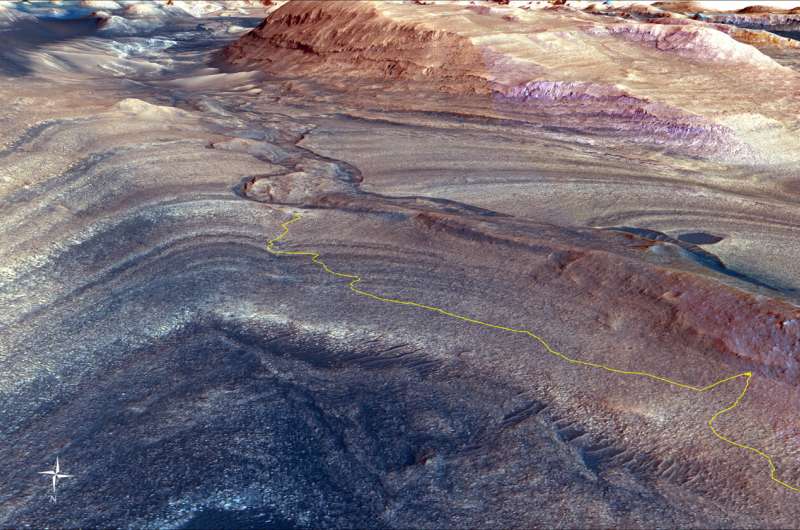
The steep trail NASA’s Interest Mars rover took to achieve Gediz Vallis channel is indicated in yellow on this visualization made with orbital knowledge. At decrease proper is the purpose the place the rover veered off to get an up-close take a look at a ridge shaped way back via particles flows from upper up on Mount Sharp. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/UC Berkeley
NASA’s Interest rover has begun exploring a brand new area of Mars, one that might disclose extra about when liquid water disappeared as soon as and for all from the Crimson Planet’s floor. Billions of years in the past, Mars used to be a lot wetter and most certainly hotter than it’s nowadays. Interest is getting a brand new glance into that extra Earth-like previous because it drives alongside and ultimately crosses the Gediz Vallis channel, a winding, snake-like characteristic that—from area, a minimum of—seems to had been carved via an historical river.
That risk has scientists intrigued. The rover workforce is on the lookout for proof that will ascertain how the channel used to be carved into the underlying bedrock. The formation’s facets are steep sufficient that the workforce does not suppose the channel used to be made via wind. Alternatively, particles flows (fast, rainy landslides) or a river wearing rocks and sediment can have had sufficient power to chisel into the bedrock. After the channel shaped, it used to be full of boulders and different particles. Scientists also are keen to be told whether or not this subject matter used to be transported via particles flows or dry avalanches.
Since 2014, Interest has been ascending the foothills of Mount Sharp, which stands 3 miles (5 kilometers) above the ground of Gale Crater. The layers on this decrease a part of the mountain shaped over thousands and thousands of years amid a converting Martian local weather, offering scientists with a strategy to find out about how the presence of each water and the chemical substances required for lifestyles modified through the years.
As an example, a decrease a part of the ones foothills integrated a layer wealthy in clay minerals the place a large number of water as soon as interacted with rock. Now the rover is exploring a layer enriched with sulfates—salty minerals that frequently shape as water evaporates.
Pan round inside of this 360-degree video to peer Gediz Vallis channel from the perspective of NASA’s Interest Mars rover. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Revising mount sharp’s timeline
It’s going to take months to completely discover the channel, and what scientists be informed may just revise the timeline for the mountain’s formation.
As soon as the sedimentary layers of decrease Mount Sharp have been deposited via wind and water, erosion whittled them down to show the layers visual nowadays. Best after those long processes—in addition to intensely dry sessions all the way through which the outside of Mount Sharp used to be a sandy wasteland—may just the Gediz Vallis channel had been carved.
Scientists suppose the boulders and different particles that due to this fact stuffed the channel got here from prime up at the mountain, the place Interest won’t ever cross, giving the workforce a glimpse of what forms of subject matter could also be up there.
“If the channel or the particles pile have been shaped via liquid water, that is in reality attention-grabbing. It could imply that somewhat past due within the tale of Mount Sharp—after an extended dry length—water got here again, and in a large manner,” stated Interest’s undertaking scientist, Ashwin Vasavada of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California.

After arriving at Gediz Vallis channel, NASA’s Interest Mars rover captured this 360-degree landscape the use of one in all its black-and-white navigation cameras on Feb. 3. The formation has scientists intrigued on account of what it will inform them concerning the historical past of water at the Crimson Planet. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech
That clarification can be in keeping with one of the crucial sudden discoveries Interest has made whilst using up Mount Sharp: Water turns out to have come and long past in stages, reasonably than regularly disappearing because the planet grew drier. Those cycles may also be observed in proof of dust cracks; shallow, salty lakes; and, without delay underneath the channel, cataclysmic particles flows that piled as much as create the sprawling Gediz Vallis ridge.
Closing 12 months, Interest made a difficult ascent to review the ridge, which drapes around the slopes of Mount Sharp and turns out to develop out of the top of the channel, suggesting each are a part of one geologic machine.
Viewing the channel up shut
Interest documented the channel with a 360-degree black-and-white landscape from the rover’s left navigation digital camera. Taken on Feb. 3 (the 4,086th Martian day, or sol, of the challenge), the picture presentations the darkish sand that fills one aspect of the channel and a particles pile emerging simply in the back of the sand. In the other way is the steep slope that Interest climbed to achieve this house.
The rover takes all these panoramas with its navigation cameras on the finish of each and every pressure. Now the science workforce is depending at the navcams much more whilst engineers attempt to get to the bottom of a topic this is proscribing the usage of one imager belonging to the colour Mast Digital camera, or Mastcam.
Quotation:
Interest rover searches for brand new clues about Mars’ historical water (2024, March 30)
retrieved 31 March 2024
from
This file is topic to copyright. With the exception of any honest dealing for the aim of personal find out about or analysis, no
section could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is equipped for info functions most effective.