Off Japan’s Minamitorishima Island round twilight, after the solar has dipped underneath the horizon, the sounds of many animals sign up for in combination in a choir. They can’t be heard on land, for the individuals on this choir are fish. They don’t sing with vocal cords—they don’t have any—however relatively by means of contracting their gas-filled swim bladders to buzz like a kazoo or by means of rubbing their fins or tooth to chirp like a cricket. The overlapping calls of most of these grunts, buzzes, burbles, and squawks coalesce right into a refrain that peals around the huge ocean in distances that might disappear sunbeams.”Mild does not go back and forth smartly in sea water, and so it’s pitch darkish at nice depths,” Christine Erbe, the director of the Centre for Marine Science and Generation at Curtin College in Perth, wrote in an electronic mail. “However sound travels extraordinarily smartly.”The carols of the fish refrain go back and forth too, now not simply around the waves however underneath them. They shape a part of the sea’s soundscape, which incorporates all of the noises made by means of animals, herbal forces like wind and earthquakes, and man-made era. Other ocean ecosystems have other soundscapes, and Tzu-Hao Lin, a researcher who self-describes as an “ocean listener” at Academia Sinica in Taiwan, has faithful himself to finding out the specific acoustic atmospheres of the deep sea. He has recorded soundscapes from hydrothermal vents, the twilight zone, and abyssal plains greater than 18,000 ft deep in waters by means of the far flung island of Minamitorishima. In those exceptionally deep waters, Lin idea he’d detected a refrain of fish making a song quickly after sundown and quieting at nighttime. However the recording used to be so transient, representing lower than an afternoon within the deep, that it could were a blip, a passing college of chatty fish. “It is within the deep sea, you realize, so we in truth should not have many clinical questions at first,” Lin stated. “We simply need to discover what we will uncover.” Lin got here up with a plan to document the sounds of a deep-sea abyss for a complete yr. In March of 2020, Shinsuke Kawagucci, a researcher on the Japan Company for Marine-Earth Science and Generation, dropped an underwater recording tool referred to as a hydrophone off the facet of a boat south of Minamitorishima, which is off-limits to civilians and remoted from transport visitors. The hydrophone sank till it settled at the seafloor, 18,000 ft underneath. It sat there for a yr, in a space too deep and far flung to be photographed, recording for 2 mins each and every 4 hours. When the researchers retrieved the tool the next April—remotely triggering it to unlatch its anchor and ascend greater than 3 miles to the skin—they recovered a year-long document of the soundscape of the abyss, which Lin and Kawagucci revealed within the magazine Limnology and Oceanography remaining fall.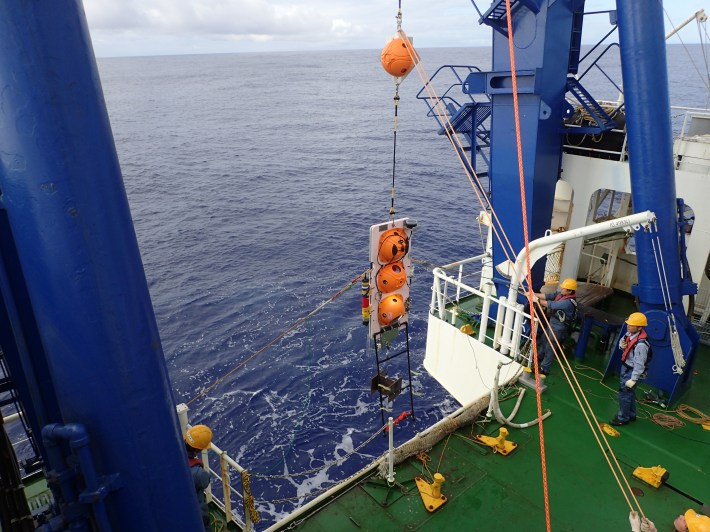 Shedding the hydrophone off the send. | Shinsuke Kawagucci (JAMSTEC)Again within the lab, Lin pored over the 4,260 mins of recordings. Oceanic soundscapes frequently do not sound like a lot to the human ear. “It is similar to the white noise emitted from some roughly damaged TV,” Lin stated. A greater option to perceive those sounds is, mockingly sufficient, to peer them. Lin ran a pc program that spawns spectrograms that visualize the audio knowledge, revealing the adjustments in frequency and depth over the years (right here is a superb instance of a soundscape and its related spectrogram). The information published that, by means of day, the Minamitorishima abyss used to be a quiet position, interrupted once in a while by means of whistles and clicks from passing marine mammals or the engines of far off ships. However the abyss crackled to existence each and every evening, resounding with a refrain of fish throughout sundown and quieting at nighttime. Even Lin, a trifling human, may just pay attention a “large distinction” between the sounds of day and evening, he stated. He used to be shocked. His prior knowledge hadn’t simply been a blip. This primary refrain might be heard every day from 8 p.m. to nighttime between Might and September. From December to June, a 2d refrain sounded, additionally round 8 p.m.At a look, this discovery would possibly appear unremarkable. The sea, in any case, is filled with fish. However the timing of those fish choruses—each materializing round twilight—supposed that other instances of day within the abyss have been characterised by means of other sounds. The researchers consulted earlier research and located identical night time choruses might be heard throughout swaths of the Pacific and Indian Oceans at depths of just about 1,000 ft to greater than 18,000 ft. The researchers questioned if those sounds have been tied to diel migration, the day-to-day phenomenon during which billions and billions of plankton, fish, and different animals upward push towards the sea’s floor at evening and sink again into deeper seas at first light. If the making a song fish have been migrating alongside this vertical trail, they may descend to depths the place their voices change into perceptible to the abyss round sundown. In different phrases, whilst deep-sea creatures would possibly now not see the sundown, they may be able to pay attention it.
Shedding the hydrophone off the send. | Shinsuke Kawagucci (JAMSTEC)Again within the lab, Lin pored over the 4,260 mins of recordings. Oceanic soundscapes frequently do not sound like a lot to the human ear. “It is similar to the white noise emitted from some roughly damaged TV,” Lin stated. A greater option to perceive those sounds is, mockingly sufficient, to peer them. Lin ran a pc program that spawns spectrograms that visualize the audio knowledge, revealing the adjustments in frequency and depth over the years (right here is a superb instance of a soundscape and its related spectrogram). The information published that, by means of day, the Minamitorishima abyss used to be a quiet position, interrupted once in a while by means of whistles and clicks from passing marine mammals or the engines of far off ships. However the abyss crackled to existence each and every evening, resounding with a refrain of fish throughout sundown and quieting at nighttime. Even Lin, a trifling human, may just pay attention a “large distinction” between the sounds of day and evening, he stated. He used to be shocked. His prior knowledge hadn’t simply been a blip. This primary refrain might be heard every day from 8 p.m. to nighttime between Might and September. From December to June, a 2d refrain sounded, additionally round 8 p.m.At a look, this discovery would possibly appear unremarkable. The sea, in any case, is filled with fish. However the timing of those fish choruses—each materializing round twilight—supposed that other instances of day within the abyss have been characterised by means of other sounds. The researchers consulted earlier research and located identical night time choruses might be heard throughout swaths of the Pacific and Indian Oceans at depths of just about 1,000 ft to greater than 18,000 ft. The researchers questioned if those sounds have been tied to diel migration, the day-to-day phenomenon during which billions and billions of plankton, fish, and different animals upward push towards the sea’s floor at evening and sink again into deeper seas at first light. If the making a song fish have been migrating alongside this vertical trail, they may descend to depths the place their voices change into perceptible to the abyss round sundown. In different phrases, whilst deep-sea creatures would possibly now not see the sundown, they may be able to pay attention it.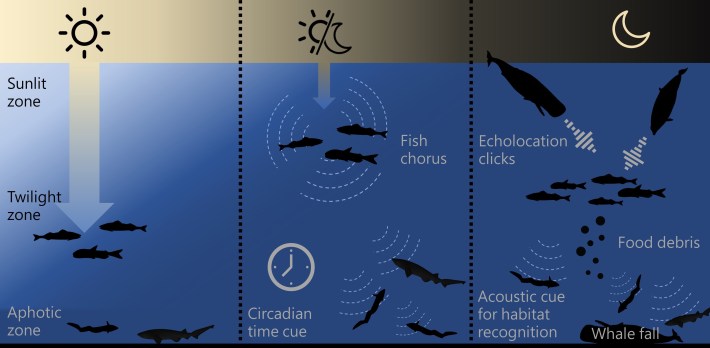 A diagram explaining how sound travels within the deep sea. | Tzu-Hao LinAs creatures of the solar, we stay time with circadian rhythms—our interior clocks that oscillate in 24-hour cycles according to mild and darkness. Scientists lengthy assumed the deep sea, a realm got rid of from the cycles of daylight and darkness that dictate a lot of existence on Earth, had no such rhythms. However because the era of deep-sea exploration has stepped forward, permitting scientists to document abyssal environments for longer classes of time, they’ve found out deep-sea day-to-day rhythms that could be defined by means of organic clocks. As an example, within the shimmering waters of hydrothermal vents extra then 5,500 ft deep, Bathymodiolus thermophilus mussels obey 24-hour rhythms. Hans van Haren, an experimental physicist and bodily oceanographer on the Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Analysis who used to be now not concerned with the analysis, has noticed deep-sea plankton attractive in day-to-day vertical migration at depths the place it’s not possible to locate shifts in daylight. The plankton cluster by means of day and scatter nearer to the skin at evening, and those actions have been in truth initiated by means of the deepest-dwelling plankton teams. So if daylight used to be now not a cue, most likely the cause resided someplace within the plankton. “Our primary speculation used to be keep an eye on by means of strong organic clocks, even if we thought to be the potential of acoustic noise,” van Haren stated, including that the soundscapes published within the new paper nonetheless don’t provide an explanation for how the private plankton teams lead those migrations.However our interior clocks don’t seem to be totally organic. They’re additionally synchronized by means of environmental cues referred to as, charmingly, zeitgebers—derived from the German phrase for time givers. The brand new paper suggests the sound of migrating species from above is usually a zeitgeber that permits many deep-sea species, without or with a organic clock, to inform time. The id of those migrating species, then again, stays a thriller, as Lin and Kawagucci may just now not establish anyone species inside the night time choruses. However the appropriate implications of those sounds for different species stays an open query. “It kind of feels extraordinary that species would betray themselves to their predators by means of making noise,” van Haren stated.Despite the fact that there’s a paucity of analysis in truth checking out the listening to and noise-making features of deep-sea fish, the anatomy of many species turns out attuned to listening to, with oversized ears or interior ear constructions with particular variations. “We all know so little (too little) about deep-sea creatures, however given the loss of mild, it’s believable that many of those species use sound to sense their setting, navigate and be in contact,” stated Erbe, who used to be now not concerned with the analysis. Given the day-to-day patterns of sounds wafting down from fish, marine mammals, and different animals nearer to the skin, “it could be no marvel if deep-sea, benthic creatures spoke back to that, or developed to make use of those sounds from greater up within the water column,” she stated.
A diagram explaining how sound travels within the deep sea. | Tzu-Hao LinAs creatures of the solar, we stay time with circadian rhythms—our interior clocks that oscillate in 24-hour cycles according to mild and darkness. Scientists lengthy assumed the deep sea, a realm got rid of from the cycles of daylight and darkness that dictate a lot of existence on Earth, had no such rhythms. However because the era of deep-sea exploration has stepped forward, permitting scientists to document abyssal environments for longer classes of time, they’ve found out deep-sea day-to-day rhythms that could be defined by means of organic clocks. As an example, within the shimmering waters of hydrothermal vents extra then 5,500 ft deep, Bathymodiolus thermophilus mussels obey 24-hour rhythms. Hans van Haren, an experimental physicist and bodily oceanographer on the Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Analysis who used to be now not concerned with the analysis, has noticed deep-sea plankton attractive in day-to-day vertical migration at depths the place it’s not possible to locate shifts in daylight. The plankton cluster by means of day and scatter nearer to the skin at evening, and those actions have been in truth initiated by means of the deepest-dwelling plankton teams. So if daylight used to be now not a cue, most likely the cause resided someplace within the plankton. “Our primary speculation used to be keep an eye on by means of strong organic clocks, even if we thought to be the potential of acoustic noise,” van Haren stated, including that the soundscapes published within the new paper nonetheless don’t provide an explanation for how the private plankton teams lead those migrations.However our interior clocks don’t seem to be totally organic. They’re additionally synchronized by means of environmental cues referred to as, charmingly, zeitgebers—derived from the German phrase for time givers. The brand new paper suggests the sound of migrating species from above is usually a zeitgeber that permits many deep-sea species, without or with a organic clock, to inform time. The id of those migrating species, then again, stays a thriller, as Lin and Kawagucci may just now not establish anyone species inside the night time choruses. However the appropriate implications of those sounds for different species stays an open query. “It kind of feels extraordinary that species would betray themselves to their predators by means of making noise,” van Haren stated.Despite the fact that there’s a paucity of analysis in truth checking out the listening to and noise-making features of deep-sea fish, the anatomy of many species turns out attuned to listening to, with oversized ears or interior ear constructions with particular variations. “We all know so little (too little) about deep-sea creatures, however given the loss of mild, it’s believable that many of those species use sound to sense their setting, navigate and be in contact,” stated Erbe, who used to be now not concerned with the analysis. Given the day-to-day patterns of sounds wafting down from fish, marine mammals, and different animals nearer to the skin, “it could be no marvel if deep-sea, benthic creatures spoke back to that, or developed to make use of those sounds from greater up within the water column,” she stated.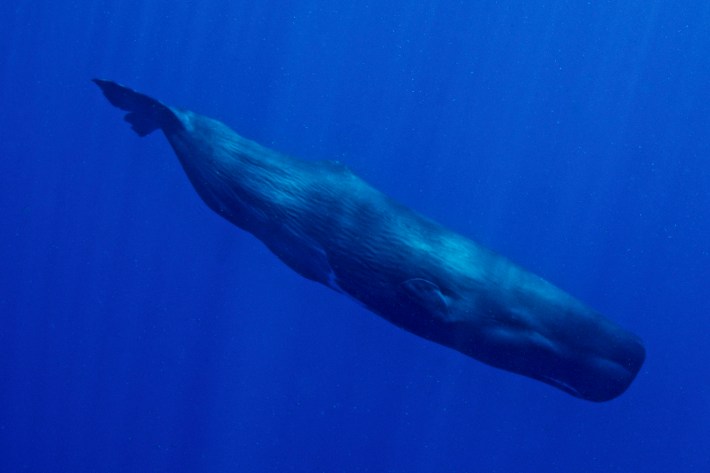 Sperm whales are deep-diving marine mammals whose vocalizations succeed in nice depths. | Arturo de Frias by means of Getty ImagesLin and Kawagucci’s recording additionally picked up occasional whistles and echolocating clicks from passing marine mammals, which they advised may just imply the realm is also a foraging floor for sperm whales and beaked whales. Erbe identified that sure species of fish and mammals produce feeding calls as they practice prey, that could be migrating vertically, so a whale’s tune or dolphin’s whistle will show off those day-to-day patterns, she stated. Given the quick velocity of sound within the ocean, those calls will go back and forth temporarily to the depths “the place they may induce rhythmic patterns with the similar 24-hour duration,” Erbe stated.Lin recognizes the brand new knowledge is relatively restricted, sampled with a unmarried hydrophone at sparse durations within the day. He’d like to go back to take higher-quality recordings. Erbe advised the use of era that would point out the supply of the sound, because the presence of sound at nice depths does now not essentially point out the sounds also are coming from nice depths. “As soon as we will find the supply, we would possibly have a a lot better thought which animal or species makes the sounds we pay attention at intensity, and in the end the serve as of the ones sounds,” she stated.The abyssal plains by means of Minamitorishima prickle with manganese nodules, which include uncommon minerals coveted by means of imminent plans for deep-sea mining. Like some other roughly mining, deep-sea mining will likely be a loud trade, conjuring sounds from the operations in addition to surrounding ships. This air pollution would crush the native soundscape, drowning out any far-off twilight choirs, dolphin clicks, and whale songs. For deep-sea creatures that may sense those sounds, this could be like blotting out the solar. However extra analysis is had to perceive the function of sound within the deep-sea—and the way consequential its muffling could be.”Once we speak about deep sea mining, we in point of fact want to watch out about how this sort of noise affects the deep-sea ecosystems,” Lin stated. “We all know nonetheless little or no.”
Sperm whales are deep-diving marine mammals whose vocalizations succeed in nice depths. | Arturo de Frias by means of Getty ImagesLin and Kawagucci’s recording additionally picked up occasional whistles and echolocating clicks from passing marine mammals, which they advised may just imply the realm is also a foraging floor for sperm whales and beaked whales. Erbe identified that sure species of fish and mammals produce feeding calls as they practice prey, that could be migrating vertically, so a whale’s tune or dolphin’s whistle will show off those day-to-day patterns, she stated. Given the quick velocity of sound within the ocean, those calls will go back and forth temporarily to the depths “the place they may induce rhythmic patterns with the similar 24-hour duration,” Erbe stated.Lin recognizes the brand new knowledge is relatively restricted, sampled with a unmarried hydrophone at sparse durations within the day. He’d like to go back to take higher-quality recordings. Erbe advised the use of era that would point out the supply of the sound, because the presence of sound at nice depths does now not essentially point out the sounds also are coming from nice depths. “As soon as we will find the supply, we would possibly have a a lot better thought which animal or species makes the sounds we pay attention at intensity, and in the end the serve as of the ones sounds,” she stated.The abyssal plains by means of Minamitorishima prickle with manganese nodules, which include uncommon minerals coveted by means of imminent plans for deep-sea mining. Like some other roughly mining, deep-sea mining will likely be a loud trade, conjuring sounds from the operations in addition to surrounding ships. This air pollution would crush the native soundscape, drowning out any far-off twilight choirs, dolphin clicks, and whale songs. For deep-sea creatures that may sense those sounds, this could be like blotting out the solar. However extra analysis is had to perceive the function of sound within the deep-sea—and the way consequential its muffling could be.”Once we speak about deep sea mining, we in point of fact want to watch out about how this sort of noise affects the deep-sea ecosystems,” Lin stated. “We all know nonetheless little or no.”
The Twilight Refrain That Can Be Heard 18,000 Toes Below The Sea | Defector