Other people with microplastics and nanoplastics in plaque lining a big blood vessel of their neck will have the next possibility of middle assault, stroke or loss of life, new analysis suggests.The findings, printed Wednesday in The New England Magazine of Medication, are the primary time scientists have connected those tiny plastic debris, the results of degraded plastic air pollution, to heart problems.Microplastics are outlined as debris smaller than 5 millimeters, and nanoplastics are some distance smaller — so tiny that they are able to be observed most effective with specialised microscopes. In recent times, their ubiquity has turn into simple: They’ve been present in recent snowstorm in Antarctica and on the depths of the Marianas Trench, in addition to in human blood; breast milk; urine; and placental, lung and liver tissue.Dr. Raffaele Marfella — a cardiology researcher within the College of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli’s division of complicated scientific and surgical sciences in Naples, Italy, and the lead writer of the brand new learn about — stated that he and his colleagues initiated the learn about to search for new possibility components for heart problems.They knew of the giant quantity of degraded plastic air pollution contaminating the planet and questioned “whether or not plastic, within the type of micro- or nanoplastics, may just additionally degrade our arteries,” Marfella stated in an e-mail. Other people can inhale and ingest the plastic debris. The plastic too can input the frame thru pores and skin.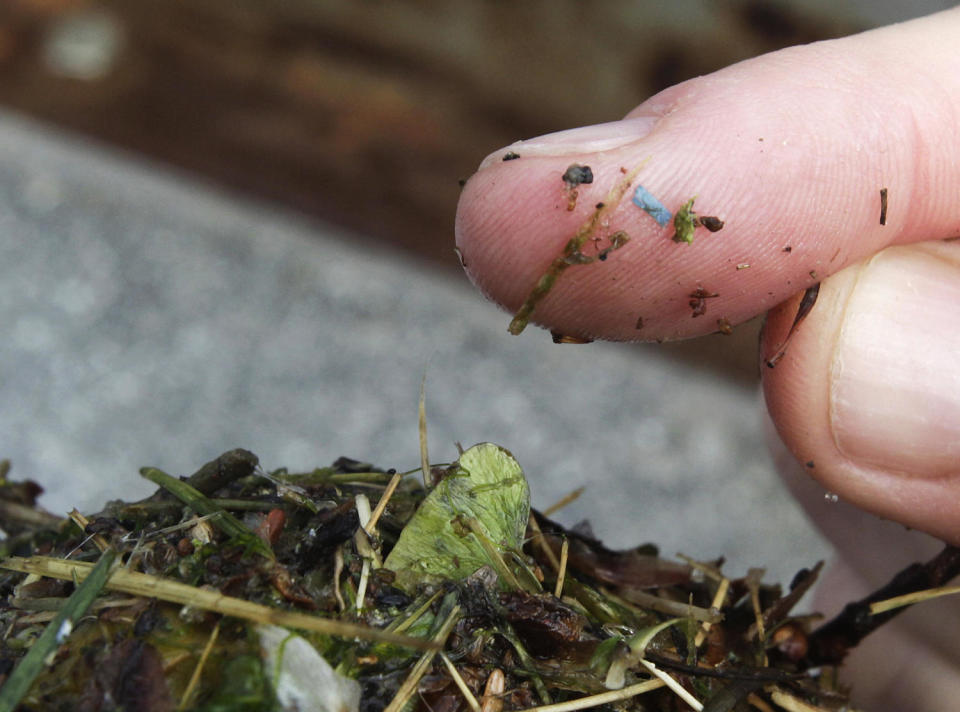
 A blue oblong piece of microplastic at the finger of a researcher in Tacoma, Wash. (Ted S. Warren / AP report )To check the results, they became to a gaggle of sufferers already scheduled to go through surgical treatment for a situation known as carotid artery stenosis, during which plaque, or fatty deposits, blocks customary blood drift. The frame’s two carotid arteries provide blood to the mind, face and neck. The researchers checked out plaque got rid of from 257 sufferers and tracked the sufferers’ well being for a median of 34 months following the surgical treatment.They discovered plastic debris — most commonly nanoplastics — within the plaque of 150 sufferers. At follow-up, nonfatal middle assault, nonfatal stroke or loss of life from any purpose came about in 20% of the ones sufferers and in 7.5% of the sufferers with out detectable plastic debris.After adjusting for age, intercourse, frame mass index and well being prerequisites similar to diabetes and atypical ldl cholesterol, the sufferers with detectable ranges of plastics had “just about a 5 instances larger possibility of a cardiovascular match” than the opposite sufferers, Marfella stated.A large number of experimental research on cells and in animals have proven that the presence of those plastic debris will increase illnesses. One learn about printed on-line in February within the Magazine of Hazardous Fabrics discovered microplastics, for the primary time, in human arteries.Earlier research discovering the tiny debris in human tissue had been “pioneering,” stated Dick Vethaak, a biologist and toxicologist at Utrecht College’s Institute for Possibility Review Sciences and coordinator of the Dutch Microplastics and Human Well being Consortium, however this learn about “is the primary of its sort.”“It’s the first person who checked out a lot of donors in such a lot element” and the primary to stick with sufferers for years to trace their well being, stated Vethaak, who wasn’t concerned with the brand new learn about.On the other hand, this sort of observational learn about can display most effective an affiliation between the plastic debris and middle assault, stroke or loss of life. It can not display that they led to those cardiovascular occasions. For that, researchers would want to behavior a randomized, managed trial, however it might be unethical to deliberately disclose folks to possible toxins.However, the learn about provides some hints concerning the courting between the presence of micro- and nanoplastics and middle illness, stated Dr. Martha Gulati, director of preventive cardiology within the Smidt Middle Institute at Cedars-Sinai in Los Angeles.“We all know that heart problems, in particular myocardial infarction, is most often brought on via an inflammatory reaction,” Gulati stated, the usage of every other time period for middle assault. The Italian researchers measured markers for irritation in sufferers and located that the ones markers greater as the extent of plastics within the plaque rose.Nonetheless, “is the irritation because of the nanoplastics or one thing else?” Gulati requested.For the reason that learn about used to be performed in an overly explicit crew of sufferers, the consequences can’t be implemented to the wider inhabitants. However it would pave the best way for long run research.“This paper would possibly impress folks to determine if we will be able to measure micro- and nanoplastics within the basic inhabitants after which read about who is going directly to expand cardiac occasions,” Gulati stated.Vethaak stated equivalent research are within the pipeline for different kinds of human tissue.The researchers additionally famous the likelihood that the plaque samples can have been infected within the lab.“Long term research carried out with using blank rooms, the place there is not any plastic in any shape excluding the fabric underneath learn about, would possibly corroborate our observations,” they wrote within the paper.“I’m hoping that this learn about, and extra paintings that it triggers, is helping us cope with our surroundings and cardiovascular well being as a result of I believe like that is one thing that in point of fact must be mentioned,” Gulati stated. “It will get little or no consideration.”This newsletter used to be firstly printed on NBCNews.com
A blue oblong piece of microplastic at the finger of a researcher in Tacoma, Wash. (Ted S. Warren / AP report )To check the results, they became to a gaggle of sufferers already scheduled to go through surgical treatment for a situation known as carotid artery stenosis, during which plaque, or fatty deposits, blocks customary blood drift. The frame’s two carotid arteries provide blood to the mind, face and neck. The researchers checked out plaque got rid of from 257 sufferers and tracked the sufferers’ well being for a median of 34 months following the surgical treatment.They discovered plastic debris — most commonly nanoplastics — within the plaque of 150 sufferers. At follow-up, nonfatal middle assault, nonfatal stroke or loss of life from any purpose came about in 20% of the ones sufferers and in 7.5% of the sufferers with out detectable plastic debris.After adjusting for age, intercourse, frame mass index and well being prerequisites similar to diabetes and atypical ldl cholesterol, the sufferers with detectable ranges of plastics had “just about a 5 instances larger possibility of a cardiovascular match” than the opposite sufferers, Marfella stated.A large number of experimental research on cells and in animals have proven that the presence of those plastic debris will increase illnesses. One learn about printed on-line in February within the Magazine of Hazardous Fabrics discovered microplastics, for the primary time, in human arteries.Earlier research discovering the tiny debris in human tissue had been “pioneering,” stated Dick Vethaak, a biologist and toxicologist at Utrecht College’s Institute for Possibility Review Sciences and coordinator of the Dutch Microplastics and Human Well being Consortium, however this learn about “is the primary of its sort.”“It’s the first person who checked out a lot of donors in such a lot element” and the primary to stick with sufferers for years to trace their well being, stated Vethaak, who wasn’t concerned with the brand new learn about.On the other hand, this sort of observational learn about can display most effective an affiliation between the plastic debris and middle assault, stroke or loss of life. It can not display that they led to those cardiovascular occasions. For that, researchers would want to behavior a randomized, managed trial, however it might be unethical to deliberately disclose folks to possible toxins.However, the learn about provides some hints concerning the courting between the presence of micro- and nanoplastics and middle illness, stated Dr. Martha Gulati, director of preventive cardiology within the Smidt Middle Institute at Cedars-Sinai in Los Angeles.“We all know that heart problems, in particular myocardial infarction, is most often brought on via an inflammatory reaction,” Gulati stated, the usage of every other time period for middle assault. The Italian researchers measured markers for irritation in sufferers and located that the ones markers greater as the extent of plastics within the plaque rose.Nonetheless, “is the irritation because of the nanoplastics or one thing else?” Gulati requested.For the reason that learn about used to be performed in an overly explicit crew of sufferers, the consequences can’t be implemented to the wider inhabitants. However it would pave the best way for long run research.“This paper would possibly impress folks to determine if we will be able to measure micro- and nanoplastics within the basic inhabitants after which read about who is going directly to expand cardiac occasions,” Gulati stated.Vethaak stated equivalent research are within the pipeline for different kinds of human tissue.The researchers additionally famous the likelihood that the plaque samples can have been infected within the lab.“Long term research carried out with using blank rooms, the place there is not any plastic in any shape excluding the fabric underneath learn about, would possibly corroborate our observations,” they wrote within the paper.“I’m hoping that this learn about, and extra paintings that it triggers, is helping us cope with our surroundings and cardiovascular well being as a result of I believe like that is one thing that in point of fact must be mentioned,” Gulati stated. “It will get little or no consideration.”This newsletter used to be firstly printed on NBCNews.com