A number one gravitational wave observatory just lately detected ripples in spacetime that scientists say got here from the collision of a useless, superdense stellar remnant and an unknown object.Making TV Historical past with Celebrity Trek: DiscoveryThe stellar remnant is what’s referred to as a neutron megastar; it’s what’s left when an enormous megastar collapses, leaving just a dense core at the back of. Neutron stars are one of the most densest gadgets within the universe, with intense gravitational fields—however now not as intense as black holes, whose gravity is so sturdy that now not even mild can break out their match horizons. Those two cosmic juggernauts dance and conflict around the universe; the primary affirmation of an seen merger between a neutron megastar and a black hollow used to be made in 2021. Their interactions produce gravitational waves—actually, stretches and squeezes of spacetime—that are detected by means of observatories just like the LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA Collaboration, which is on the center of the newest analysis.LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA detected a gravitational wave sign in Would possibly 2023, simply days after the observatory resumed operations following some upgrades that decreased the quantity of noise within the detector, making improvements to its sensitivity to the delicate perturbations of spacetime.The original gravitational wave sign travelled 650 million light-years to get to the LIGO Livingston Observatory in Louisiana. Researchers made up our minds the sign got here from the merger of 2 gadgets. Probably the most gadgets used to be between 1.2 and a pair of instances the mass of our Solar, and the opposite used to be about 2.5 to 4.5 sun plenty. The sign is dubbed GW230529_181500, or GW230529 for brief.The smaller object, the astrophysicists concluded, is most certainly a neutron megastar. However the higher object is extra large than any recognized neutron megastar, indicating that it can be an itsy-bitsy black hollow. Their paper describing the sign and its most likely origins is these days hosted at the LIGO site.
Numerical simulation of the compact binary device GW230529: Subject and wavesThe unknown object occupies the plain mass hole that exists between the heaviest recognized neutron megastar and the lightest black hollow. Additional scrutiny of the collision will point out whether or not the unknown object is a low-mass black hollow, because the group suspects, or one thing else.The detection “unearths that there is also the next charge of an identical collisions between neutron stars and low-mass black holes than we in the past concept,” mentioned Jess McIver, an astronomer on the College of British Columbia and Deputy Spokesperson of the LIGO Clinical Collaboration, in a collaboration unencumber.The discharge famous that out of just about 200 measurements of compact object plenty, just one different merger concerned an object within the obvious mass hole, that one merging with a black hollow. (For gravitational wave connoisseurs, that sign used to be GW190814.) However the fresh remark used to be the primary between a mass-gap object and a neutron megastar. LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA’s fourth staring at run will restart on April 10 and can proceed with out deliberate breaks till February 2025, in which time the collaboration anticipates greater than 200 gravitational wave alerts can have been seen. 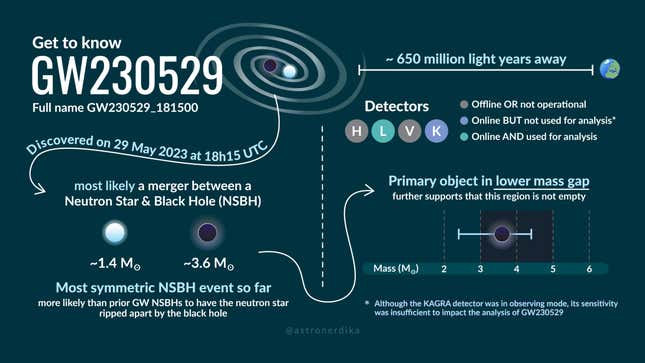 It’s been a productive couple of years for gravitational wave science, with extra pleasure at the horizon. Ultimate yr, a handful of pulsar timing consortia independently showed the primary indicators of a gravitational wave background—the consistent murmur of gravitational waves during the universe which they imagine comes from the dances of supermassive black hollow binaries.Previous this yr, ESA officially followed plans for LISA, a space-based gravitational wave observatory. LISA would consist of 3 spacecraft spinning via area in a triangular formation. LISA will pay attention for gravitational waves with none of the noise that happens on Earth, which will muddle the information accumulated by means of LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA.There are nonetheless 80 vital sign applicants that the group must sift via. So there are heady days forward for staring at the gravitational universe.Extra: Those Violent Collisions May just Be Generating Darkish Subject
It’s been a productive couple of years for gravitational wave science, with extra pleasure at the horizon. Ultimate yr, a handful of pulsar timing consortia independently showed the primary indicators of a gravitational wave background—the consistent murmur of gravitational waves during the universe which they imagine comes from the dances of supermassive black hollow binaries.Previous this yr, ESA officially followed plans for LISA, a space-based gravitational wave observatory. LISA would consist of 3 spacecraft spinning via area in a triangular formation. LISA will pay attention for gravitational waves with none of the noise that happens on Earth, which will muddle the information accumulated by means of LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA.There are nonetheless 80 vital sign applicants that the group must sift via. So there are heady days forward for staring at the gravitational universe.Extra: Those Violent Collisions May just Be Generating Darkish Subject
Ripples in Spacetime Divulge Thriller Object Colliding With a Celebrity's Corpse