This symbol from ESA’s Mars Categorical displays Aganippe Fossa, an interesting groove on the foot of Mars’s colossal Arsia Mons volcano. Credit score: ESA/DLR/FU BerlinA attention-grabbing function takes middle degree on this new symbol from ESA’s Mars Categorical: a gloomy, asymmetric scar chopping thru marbled flooring on the foot of a big volcano.This scar, referred to as Aganippe Fossa, is a patchy, more or less 600-km-long function referred to as a ‘graben’: a ditch-like groove with steep partitions on both sides.Aganippe Fossa cuts around the decrease flank of one in all Mars’s greatest volcanoes, Arsia Mons. Mars Categorical frequently observes Arsia Mons and its within reach partners within the area of Tharsis, the place a number of of Mars’s behemoth volcanoes are discovered. This comprises Olympus Mons, the tallest volcano within the Sun Gadget (visual within the context map related to this new symbol, as is Arsia Mons).Arsia Mons itself measures 435 km in diameter and rises greater than 9 km above the encompassing plains. For context, the easiest dormant volcano on Earth, Ojos del Salado at the Argentina-Chile border, tops out at underneath 7 km.
This symbol from ESA’s Mars Categorical displays Aganippe Fossa, an interesting groove on the foot of Mars’s colossal Arsia Mons volcano. Credit score: ESA/DLR/FU BerlinA attention-grabbing function takes middle degree on this new symbol from ESA’s Mars Categorical: a gloomy, asymmetric scar chopping thru marbled flooring on the foot of a big volcano.This scar, referred to as Aganippe Fossa, is a patchy, more or less 600-km-long function referred to as a ‘graben’: a ditch-like groove with steep partitions on both sides.Aganippe Fossa cuts around the decrease flank of one in all Mars’s greatest volcanoes, Arsia Mons. Mars Categorical frequently observes Arsia Mons and its within reach partners within the area of Tharsis, the place a number of of Mars’s behemoth volcanoes are discovered. This comprises Olympus Mons, the tallest volcano within the Sun Gadget (visual within the context map related to this new symbol, as is Arsia Mons).Arsia Mons itself measures 435 km in diameter and rises greater than 9 km above the encompassing plains. For context, the easiest dormant volcano on Earth, Ojos del Salado at the Argentina-Chile border, tops out at underneath 7 km.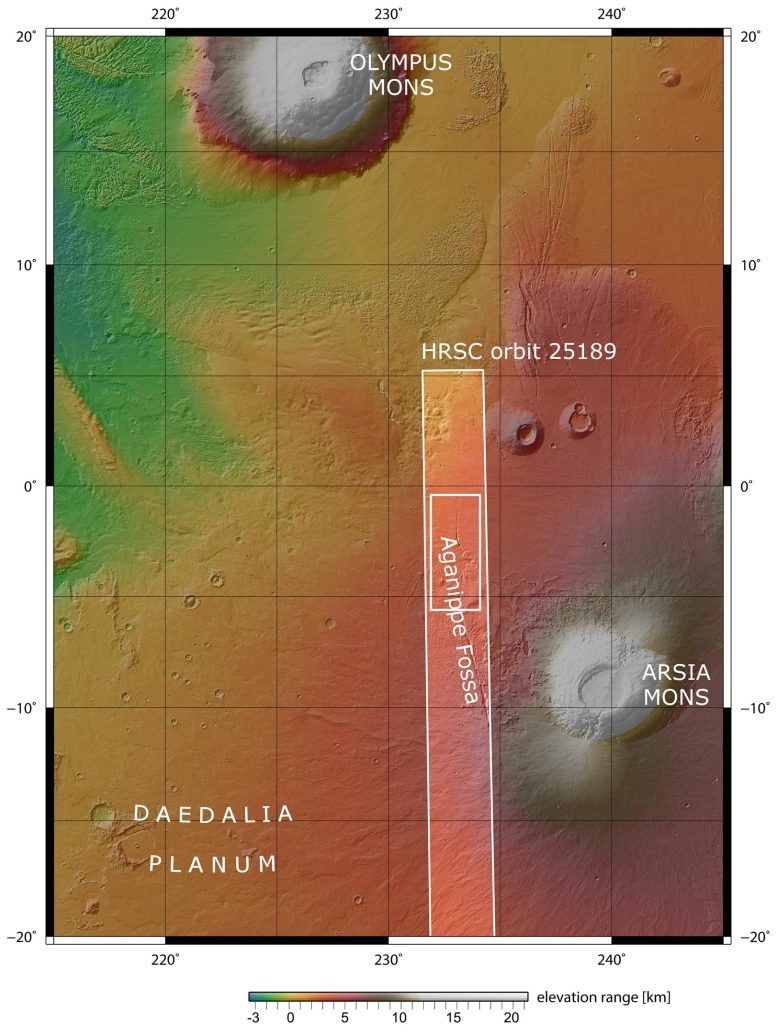 This symbol displays Aganippe Fossa, a snaking groove discovered on the foot of Mars’s large Arsia Mons volcano, in a much wider context. The realm defined by means of the bigger white field signifies the realm imaged by means of the Prime Answer Stereo Digital camera aboard ESA’s Mars Categorical orbiter on December 13, 2023, all through orbit 25189, whilst the smaller white field displays the a part of the outside featured in those new pictures. Credit score: NASA/MGS/MOLA Science TeamSeeping LavaWe’re nonetheless undecided of the way and when Aganippe Fossa got here to be, however it kind of feels most probably that it used to be shaped as magma emerging beneath the colossal mass of the Tharsis volcanoes led to Mars’s crust to stretch and crack.On this view, Mars Categorical’s Prime Answer Stereo Digital camera (HRSC) captures two other varieties of terrain: so-called hummocky terrain, which incorporates many irregularly fashioned mounds and valleys all clustered in combination, and lobate terrain, which is shaped of gently sloping cliffs and rocky particles.
This symbol displays Aganippe Fossa, a snaking groove discovered on the foot of Mars’s large Arsia Mons volcano, in a much wider context. The realm defined by means of the bigger white field signifies the realm imaged by means of the Prime Answer Stereo Digital camera aboard ESA’s Mars Categorical orbiter on December 13, 2023, all through orbit 25189, whilst the smaller white field displays the a part of the outside featured in those new pictures. Credit score: NASA/MGS/MOLA Science TeamSeeping LavaWe’re nonetheless undecided of the way and when Aganippe Fossa got here to be, however it kind of feels most probably that it used to be shaped as magma emerging beneath the colossal mass of the Tharsis volcanoes led to Mars’s crust to stretch and crack.On this view, Mars Categorical’s Prime Answer Stereo Digital camera (HRSC) captures two other varieties of terrain: so-called hummocky terrain, which incorporates many irregularly fashioned mounds and valleys all clustered in combination, and lobate terrain, which is shaped of gently sloping cliffs and rocky particles.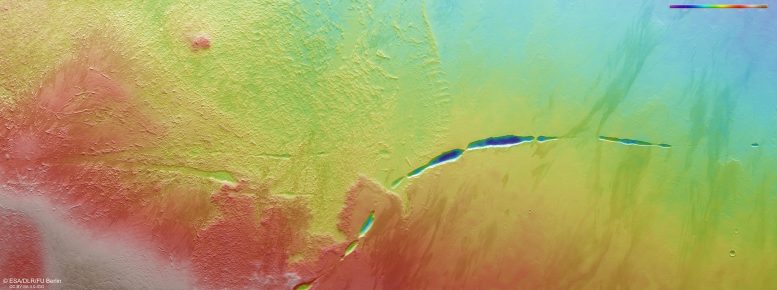 This colour-coded topographic symbol displays Aganippe Fossa, a snaking groove discovered on the foot of Mars’s large Arsia Mons volcano. It used to be constructed from knowledge gathered by means of ESA’s Mars Categorical on December 13, 2023, and is in accordance with a virtual terrain style of the area, from which the topography of the panorama can also be derived. Decrease altitude portions of the outside are proven in blues and purples, whilst upper altitude areas display up in whites and reds, as indicated at the scale to the highest proper. Credit score: ESA/DLR/FU BerlinThese terrains are feature of Arsia Mons’s ring-shaped ‘aureole’, a 100,000-square-kilometer disc across the base of the volcano, in all probability related to historical glaciers. Intriguingly, this aureole has handiest constructed up at the northwestern flank of the volcano, most probably because of prevailing winds from the other way controlling the place ice settled over the years.Windblown mud and sand have additionally fashioned this patch of Mars, developing attention-grabbing zebra-like patterns to the correct of the body as darker subject material is deposited on lighter flooring (or vice versa!). The outside right here additionally displays proof of lava flows, courting from when the volcano used to be energetic.
This colour-coded topographic symbol displays Aganippe Fossa, a snaking groove discovered on the foot of Mars’s large Arsia Mons volcano. It used to be constructed from knowledge gathered by means of ESA’s Mars Categorical on December 13, 2023, and is in accordance with a virtual terrain style of the area, from which the topography of the panorama can also be derived. Decrease altitude portions of the outside are proven in blues and purples, whilst upper altitude areas display up in whites and reds, as indicated at the scale to the highest proper. Credit score: ESA/DLR/FU BerlinThese terrains are feature of Arsia Mons’s ring-shaped ‘aureole’, a 100,000-square-kilometer disc across the base of the volcano, in all probability related to historical glaciers. Intriguingly, this aureole has handiest constructed up at the northwestern flank of the volcano, most probably because of prevailing winds from the other way controlling the place ice settled over the years.Windblown mud and sand have additionally fashioned this patch of Mars, developing attention-grabbing zebra-like patterns to the correct of the body as darker subject material is deposited on lighter flooring (or vice versa!). The outside right here additionally displays proof of lava flows, courting from when the volcano used to be energetic. This stereoscopic symbol displays Aganippe Fossa, a snaking groove discovered on the foot of Mars’s large Arsia Mons volcano. The anaglyph gives a 3-dimensional view when seen the usage of red-green or red-blue glasses. Credit score: ESA/DLR/FU BerlinExploring MarsMars Categorical has been orbiting the Pink Planet since 2003. It’s imaging Mars’s floor, mapping its minerals, figuring out the composition and circulate of its tenuous environment, probing underneath its crust, and exploring how more than a few phenomena have interaction within the Martian atmosphere.The spacecraft’s HRSC, answerable for those pictures, has published a lot about Mars’s numerous floor previously two decades. Its pictures display the whole lot from wind-sculpted ridges and grooves to sinkholes at the flanks of colossal volcanoes to have an effect on craters, tectonic faults, river channels, and historical lava swimming pools. The challenge has been immensely productive over its lifetime, making a some distance fuller and extra correct working out of our planetary neighbor than ever prior to.The Prime Answer Stereo Digital camera (HRSC) at the Mars Categorical spacecraft is a complicated imaging device designed to check Mars in excessive element. Introduced by means of the Eu Area Company (ESA) in 2003, the HRSC captures high-resolution, 3-dimensional pictures of the Martian floor, enabling scientists to inspect the planet’s topography and morphology in unparalleled element. This digital camera device makes use of stereo imaging ways to supply colour pictures in conjunction with topographic maps, serving to researchers analyze the geology, composition, and bodily processes of Mars. The HRSC has been instrumental in offering insights into the planet’s previous water process, volcanic process, and different dynamic processes.
This stereoscopic symbol displays Aganippe Fossa, a snaking groove discovered on the foot of Mars’s large Arsia Mons volcano. The anaglyph gives a 3-dimensional view when seen the usage of red-green or red-blue glasses. Credit score: ESA/DLR/FU BerlinExploring MarsMars Categorical has been orbiting the Pink Planet since 2003. It’s imaging Mars’s floor, mapping its minerals, figuring out the composition and circulate of its tenuous environment, probing underneath its crust, and exploring how more than a few phenomena have interaction within the Martian atmosphere.The spacecraft’s HRSC, answerable for those pictures, has published a lot about Mars’s numerous floor previously two decades. Its pictures display the whole lot from wind-sculpted ridges and grooves to sinkholes at the flanks of colossal volcanoes to have an effect on craters, tectonic faults, river channels, and historical lava swimming pools. The challenge has been immensely productive over its lifetime, making a some distance fuller and extra correct working out of our planetary neighbor than ever prior to.The Prime Answer Stereo Digital camera (HRSC) at the Mars Categorical spacecraft is a complicated imaging device designed to check Mars in excessive element. Introduced by means of the Eu Area Company (ESA) in 2003, the HRSC captures high-resolution, 3-dimensional pictures of the Martian floor, enabling scientists to inspect the planet’s topography and morphology in unparalleled element. This digital camera device makes use of stereo imaging ways to supply colour pictures in conjunction with topographic maps, serving to researchers analyze the geology, composition, and bodily processes of Mars. The HRSC has been instrumental in offering insights into the planet’s previous water process, volcanic process, and different dynamic processes.
A Snaking Scar Throughout Mars: The Thriller of Aganippe Fossa