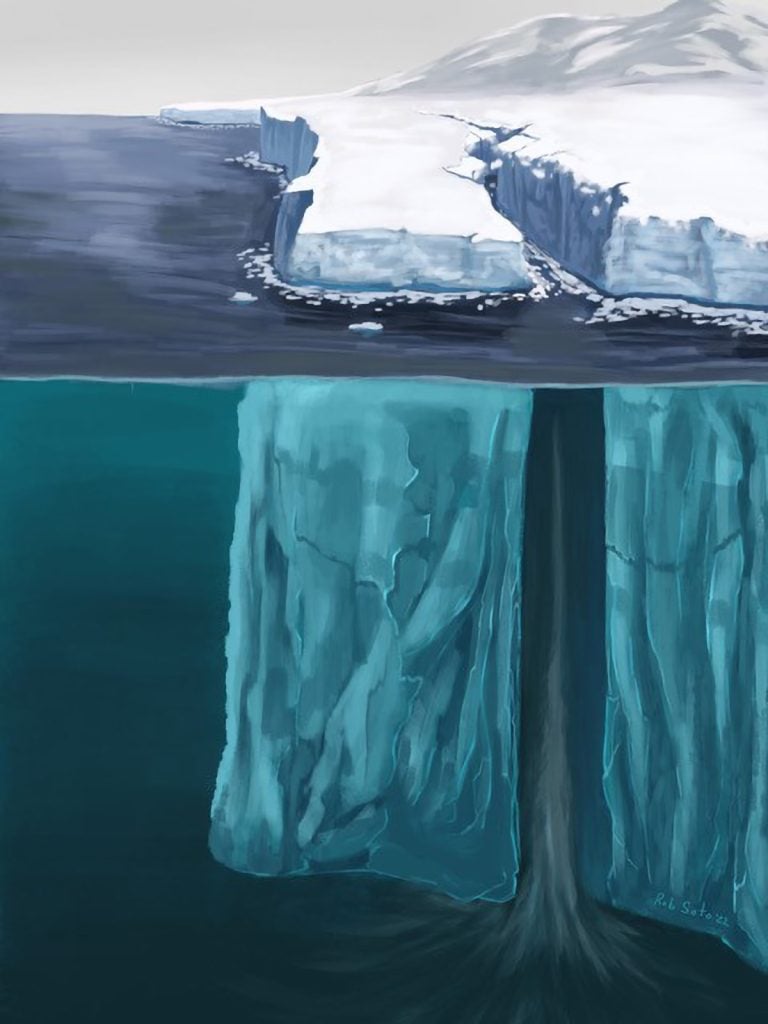
 On this representation, seawater flows deep underneath the skin into an actively opening ice shelf rift in Antarctica. New analysis presentations that such rifts can open in no time, and that the seawater speeding in is helping keep an eye on the rate of ice shelf breakage. Credit score: Rob SotoThere’s sufficient water frozen in Greenland and Antarctic glaciers that in the event that they melted, world seas would upward push by way of many toes. What’s going to occur to those glaciers over the approaching a long time is the largest unknown at some point of emerging seas, partially as a result of glacier fracture physics isn’t but totally understood.A vital query is how hotter oceans may purpose glaciers to damage aside extra briefly. College of Washington researchers have demonstrated the fastest-known large-scale breakage alongside an Antarctic ice shelf. The learn about, just lately printed in AGU Advances, presentations {that a} 6.5-mile (10.5 kilometer) crack shaped in 2012 on Pine Island Glacier — a backing out ice shelf that holds again the bigger West Antarctic ice sheet — in about 5 and a part mins. That implies the rift opened at about 115 toes (35 meters) consistent with 2nd, or about 80 miles consistent with hour.“That is to our wisdom the quickest rift-opening tournament that’s ever been seen,” stated lead writer Stephanie Olinger, who did the paintings as a part of her doctoral analysis on the UW and Harvard College, and is now a postdoctoral researcher at Stanford College. “This presentations that below sure cases, an ice shelf can shatter. It tells us we want to glance out for this kind of conduct at some point, and it informs how we may cross about describing those fractures in large-scale ice sheet fashions.”The Importance of Rift FormationA rift is a crack that passes during the kind of 1,000 toes (300 meters) of floating ice for a standard Antarctic ice shelf. Those cracks are the precursor to ice shelf calving, during which vast chunks of ice smash off a glacier and fall into the ocean. Such occasions occur frequently at Pine Island Glacier — the iceberg seen within the learn about has lengthy since separated from the continent.
On this representation, seawater flows deep underneath the skin into an actively opening ice shelf rift in Antarctica. New analysis presentations that such rifts can open in no time, and that the seawater speeding in is helping keep an eye on the rate of ice shelf breakage. Credit score: Rob SotoThere’s sufficient water frozen in Greenland and Antarctic glaciers that in the event that they melted, world seas would upward push by way of many toes. What’s going to occur to those glaciers over the approaching a long time is the largest unknown at some point of emerging seas, partially as a result of glacier fracture physics isn’t but totally understood.A vital query is how hotter oceans may purpose glaciers to damage aside extra briefly. College of Washington researchers have demonstrated the fastest-known large-scale breakage alongside an Antarctic ice shelf. The learn about, just lately printed in AGU Advances, presentations {that a} 6.5-mile (10.5 kilometer) crack shaped in 2012 on Pine Island Glacier — a backing out ice shelf that holds again the bigger West Antarctic ice sheet — in about 5 and a part mins. That implies the rift opened at about 115 toes (35 meters) consistent with 2nd, or about 80 miles consistent with hour.“That is to our wisdom the quickest rift-opening tournament that’s ever been seen,” stated lead writer Stephanie Olinger, who did the paintings as a part of her doctoral analysis on the UW and Harvard College, and is now a postdoctoral researcher at Stanford College. “This presentations that below sure cases, an ice shelf can shatter. It tells us we want to glance out for this kind of conduct at some point, and it informs how we may cross about describing those fractures in large-scale ice sheet fashions.”The Importance of Rift FormationA rift is a crack that passes during the kind of 1,000 toes (300 meters) of floating ice for a standard Antarctic ice shelf. Those cracks are the precursor to ice shelf calving, during which vast chunks of ice smash off a glacier and fall into the ocean. Such occasions occur frequently at Pine Island Glacier — the iceberg seen within the learn about has lengthy since separated from the continent.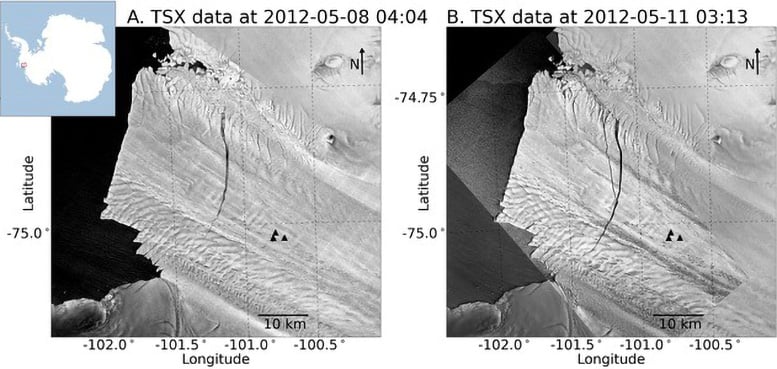 Satellite tv for pc pictures taken Would possibly 8 (left) and Would possibly 11 (proper), 3 days aside in 2012, display a brand new crack that paperwork a “Y” branching off to the left of the former rift. 3 seismic tools (black triangles) recorded vibrations that had been used to calculate rift propagation speeds of as much as 80 miles consistent with hour. Credit score: Olinger et al./AGU Advances“Ice cabinets exert a in reality essential stabilizing affect on the remainder of the Antarctic ice sheet. If an ice shelf breaks up, the glacier ice at the back of in reality hurries up,” Olinger stated. “This rifting procedure is largely how Antarctic ice cabinets calve vast icebergs.”In different portions of Antarctica, rifts frequently broaden over months or years. However it may well occur extra briefly in a fast-evolving panorama like Pine Island Glacier, the place researchers consider the West Antarctic Ice Sheet has already handed a tipping level on its cave in into the sea.Demanding situations in Watching Glacial ChangesSatellite pictures supply ongoing observations. However orbiting satellites move by way of every level on Earth handiest each and every 3 days. What occurs all through the ones 3 days is more difficult to pin down, particularly within the bad panorama of a delicate Antarctic ice shelf.For the brand new learn about, the researchers mixed equipment to grasp the rift’s formation. They used seismic knowledge recorded by way of tools positioned at the ice shelf by way of different researchers in 2012 with radar observations from satellites.Glacier ice acts like a forged on brief timescales, but it surely’s extra like a viscous liquid on lengthy timescales.“Is rift formation extra like glass breaking or like Foolish Putty being pulled aside? That used to be the query,” Olinger stated. “Our calculations for this tournament display that it’s much more like glass breaking.”The Function of Seawater and Long term ResearchIf the ice had been a easy brittle subject matter, it must have shattered even quicker, Olinger stated. Additional investigation pointed to the position of seawater. Seawater within the rifts holds the distance open towards the inward forces of the glacier. And because seawater has viscosity, floor stress, and mass, it may well’t simply immediately fill the void. As an alternative, the tempo at which seawater fills the hole crack is helping sluggish the rift’s unfold.“Sooner than we will be able to toughen the efficiency of large-scale ice sheet fashions and projections of long run sea-level upward push, we need to have a excellent, physics-based working out of the various other processes that affect ice shelf balance,” Olinger stated.Reference: “Ocean Coupling Limits Rupture Speed of Quickest Seen Ice Shelf Rift Propagation Match” by way of Stephanie D. Olinger, Bradley P. Lipovsky and Marine A. Denolle, 05 February 2024, AGU Advances.
Satellite tv for pc pictures taken Would possibly 8 (left) and Would possibly 11 (proper), 3 days aside in 2012, display a brand new crack that paperwork a “Y” branching off to the left of the former rift. 3 seismic tools (black triangles) recorded vibrations that had been used to calculate rift propagation speeds of as much as 80 miles consistent with hour. Credit score: Olinger et al./AGU Advances“Ice cabinets exert a in reality essential stabilizing affect on the remainder of the Antarctic ice sheet. If an ice shelf breaks up, the glacier ice at the back of in reality hurries up,” Olinger stated. “This rifting procedure is largely how Antarctic ice cabinets calve vast icebergs.”In different portions of Antarctica, rifts frequently broaden over months or years. However it may well occur extra briefly in a fast-evolving panorama like Pine Island Glacier, the place researchers consider the West Antarctic Ice Sheet has already handed a tipping level on its cave in into the sea.Demanding situations in Watching Glacial ChangesSatellite pictures supply ongoing observations. However orbiting satellites move by way of every level on Earth handiest each and every 3 days. What occurs all through the ones 3 days is more difficult to pin down, particularly within the bad panorama of a delicate Antarctic ice shelf.For the brand new learn about, the researchers mixed equipment to grasp the rift’s formation. They used seismic knowledge recorded by way of tools positioned at the ice shelf by way of different researchers in 2012 with radar observations from satellites.Glacier ice acts like a forged on brief timescales, but it surely’s extra like a viscous liquid on lengthy timescales.“Is rift formation extra like glass breaking or like Foolish Putty being pulled aside? That used to be the query,” Olinger stated. “Our calculations for this tournament display that it’s much more like glass breaking.”The Function of Seawater and Long term ResearchIf the ice had been a easy brittle subject matter, it must have shattered even quicker, Olinger stated. Additional investigation pointed to the position of seawater. Seawater within the rifts holds the distance open towards the inward forces of the glacier. And because seawater has viscosity, floor stress, and mass, it may well’t simply immediately fill the void. As an alternative, the tempo at which seawater fills the hole crack is helping sluggish the rift’s unfold.“Sooner than we will be able to toughen the efficiency of large-scale ice sheet fashions and projections of long run sea-level upward push, we need to have a excellent, physics-based working out of the various other processes that affect ice shelf balance,” Olinger stated.Reference: “Ocean Coupling Limits Rupture Speed of Quickest Seen Ice Shelf Rift Propagation Match” by way of Stephanie D. Olinger, Bradley P. Lipovsky and Marine A. Denolle, 05 February 2024, AGU Advances.
DOI: 10.1029/2023AV001023The analysis used to be funded by way of the Nationwide Science Basis. Co-authors are Brad Lipovsky and Marine Denolle, each UW college contributors in Earth and area sciences who started advising the paintings whilst at Harvard College.
The 80 MPH Glacier Fracture: A Wake-Up Name From Antarctica














