confirm that this patch in the survey was not a mistake but indeed an extremely diffuse object. Due to its faintness, determining the exact distance of Nube has been challenging. An observation obtained with the Green Bank Telescope (GBT) in the United States led the authors to estimate the distance of Nube to be 300 million light years. However, upcoming observations with the Very Large Array (VLA) radiotelescope and the optical William Herschel Telescope (WHT) at the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory, La Palma, should help verify this distance. “If the galaxy turns out to be nearer, it will still be a very strange object, and offer major challenges to astrophysics,” comments Ignacio Trujillo.Another challenge to the current dark matter model?Traditionally, galaxies exhibit a much higher density of stars in their inner regions, with this density decreasing rapidly as distance from the center increases. However, Montes highlights that in Nube, “the density of stars varies very little throughout the object, which is why it is so faint, and we have not been able to observe it well until we had the ultra-deep images from the GTC.”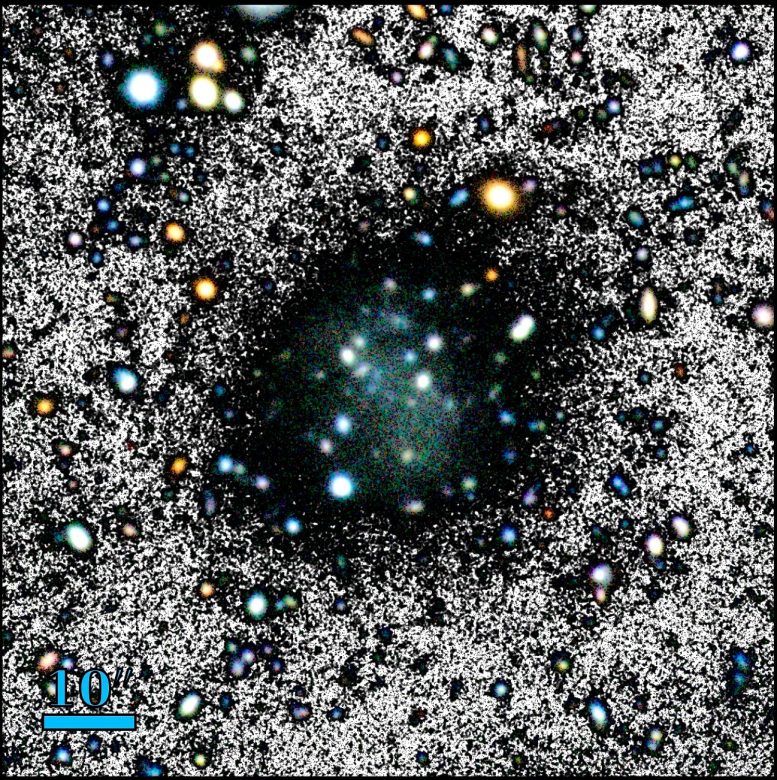 The Nube galaxy. This image is a composite of a color image and a black and white image, highlighting the background. Credit: GTC/Mireia MontesNube has left astronomers puzzled. At first glance, the team explains, there are no interactions or other indications of its peculiar properties. Cosmological simulations have been unable to replicate its “extreme” characteristics, even under different scenarios. “We are unable to provide a plausible explanation within the currently accepted cosmological model, that of cold dark matter,” explains Montes.The cold dark matter model can simulate the large-scale structures in the universe, but it struggles to provide satisfactory answers for small-scale scenarios, such as in the case of Nube. The team has demonstrated that the different theoretical models are incapable of producing it, making it one of the most extreme cases known thus far. “It is possible that with this galaxy, and similar ones which we might find, we can find additional clues which will open a new window on the understanding of the universe,” comments Montes.”One attractive possibility is that the unusual properties of Nube are indicating that the particles composing dark matter have an extremely small mass,” says Ignacio Trujillo. If confirmed, the unusual properties of this galaxy would demonstrate the properties of quantum physics on a galactic scale. “If this hypothesis is confirmed, it would be one of the most beautiful demonstrations of nature, unifying the world of the smallest with that of the largest,” he concludes.Reference: “An almost dark galaxy with the mass of the Small Magellanic Cloud” by Mireia Montes, Ignacio Trujillo, Ananthan Karunakaran, Raúl Infante-Sainz, Kristine Spekkens, Giulia Golini, Michael Beasley, Maria Cebrián, Nushkia Chamba, Mauro D’Onofrio, Lee Kelvin and Javier Román, 9 January 2024, Astronomy & Astrophysics.
The Nube galaxy. This image is a composite of a color image and a black and white image, highlighting the background. Credit: GTC/Mireia MontesNube has left astronomers puzzled. At first glance, the team explains, there are no interactions or other indications of its peculiar properties. Cosmological simulations have been unable to replicate its “extreme” characteristics, even under different scenarios. “We are unable to provide a plausible explanation within the currently accepted cosmological model, that of cold dark matter,” explains Montes.The cold dark matter model can simulate the large-scale structures in the universe, but it struggles to provide satisfactory answers for small-scale scenarios, such as in the case of Nube. The team has demonstrated that the different theoretical models are incapable of producing it, making it one of the most extreme cases known thus far. “It is possible that with this galaxy, and similar ones which we might find, we can find additional clues which will open a new window on the understanding of the universe,” comments Montes.”One attractive possibility is that the unusual properties of Nube are indicating that the particles composing dark matter have an extremely small mass,” says Ignacio Trujillo. If confirmed, the unusual properties of this galaxy would demonstrate the properties of quantum physics on a galactic scale. “If this hypothesis is confirmed, it would be one of the most beautiful demonstrations of nature, unifying the world of the smallest with that of the largest,” he concludes.Reference: “An almost dark galaxy with the mass of the Small Magellanic Cloud” by Mireia Montes, Ignacio Trujillo, Ananthan Karunakaran, Raúl Infante-Sainz, Kristine Spekkens, Giulia Golini, Michael Beasley, Maria Cebrián, Nushkia Chamba, Mauro D’Onofrio, Lee Kelvin and Javier Román, 9 January 2024, Astronomy & Astrophysics.
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202347667
Ghost in the Cosmos: Discovery of Nube, an Almost Invisible Galaxy, Challenges Existing Astrophysical Models