Smacking a spacecraft into an asteroid will have had some attention-grabbing uncomfortable side effects.Consistent with an research of a collision between NASA’s DART probe and the asteroid Dimorphos again in September 2022, the tiny asteroid’s form will have modified considerably as an immediate results of the influence.This gives some clues about how the asteroid shaped within the first position, whilst additionally suggesting the impending undertaking to research Dimorphos will to find now not an influence crater, however a smartly reformed pile of house rock.The DART undertaking – Double Asteroid Redirection Check – used to be considered one of planetary protection. Scientists sought after to peer if they might divert the process an asteroid via ramming it with a spacecraft. Dimorphos used to be the selected goal – a small asteroid in a mutual orbit with a bigger binary better half referred to as Didymos. For the reason that orbital length of the binary object used to be widely recognized, any adjustments within the timing of this era would imply that the undertaking used to be a hit.And a luck it used to be: the influence had a far larger impact at the timing of the length than scientists anticipated. However the DART undertaking used to be the primary time humanity had ever attempted this kind of factor; we did not know if there could be ongoing results to watch, what the ones results could be, what they might imply for asteroid redirection, and what, if the rest, they’d let us know about Dimorphos.Clearly, scientists had been tracking the gap rock for adjustments. However a staff led via planetary scientist Sabina Raducan of the College of Bern in Switzerland took a distinct way. They took a simulated Dimorphos and a simulated DART spacecraft, and attempted to duplicate the seen results of the influence.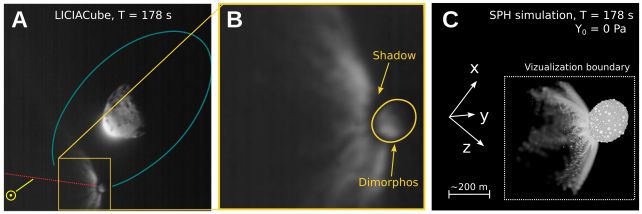 A comparability of the commentary of the DART influence (left, middle) and the simulation (proper). (Raducan et al., Nature Astronomy, 2024)That incorporates the transferral of momentum from the spacecraft to the asteroid, the volume of subject material that erupted from Dimorphos, and the form that subject material shaped because it spewed into house, referred to as the ejecta cone.To try this, they had to tweak unknown variables: the composition and density of Dimorphos.Now not all asteroids are constructed alike. Some are extra dense, corresponding to chunks of planets arrested of their construction via massive affects and damaged up into smaller fragments. And a few are what are referred to as “rubble piles”, which is just about what it seems like: looser agglomerations of mud and pebbles that experience come in combination, however could be extra vulnerable to coming aside beneath gravitational pressure, for instance.We already knew that each Didymos and Dimorphos fall into the rubble pile class. However the DART influence can let us know precisely what Dimorphos is manufactured from.Raducan and her colleagues have been ready to supply simulations in line with the seen results of the DART undertaking. And, in those simulations, the asteroid is held in combination so loosely that DART did not go away a scar at the floor; as an alternative, the spacecraft brought about international deformation and resurfacing.For this to happen, the asteroid must be an excessively susceptible rubble pile; its cohesive energy, the staff’s calculations counsel, is not up to a couple of pascals. That is similar to asteroids Ryugu and Bennu, either one of which were visited via human spacecraft for knowledge and pattern assortment.The simulations additionally counsel that the density of Dimorphos could be very low, round 2.4 grams in line with cubic centimeter. That is quite denser than Ryugu and Bennu, which sit down round 1.28 and 1.26 grams in line with cubic centimeter, respectively. The density of Earth, for context, is 5.51 grams in line with cubic centimeter.The boulder density of the simulated Dimorphos used to be in line with the density bought from DART observations.
A comparability of the commentary of the DART influence (left, middle) and the simulation (proper). (Raducan et al., Nature Astronomy, 2024)That incorporates the transferral of momentum from the spacecraft to the asteroid, the volume of subject material that erupted from Dimorphos, and the form that subject material shaped because it spewed into house, referred to as the ejecta cone.To try this, they had to tweak unknown variables: the composition and density of Dimorphos.Now not all asteroids are constructed alike. Some are extra dense, corresponding to chunks of planets arrested of their construction via massive affects and damaged up into smaller fragments. And a few are what are referred to as “rubble piles”, which is just about what it seems like: looser agglomerations of mud and pebbles that experience come in combination, however could be extra vulnerable to coming aside beneath gravitational pressure, for instance.We already knew that each Didymos and Dimorphos fall into the rubble pile class. However the DART influence can let us know precisely what Dimorphos is manufactured from.Raducan and her colleagues have been ready to supply simulations in line with the seen results of the DART undertaking. And, in those simulations, the asteroid is held in combination so loosely that DART did not go away a scar at the floor; as an alternative, the spacecraft brought about international deformation and resurfacing.For this to happen, the asteroid must be an excessively susceptible rubble pile; its cohesive energy, the staff’s calculations counsel, is not up to a couple of pascals. That is similar to asteroids Ryugu and Bennu, either one of which were visited via human spacecraft for knowledge and pattern assortment.The simulations additionally counsel that the density of Dimorphos could be very low, round 2.4 grams in line with cubic centimeter. That is quite denser than Ryugu and Bennu, which sit down round 1.28 and 1.26 grams in line with cubic centimeter, respectively. The density of Earth, for context, is 5.51 grams in line with cubic centimeter.The boulder density of the simulated Dimorphos used to be in line with the density bought from DART observations.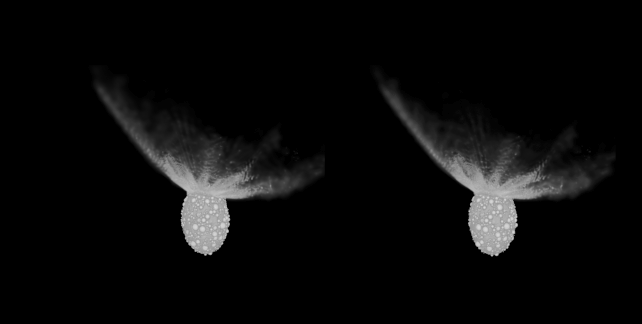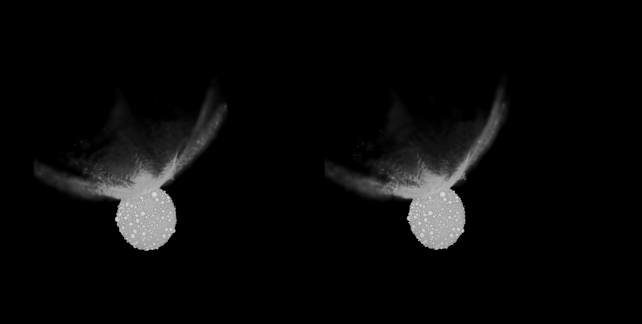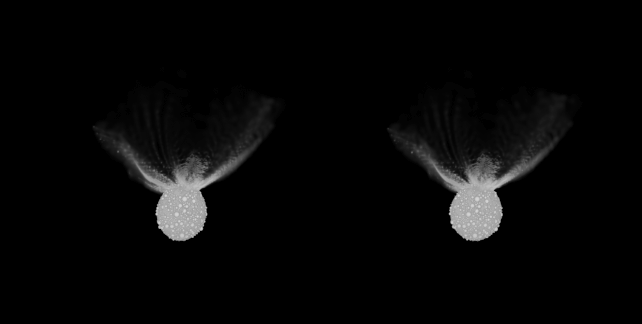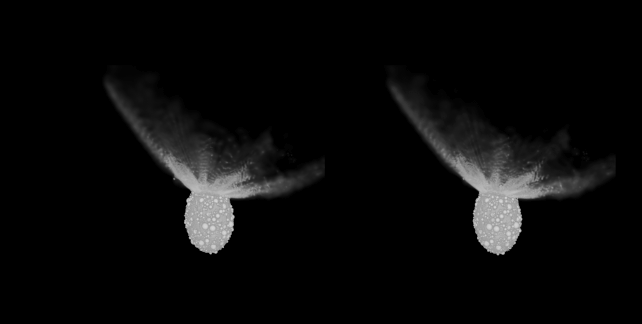 A stereoscopic film generated from the simulations appearing Dimorphos at roughly 178 seconds post-impact. (S.D. Raducan/C. Manzoni/B.H. Might)Those findings counsel that Dimorphos is also Didymos’ asteroid child. Didymos could also be a rubble pile, and we all know that rubble piles continuously shed particles as they spin, due to centrifugal pressure. A few of this shed particles stays in orbit with Didymos, in line with this style of Dimorphos’ formation; over the years, it clumped in combination to develop into the free rubble pile we walloped with a spaceship.We do not know if they are proper, now not but. However we will be able to. Later this yr, the Ecu Area Company is launching the Hera undertaking to check Didymos and Dimorphos. If what Hera reveals is in line with the staff’s simulations, we’re going to know much more about Dimorphos than we did.And this has implications, now not only for our figuring out of the continued evolution of the binary, however asteroids, asteroid binaries, and the way we plan and execute any upcoming asteroid redirection missions.”For the reason that DART spacecraft almost definitely brought about international deformation of Dimorphos, we will infer that in a similar way shaped asteroid moons are simply reshaped and their surfaces are rather younger,” the researchers write of their paper.”Total, the findings of this find out about supply precious data for figuring out the formation and traits of binary asteroids and can tell long run exploration and asteroid deflection efforts.”The analysis has been printed in Nature Astronomy.
A stereoscopic film generated from the simulations appearing Dimorphos at roughly 178 seconds post-impact. (S.D. Raducan/C. Manzoni/B.H. Might)Those findings counsel that Dimorphos is also Didymos’ asteroid child. Didymos could also be a rubble pile, and we all know that rubble piles continuously shed particles as they spin, due to centrifugal pressure. A few of this shed particles stays in orbit with Didymos, in line with this style of Dimorphos’ formation; over the years, it clumped in combination to develop into the free rubble pile we walloped with a spaceship.We do not know if they are proper, now not but. However we will be able to. Later this yr, the Ecu Area Company is launching the Hera undertaking to check Didymos and Dimorphos. If what Hera reveals is in line with the staff’s simulations, we’re going to know much more about Dimorphos than we did.And this has implications, now not only for our figuring out of the continued evolution of the binary, however asteroids, asteroid binaries, and the way we plan and execute any upcoming asteroid redirection missions.”For the reason that DART spacecraft almost definitely brought about international deformation of Dimorphos, we will infer that in a similar way shaped asteroid moons are simply reshaped and their surfaces are rather younger,” the researchers write of their paper.”Total, the findings of this find out about supply precious data for figuring out the formation and traits of binary asteroids and can tell long run exploration and asteroid deflection efforts.”The analysis has been printed in Nature Astronomy.
Asteroid Struck via a Spacecraft May Be 'Therapeutic' as Its Floor Reforms









/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25752946/1183652392.jpg)