Earth’s general recent water has plummeted to an alarming new low, and it can be a signal that local weather alternate is pushing the arena into a deadly segment of world drying, in line with a brand new learn about.Since 2015, our planet’s lakes, rivers and aquifers have misplaced 290 cubic miles (1,200 cubic km) of clean water, the similar of emptying Lake Erie two and a part instances.This drop coincided with a 2014 to 2016 length of El Niño warming. Scientists normally be expecting freshwater ranges to rebound after the local weather oscillation ends, however satellite tv for pc measurements, made as much as 2023, disclose that the freshwater ranges haven’t begun to get better — and might by no means come again.”We do not assume this can be a twist of fate, and it can be a harbinger of what is to return,” learn about lead writer Matthew Rodell, a hydrologist at NASA’s Goddard House Flight Middle, stated in a observation.The researchers printed their findings Nov. 4 within the magazine Surveys in Geophysics.Comparable: Will the United States run out of water?As local weather alternate reasons temperatures to upward thrust around the world, water evaporates extra readily from its surfaces, and the ambience positive aspects an ever expanding capability to soak up it. Because of this when downpours do happen, they’re extra torrential — dumping extra rain in sooner and extra robust storms which are much more likely to run off than to seep into drier and extra compact surfaces.Get the arena’s most enticing discoveries delivered directly on your inbox.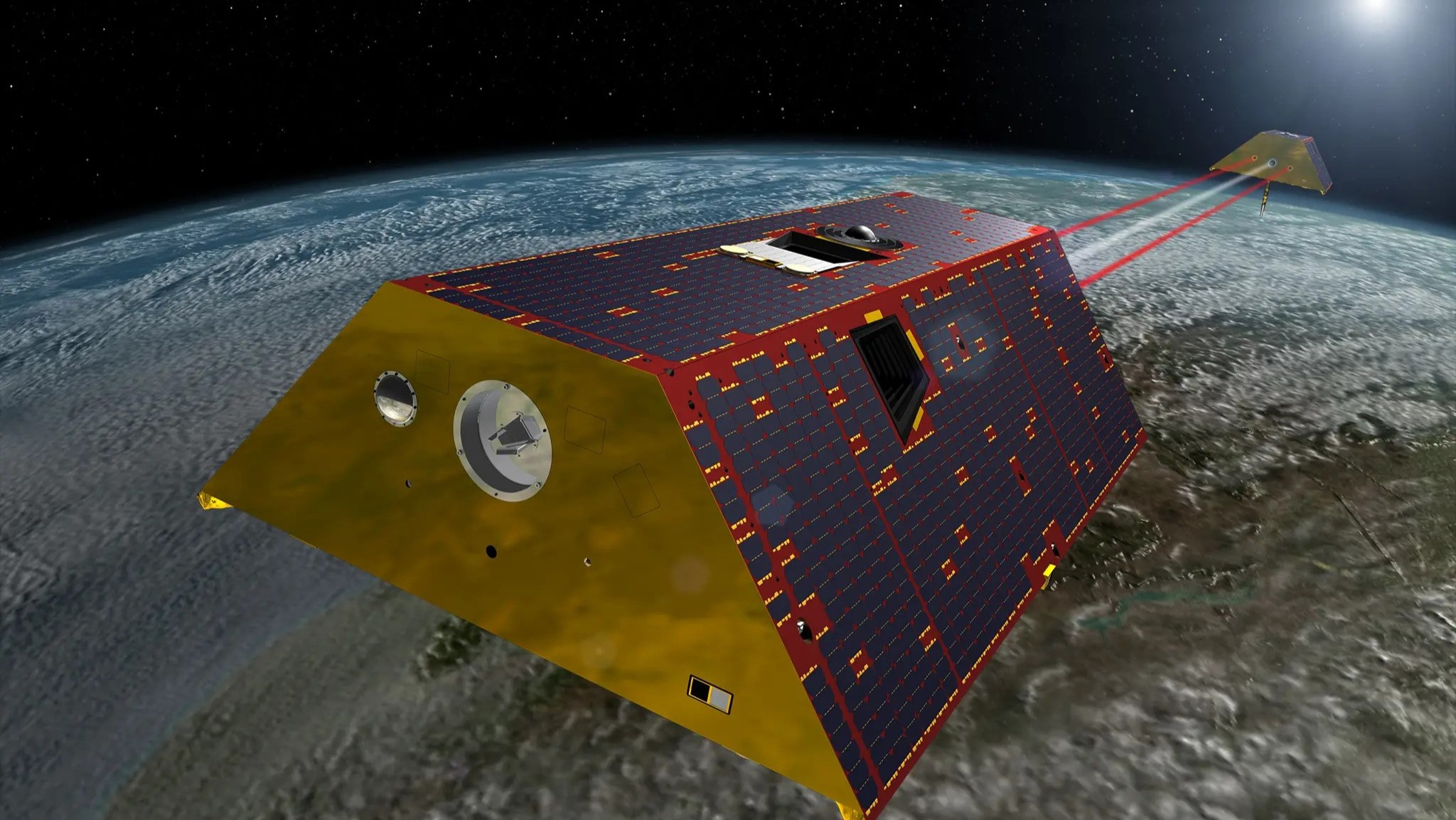 An artist’s representation of the 2 GRACE-FO satellites in area. The satellites paintings in pairs separated through 136 miles (220 kilometers) and will hit upon adjustments smaller than a micrometer in keeping with 2nd in relative pace. (Symbol credit score: NASA)This factor, along damaging land use and the mismanagement of water sources, signifies that just about 3 billion folks and over part of world meals manufacturing are going through “unparalleled rigidity” on their water methods, in line with one fresh learn about.To research the level of our planet’s drying, the researchers in the back of the brand new learn about grew to become to 2 pairs of satellites that orbit above the North Pole. The satellites measured water ranges through detecting the minute fluctuations that water’s mass produces to Earth’s gravitational box.By way of exactly measuring the adjustments to the tugs of Earth’s gravity from 2015 to 2023, the scientists discovered that the 290 cubic miles of water that was once misplaced from the arena’s floor all through the remaining El Niño by no means returned, and that 13 of the arena’s 30 maximum intense droughts observed through the satellites came about since January 2015.The result’s an ominous one. The satellites used within the learn about are set to supply six extra years of readings prior to they’re retired. Whether or not recent water will rebound to pre-2015 ranges all through that length, keep on the identical worth or proceed to say no stays unclear. However the researchers are a long way from hopeful.”There’s a lot debate and little consensus about how patterns of wetting and drying will manifest in a warming global,” they wrote within the learn about. “Therefore, it’s tough to guage whether or not the noticed patterns are in step with predictions and more likely to persist.”
An artist’s representation of the 2 GRACE-FO satellites in area. The satellites paintings in pairs separated through 136 miles (220 kilometers) and will hit upon adjustments smaller than a micrometer in keeping with 2nd in relative pace. (Symbol credit score: NASA)This factor, along damaging land use and the mismanagement of water sources, signifies that just about 3 billion folks and over part of world meals manufacturing are going through “unparalleled rigidity” on their water methods, in line with one fresh learn about.To research the level of our planet’s drying, the researchers in the back of the brand new learn about grew to become to 2 pairs of satellites that orbit above the North Pole. The satellites measured water ranges through detecting the minute fluctuations that water’s mass produces to Earth’s gravitational box.By way of exactly measuring the adjustments to the tugs of Earth’s gravity from 2015 to 2023, the scientists discovered that the 290 cubic miles of water that was once misplaced from the arena’s floor all through the remaining El Niño by no means returned, and that 13 of the arena’s 30 maximum intense droughts observed through the satellites came about since January 2015.The result’s an ominous one. The satellites used within the learn about are set to supply six extra years of readings prior to they’re retired. Whether or not recent water will rebound to pre-2015 ranges all through that length, keep on the identical worth or proceed to say no stays unclear. However the researchers are a long way from hopeful.”There’s a lot debate and little consensus about how patterns of wetting and drying will manifest in a warming global,” they wrote within the learn about. “Therefore, it’s tough to guage whether or not the noticed patterns are in step with predictions and more likely to persist.”











