Experimental pc recollections and processors constructed from magnetic fabrics use a long way much less calories than conventional silicon-based gadgets. Two-dimensional magnetic fabrics, composed of layers which can be only some atoms thick, have fantastic homes that might permit magnetic-based gadgets to succeed in remarkable velocity, potency, and scalability.
Whilst many hurdles will have to be triumph over till those so-called van der Waals magnetic fabrics will also be built-in into functioning computer systems, MIT researchers took a very powerful step on this route via demonstrating exact keep watch over of a van der Waals magnet at room temperature.
That is key, since magnets composed of atomically skinny van der Waals fabrics can in most cases handiest be managed at extraordinarily chilly temperatures, making them tricky to deploy outdoor a laboratory.
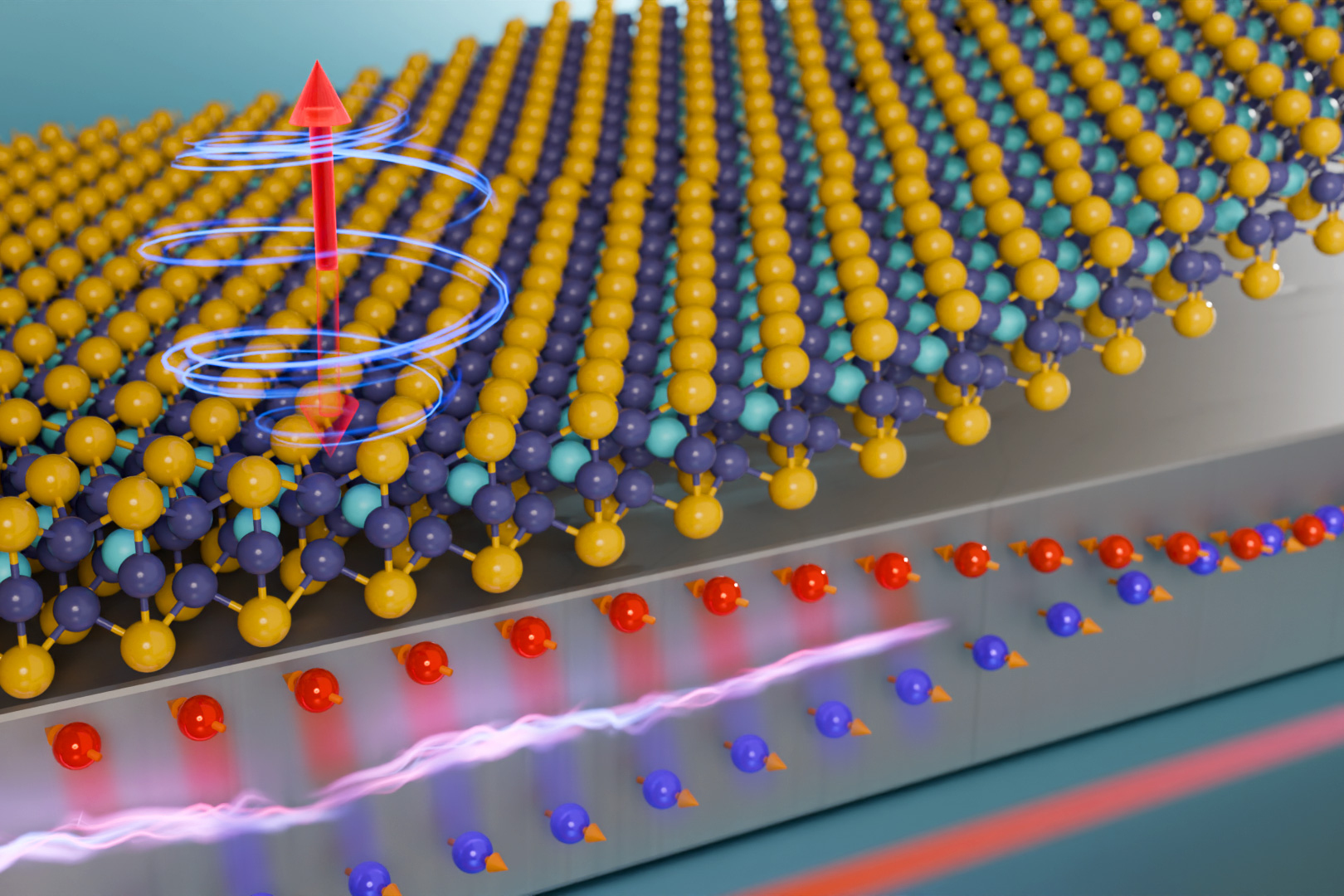
The researchers used pulses {of electrical} present to change the route of the software’s magnetization at room temperature. Magnetic switching can be utilized in computation, the similar approach a transistor switches between open and closed to constitute 0s and 1s in binary code, or in pc reminiscence, the place switching allows knowledge garage.
The workforce fired bursts of electrons at a magnet fabricated from a brand new subject material that may maintain its magnetism at upper temperatures. The experiment leveraged a elementary assets of electrons referred to as spin, which makes the electrons behave like tiny magnets. Via manipulating the spin of electrons that strike the software, the researchers can transfer its magnetization.
“The heterostructure software we’ve got advanced calls for an order of magnitude decrease electric present to change the van der Waals magnet, in comparison to that required for bulk magnetic gadgets,” says Deblina Sarkar, the AT&T Profession Building Assistant Professor within the MIT Media Lab and Heart for Neurobiological Engineering, head of the Nano-Cybernetic Biotrek Lab, and the senior writer of a paper in this methodology. “Our software could also be extra calories effective than different van der Waals magnets which can be not able to change at room temperature.”
At some point, this kind of magnet may well be used to construct sooner computer systems that devour much less electrical energy. It will additionally permit magnetic pc recollections which can be nonvolatile, this means that they don’t leak data when powered off, or processors that make advanced AI algorithms extra energy-efficient.
“There may be numerous inertia round looking to make stronger fabrics that labored neatly up to now. However we’ve got proven that if you’re making radical adjustments, beginning via rethinking the fabrics you’re the usage of, you’ll be able to probably get a lot better answers,” says Shivam Kajale, a graduate pupil in Sarkar’s lab and co-lead writer of the paper.
Kajale and Sarkar are joined at the paper via co-lead writer Thanh Nguyen, a graduate pupil within the Division of Nuclear Science and Engineering (NSE); Corson Chao, a graduate pupil within the Division of Fabrics Science and Engineering (DSME); David Bono, a DSME analysis scientist; Artittaya Boonkird, an NSE graduate pupil; and Mingda Li, affiliate professor of nuclear science and engineering. The analysis seems this week in Nature Communications.
An atomically skinny benefit
The best way to fabricate tiny pc chips in a blank room from bulk fabrics like silicon can abate gadgets. As an example, the layers of subject material is also slightly 1 nanometer thick, so minuscule tough spots at the floor will also be serious sufficient to degrade efficiency.
In contrast, van der Waals magnetic fabrics are intrinsically layered and structured in this kind of approach that the skin stays completely easy, at the same time as researchers peel off layers to make thinner gadgets. As well as, atoms in a single layer received’t leak into different layers, enabling the fabrics to retain their distinctive homes when stacked in gadgets.
“In relation to scaling and making those magnetic gadgets aggressive for business programs, van der Waals fabrics are pass,” Kajale says.
However there’s a catch. This new elegance of magnetic fabrics have in most cases handiest been operated at temperatures under 60 kelvins (-351 levels Fahrenheit). To construct a magnetic pc processor or reminiscence, researchers want to use electric present to function the magnet at room temperature.
To succeed in this, the workforce desirous about an rising subject material referred to as iron gallium telluride. This atomically skinny subject material has all of the homes wanted for efficient room temperature magnetism and doesn’t include uncommon earth components, which might be unwanted as a result of extracting them is particularly harmful to the surroundings.
Nguyen moderately grew bulk crystals of this 2D subject material the usage of a different methodology. Then, Kajale fabricated a two-layer magnetic software the usage of nanoscale flakes of iron gallium telluride beneath a six-nanometer layer of platinum.
Tiny software in hand, they used an intrinsic assets of electrons referred to as spin to change its magnetization at room temperature.
Electron ping-pong
Whilst electrons don’t technically “spin” like a best, they do possess the similar roughly angular momentum. That spin has a route, both up or down. The researchers can leverage a assets referred to as spin-orbit coupling to keep watch over the spins of electrons they fireplace on the magnet.
The similar approach momentum is transferred when one ball hits some other, electrons will switch their “spin momentum” to the 2D magnetic subject material once they strike it. Relying at the route in their spins, that momentum switch can opposite the magnetization.
In a way, this switch rotates the magnetization from as much as down (or vice-versa), so it is named a “torque,” as in spin-orbit torque switching. Making use of a damaging electrical pulse reasons the magnetization to head downward, whilst a good pulse reasons it to head upward.
The researchers can do that switching at room temperature for 2 causes: the particular homes of iron gallium telluride and the truth that their methodology makes use of small quantities {of electrical} present. Pumping an excessive amount of present into the software would purpose it to overheat and demagnetize.
The workforce confronted many demanding situations over the 2 years it took to succeed in this milestone, Kajale says. Discovering the correct magnetic subject material used to be handiest part the struggle. Since iron gallium telluride oxidizes temporarily, fabrication will have to be accomplished inside of a glovebox stuffed with nitrogen.
“The software is handiest uncovered to air for 10 or 15 seconds, however even after that I’ve to do a step the place I polish it to take away any oxide,” he says.
Now that they have got demonstrated room-temperature switching and bigger calories potency, the researchers plan to stay pushing the efficiency of magnetic van der Waals fabrics.
“Our subsequent milestone is to succeed in switching with out the desire for any exterior magnetic fields. Our intention is to reinforce our era and scale as much as convey the flexibility of van der Waals magnet to business programs,” Sarkar says.
This paintings used to be performed, partly, the usage of the amenities at MIT.Nano and the Harvard College Heart for Nanoscale Programs.