This newsletter has been reviewed in line with Science X’s editorial procedure
and insurance policies.
Editors have highlighted the next attributes whilst making sure the content material’s credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed newsletter
depended on supply
proofread
Adequate!
through Tejasri Gururaj
, Phys.org
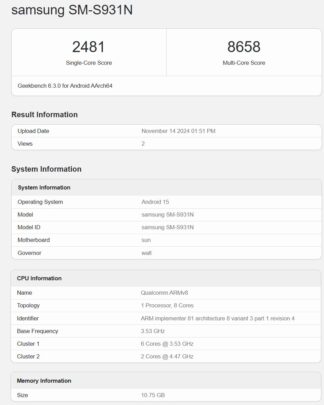
A high-resolution symbol of the magnetic subject within the El Gordo cluster, together with the Chandra X-ray symbol (blue a part of the picture), the NASA JWST infrared symbol (background galaxies of the picture), and the measured magnetic fields (streamlines). Credit: Chandra X-ray: NASA/CXC/Rutgers; JWST infrared: NASA/ESA/CSA; Magnetic subject traces: Yue Hu.
× shut
A high-resolution symbol of the magnetic subject within the El Gordo cluster, together with the Chandra X-ray symbol (blue a part of the picture), the NASA JWST infrared symbol (background galaxies of the picture), and the measured magnetic fields (streamlines). Credit: Chandra X-ray: NASA/CXC/Rutgers; JWST infrared: NASA/ESA/CSA; Magnetic subject traces: Yue Hu.
In a brand new find out about, scientists have mapped magnetic fields in galaxy clusters, revealing the have an effect on of galactic mergers on magnetic-field constructions and difficult earlier assumptions concerning the potency of turbulent dynamo processes within the amplification of those fields.
Galaxy clusters are vast, gravitationally sure methods containing a lot of galaxies, scorching gasoline, and darkish topic. They constitute one of the maximum large constructions within the universe. Those clusters can encompass loads to hundreds of galaxies, sure in combination through gravity, and are embedded in huge halos of scorching gasoline referred to as the intracluster medium (ICM).
ICM, consisting principally of ionized hydrogen and helium, is held in combination through the gravitational pull of the cluster itself. Magnetic fields in large-scale constructions, like galaxy clusters, play pivotal roles in shaping astrophysical processes. They affect the ICM, have an effect on galaxy formation and evolution, give a contribution to cosmic ray delivery, take part in cosmic magnetization, and function tracers of large-scale construction evolution.
Prior research and simulations have urged that magnetic fields inside of clusters evolve, indicating their susceptibility to the dynamics of the cluster and experiencing amplification right through merging occasions.
The find out about, revealed in Nature Communications, makes use of one way referred to as synchrotron depth gradient (SIG) to map magnetic fields in clusters, particularly right through galaxy mergers. This technique supplies a singular viewpoint on magnetic subject constructions and provides a device to match numerical expectancies from simulations with observational knowledge.
Lead writer of the find out about, Prof. Alex Lazarian from UW-Madison, spoke to Phys.org about his motivation to check magnetic fields in galaxy clusters, announcing, “The focal point of my analysis lies in working out the position of magnetic fields in astrophysical environments, specifically in magnetized and turbulent media.”
“During the last 20 years, I have widely studied magnetic turbulence and reconnection processes in collaboration with my scholars. The methodology used to map magnetic fields in galaxy clusters is grounded within the theoretical and numerical insights won from years of study.”
Synchrotron depth gradient
Synchrotron depth refers back to the radiation emitted through charged debris, usually electrons, as they spiral alongside magnetic subject traces at relativistic speeds. This phenomenon is referred to as synchrotron radiation.
The SIG way introduces a singular viewpoint through mapping magnetic fields via a procedure rooted within the synchrotron depth gradient. The fundamental theory at the back of the implemented methodology comes to using the interactions between magnetic fields and conductive fluids, in particular ionized gasoline or plasma.
The important thing thought is that magnetic fields affect the movement of those fluids, and their resistance to bending makes it more straightforward to discern their course. Prof. Lazarian defined, “Those motions lead to pace gradients, and magnetic subject fluctuations are perpendicular to the magnetic subject. By means of measuring those gradients, one can download the course of the magnetic subject.”
This way represents a singular method of measuring magnetic fields, evolved through Prof. Lazarian’s staff in accordance with basic research of magnetohydrodynamics.
“It makes use of knowledge to start with deemed beside the point for magnetic subject research, permitting us to derive vital effects from various archival datasets amassed for functions unrelated to magnetic subject investigations,” mentioned Prof. Lazarian.
Mapping magnetic fields
The researchers bought maps of magnetic fields on the biggest scales ever studied, in particular within the halos of galaxies inside of galaxy clusters.
“We showed the accuracy of this method through evaluating the magnetic subject instructions bought with our methodology with the ones bought with the normal one in accordance with measuring polarization. We additionally gauged the accuracy of SIGs with numerical simulations,” mentioned Prof. Lazarian.
The find out about demonstrated that SIGs open a brand new street to map magnetic fields over unprecedentedly vast scales. The complexity of plasma movement inside of merging galaxy clusters used to be printed throughout the construction of the magnetic subject.
The findings have implications for our working out of cluster dynamics and evolution, providing distinctive insights into the position of magnetic fields in key processes inside of galaxy clusters.
Overcoming depolarization
In conventional synchrotron polarization measurements, depolarization demanding situations mapping magnetic fields in galaxy cluster areas, except for for relics. In contrast to different strategies, SIGs stay unaffected through depolarization. This find out about aimed to make sure if SIGs and polarization point out the similar magnetic subject instructions the place polarization is provide.
First writer Ph.D. pupil Yue Hu, with Italian scientists Dr. Annalisa Bonafede and Dr. Chiara Stuardi, effectively examined magnetic subject measurements inside of relics, confirming the reliability of SIG magnetic subject maps. Prof. Lazarian’s Ph.D. pupil Ka Wai Ho’s fluid dynamics simulations additional affirmed map accuracy.
SIGs supply a singular method to cope with longstanding questions concerning the foundation, evolution, and results of magnetic fields in galaxy clusters with out dealing with the demanding situations that conventional measurements do.
Warmth conduction in ICM
SIGs additionally permit researchers to check and validate current theories relating to warmth conduction within the ICM and the improvement of cooling flows, a poorly understood procedure.
“Warmth conduction in intracluster plasma (totally ionized gasoline) of ICM is considerably diminished within the course perpendicular to the magnetic subject. Thus, the power of warmth to be transported in several instructions relies on the construction of the magnetic subject. The adjustments in warmth conductivity keep watch over the formation of chilly gasoline streams surrounded through scorching gasoline, the so-called cooling flows,” defined Prof. Lazarian.
Cosmic ray acceleration
Cosmic rays are high-energy charged debris that strongly have interaction with magnetic fields in galaxy cluster halos. Dr. Gianfranco Brunetti, a co-author of the paper, is the main professional within the processes of cosmic ray acceleration in galaxy clusters. He’s interested by revealing the sooner enigmatic construction of magnetic fields.
“Clusters of galaxies are recognized to boost up cosmic rays throughout the interplay of cosmic rays with transferring magnetic fields. The image of this acceleration continues to be unclear and relies on magnetic subject dynamics,” mentioned Prof. Lazarian.
Moreover, cosmic rays practice the trails of magnetic subject traces, which means that their get away from the clusters is influenced through the precise construction of those magnetic fields.
The dynamics of the magnetic fields throughout the clusters can now be mapped the usage of the SIG methodology, serving to us perceive the operation of the most important particle accelerators within the universe.
Concluding ideas
SIGs, with their skill to map magnetic fields in areas the place polarization data is misplaced, be offering precious insights into the halos of galaxy clusters or even greater synchrotron-emitting constructions, the just lately found out Megahalos.
Because the astrophysical group eagerly awaits the Sq. Kilometer Array (SKA) telescope’s commissioning in 2027, the way forward for magnetic subject mapping in galaxy clusters seems promising. The SKA will supply synchrotron depth for the SIG methodology in addition to polarization that may be hired through different tactics evolved through Prof. Lazarian’s staff to check the detailed 3-d construction of astrophysical magnetic fields.
Prof. Lazarian mentioned, “The gradient methodology is a realistic fruit of a higher working out of basic magnetohydrodynamical processes, propelling us to delve deeper into those crucial processes. Whilst some great benefits of basic research won’t at all times be right away obvious, advances in working out key bodily processes induce tectonic adjustments that impact many sides of science and engineering.”
Additional info:
Yue Hu et al, Synchrotron depth gradient revealing magnetic fields in galaxy clusters, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45164-8.
Magazine data:
Nature Communications
© 2024 Science X Community