One of the most largest clinical mysteries is the place existence on Earth began.Analysis has continuously centered at the function of deep-sea hydrothermal vents – the ones towering buildings at the ocean ground continuously pumping out a melange of natural and inorganic subject matter.
Inside those plumes are minerals known as iron sulfides, which scientists imagine may have helped cause early chemical reactions that created existence.
Those similar minerals also are present in scorching springs these days, such because the Grand Prismatic Spring in Yellowstone Nationwide Park in the US. Sizzling springs are our bodies of groundwater heated by means of volcanic process underneath Earth’s floor.
Our new analysis provides to a small however rising frame of proof that historical variations of those scorching springs may have performed a pivotal function within the emergence of existence on Earth. This is helping bridge the distance between competing hypotheses referring to the place existence may have emerged.
Geochemistry to biologyCarbon fixation is the method wherein dwelling organisms convert carbon dioxide, within the air and dissolved in water, into natural molecules.
Many existence paperwork, together with vegetation, micro organism and microorganisms referred to as archaea, have other pathways for attaining this. Photosynthesis is one instance.
Every of those pathways incorporates a cascade of enzymes and proteins, a few of which include cores product of iron and sulfur.
We will be able to in finding proteins with those iron-sulfur clusters in all types of existence. In truth, researchers suggest they date again to the Ultimate Common Not unusual Ancestor – an historical ancestral cellular from which scientists suggest existence as we are aware of it developed and different.
Iron sulfides are minerals that shape when dissolved iron reacts with hydrogen sulfide – the volcanic gasoline that makes scorching springs scent like rotten eggs.
For those who glance carefully on the construction of those iron sulfides, you’re going to in finding that a few of them glance extremely very similar to iron-sulfur clusters.
This connection between iron sulfides and carbon fixation has led some researchers to suggest that those minerals performed a an important function within the transition from early Earth geochemistry to biology.
Our newly revealed analysis expands in this wisdom by means of investigating the chemical process of iron sulfides in historical land-based scorching springs that have an identical geochemistry to deep-sea vents.
frameborder=”0″ allowfullscreen=”allowfullscreen”>
Customized-built chamberWe custom-built a small chamber that will let us simulate scorching spring environments on early Earth.
Then we unfold synthesised iron sulfide samples in the course of the chamber. Some had been natural. Others had been dosed with different metals often present in scorching springs. A lamp above those samples simulated daylight at the early Earth’s floor. Other lamps had been used to imitate lights with other quantities of ultraviolet radiation.
Carbon dioxide and hydrogen gasoline had been continuously pumped in the course of the chamber. Those gases were proven to be essential for carbon fixation in deep-sea vent experiments.
We discovered that all the iron sulfide samples synthesised had been in a position to generating methanol, a made of carbon fixation, to various extents. Those effects confirmed that iron sulfides can facilitate carbon fixation now not simplest in deep-sea hydrothermal vents however land-based scorching springs too.
Methanol manufacturing additionally larger with visual mild irradiation and at upper temperatures.
Experiments with various temperatures, lights and water-vapour content material demonstrated that iron sulfides most probably facilitated carbon fixation in land-based scorching springs on early Earth.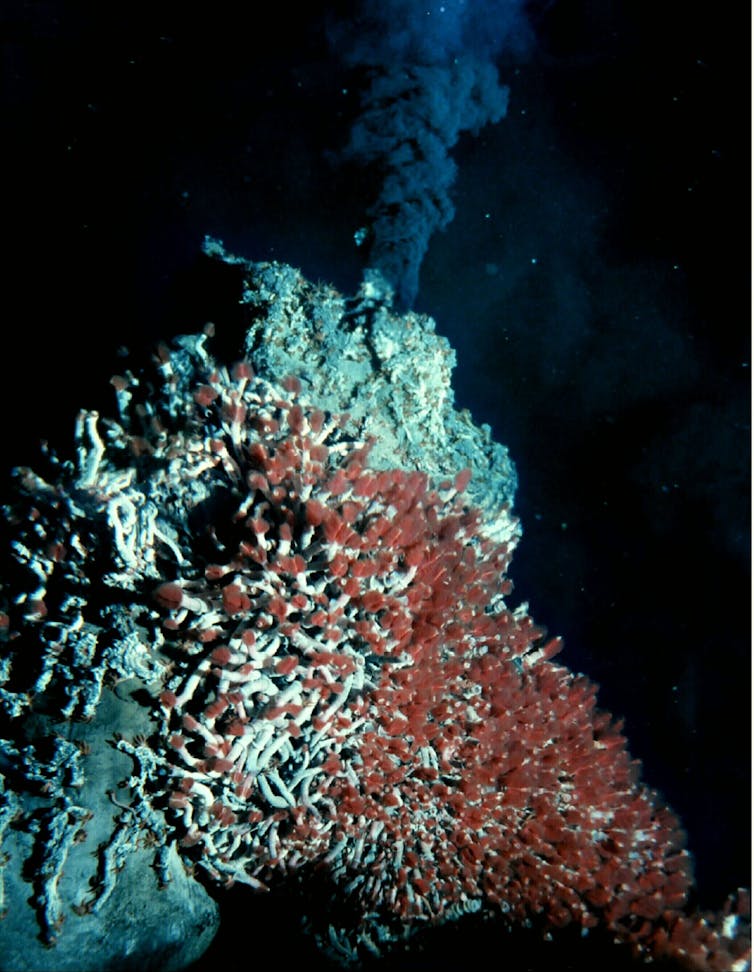 Sizzling springs have an identical chemistry as deep-sea hyrdothermal vents, akin to this one at the Juan de Fuca Ridge off the coast of North The usa. (College of Washington; NOAA/OAR/OER, CC BY-NC-ND)An historical pathwayAdditional experiments and theoretical calculations published that the manufacturing of methanol came about thru a mechanism known as a opposite water-gas shift.
Sizzling springs have an identical chemistry as deep-sea hyrdothermal vents, akin to this one at the Juan de Fuca Ridge off the coast of North The usa. (College of Washington; NOAA/OAR/OER, CC BY-NC-ND)An historical pathwayAdditional experiments and theoretical calculations published that the manufacturing of methanol came about thru a mechanism known as a opposite water-gas shift.
We see a an identical response within the pathway some micro organism and archaea use to show carbon dioxide into meals. This pathway is known as the “acetyl-CoA” or “Picket-Ljungdahl” pathway. It’s proposed to be the earliest type of carbon fixation that emerged in early existence.
This similarity between the 2 processes is attention-grabbing for the reason that former occurs on dry land, on the fringe of scorching springs, whilst the latter takes position within the rainy setting inside of cells.
Our learn about demonstrates methanol manufacturing in quite a lot of stipulations that may have been present in early Earth’s scorching springs.
Our findings make bigger the variety of stipulations the place iron sulfides can facilitate carbon fixation. They display it could actually occur each within the deep sea and on land – albeit by way of other mechanisms.As such, we imagine those effects strengthen the present clinical consensus suggesting that iron-sulfur clusters and the acetyl-CoA pathway are historical and most probably performed a very powerful function within the emergence of existence – without reference to whether or not it took place on land or on the backside of the ocean.![]()
Quoc Phuong Tran, PhD Candidate in Prebiotic Chemistry, UNSW SydneyThis article is republished from The Dialog underneath a Inventive Commons license. Learn the unique article.
A Hidden Procedure in Sizzling Springs Would possibly Have Been Necessary For Lifestyles on Earth