One thing is awry in our increasing cosmos.Just about a century in the past, the astronomer Edwin Hubble found out the balloon-like inflation of the universe and the accelerating rush of all galaxies clear of each and every different. Following that growth backward in time ended in our present highest working out of ways the whole lot started — the Large Bang. However during the last decade, an alarming hollow has been rising on this image: Relying on the place astronomers glance, the speed of the universe’s growth (a worth referred to as the Hubble consistent) varies considerably.Similar: Einstein should be flawed: How basic relativity fails to provide an explanation for the universeNow, on the second one anniversary of its release, the James Webb House Telescope (JWST) has cemented the discrepancy with stunningly exact new observations that threaten to upend the usual style of cosmology. The brand new physics had to alter and even change the 40-year-old idea is now an issue of fierce debate.”It is a confrontation that has to make us wonder whether we truly do perceive the composition of the universe and the physics of the universe,” Adam Riess, a professor of astronomy at Johns Hopkins College who led the group that made the brand new JWST measurements, advised Reside Science. Reiss, Saul Perlmutter and Brian P. Schmidt gained the 2011 Nobel Prize in physics for his or her 1998 discovery of darkish power, the mysterious pressure at the back of the universe’s accelerating growth. Beginning with a bangOn this a lot cosmologists can agree: It began with a bang.Then right away, the younger cosmos was once shaped: an increasing, roiling plasma broth of topic and antimatter debris that popped into lifestyles, simplest to annihilate each and every different upon touch. Left to their very own units, the topic and antimatter inside of this plasma mire will have to have fed on each and every different fully. However scientists imagine that some unknown imbalance enabled extra topic than antimatter to be produced, saving the universe from rapid self-destruction.Gravity compressed the plasma wallet, squeezing and heating the topic in order that sound waves touring simply over part the velocity of sunshine, referred to as baryon acoustic oscillations, rippled throughout their floor.In the meantime, the top power density of the early universe’s crowded contents stretched space-time, pulling a small fraction of this topic safely from the fray. Because the universe inflated like a balloon, the usual tale is going, extraordinary topic (which interacts with mild) congealed round clumps of invisible darkish topic to create the primary galaxies, attached in combination through an unlimited cosmic internet.Similar: James Webb telescope detects the earliest strand within the ‘cosmic internet’ ever seenInitially because the universe’s contents unfold out, its power density and due to this fact its growth fee lowered. However then, kind of 5 billion years in the past, galaxies started to recede all over again at an ever-faster fee. The purpose, consistent with this image, was once some other invisible and mysterious entity referred to as darkish power.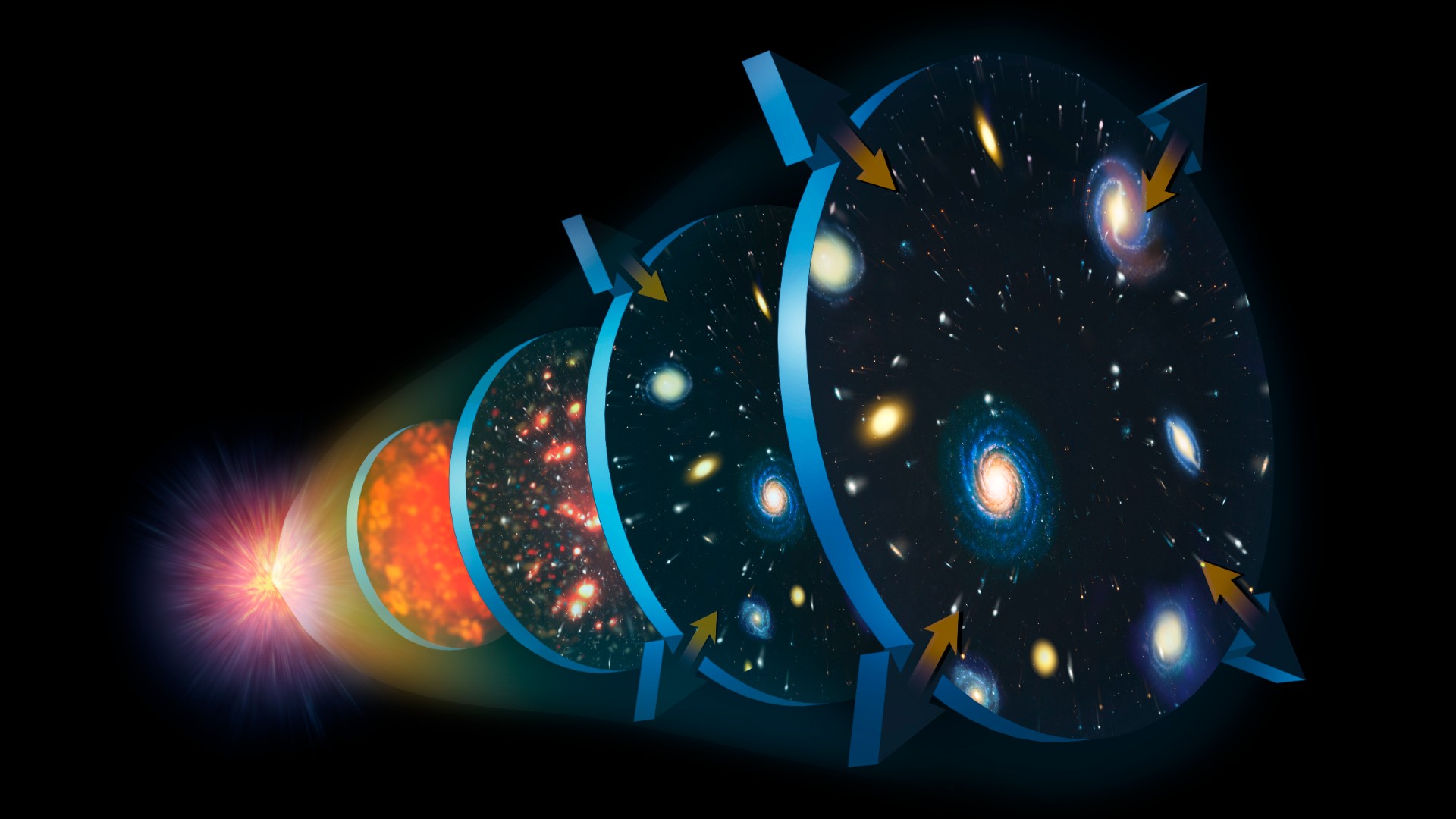 An indication of the growth of the Universe. The Large Bang is right away adopted through a speedy expansionary length referred to as inflation. Then, as protons and electrons mix to shape atoms, mild can shuttle freely; leaving the cosmic microwave background imprinted upon the sky. The universe’s growth slowed round 10 billion years in the past, and it all started to fill with galaxies, stars and big black holes. Round 5 billion years in the past, darkish power brought about this cosmic growth to unexpectedly boost up. To this present day, it presentations no indicators of forestalling. (Symbol credit score: Mark Garlick/Science Picture Library by way of Getty Photographs)The most simple and hottest reason behind darkish power is that this can be a cosmological consistent — an inflationary power that’s the similar all over and at each second; woven into the stretching cloth of space-time. Einstein named it lambda in his idea of basic relativity. As our cosmos grew, its total topic density dropped whilst the darkish power density remained the similar, steadily making the latter the most important contributor to its total growth.Added in combination the power densities of extraordinary topic, darkish topic, darkish power and effort from mild set the higher pace prohibit of the universe’s growth. They’re additionally key components within the Lambda chilly darkish topic (Lambda-CDM) style of cosmology, which maps the expansion of the cosmos and predicts its finish — with topic in the end unfold so skinny it studies a warmth demise referred to as the Large Freeze.However here is the place the issues start. Regardless of a lot looking, astronomers don’t have any clue what darkish topic or darkish power are.”Most of the people agree that the universe’s provide composition is 5% extraordinary, atomic topic; 25% chilly, darkish topic; and 70% darkish power,” Ofer Lahav, a professor of astronomy at College Faculty London who’s all in favour of galaxy surveys of darkish power, advised Reside Science. “The embarrassing truth is, we do not perceive the closing two of them.”However a fair larger risk to Lambda-CDM lurks some of the stars: Relying on what approach astrophysicists use, the universe seems to be rising at other charges — a disparity referred to as the Hubble rigidity. And strategies that peer into the early universe display it increasing considerably quicker than Lambda-CDM predicts. The ones strategies had been vetted and verified through numerous observations.”So the one explanation why that I will be able to perceive, at this level, for them to disagree is that the style that we have got between them is possibly lacking one thing,” Riess mentioned.Mountain climbing the cosmic ladder
An indication of the growth of the Universe. The Large Bang is right away adopted through a speedy expansionary length referred to as inflation. Then, as protons and electrons mix to shape atoms, mild can shuttle freely; leaving the cosmic microwave background imprinted upon the sky. The universe’s growth slowed round 10 billion years in the past, and it all started to fill with galaxies, stars and big black holes. Round 5 billion years in the past, darkish power brought about this cosmic growth to unexpectedly boost up. To this present day, it presentations no indicators of forestalling. (Symbol credit score: Mark Garlick/Science Picture Library by way of Getty Photographs)The most simple and hottest reason behind darkish power is that this can be a cosmological consistent — an inflationary power that’s the similar all over and at each second; woven into the stretching cloth of space-time. Einstein named it lambda in his idea of basic relativity. As our cosmos grew, its total topic density dropped whilst the darkish power density remained the similar, steadily making the latter the most important contributor to its total growth.Added in combination the power densities of extraordinary topic, darkish topic, darkish power and effort from mild set the higher pace prohibit of the universe’s growth. They’re additionally key components within the Lambda chilly darkish topic (Lambda-CDM) style of cosmology, which maps the expansion of the cosmos and predicts its finish — with topic in the end unfold so skinny it studies a warmth demise referred to as the Large Freeze.However here is the place the issues start. Regardless of a lot looking, astronomers don’t have any clue what darkish topic or darkish power are.”Most of the people agree that the universe’s provide composition is 5% extraordinary, atomic topic; 25% chilly, darkish topic; and 70% darkish power,” Ofer Lahav, a professor of astronomy at College Faculty London who’s all in favour of galaxy surveys of darkish power, advised Reside Science. “The embarrassing truth is, we do not perceive the closing two of them.”However a fair larger risk to Lambda-CDM lurks some of the stars: Relying on what approach astrophysicists use, the universe seems to be rising at other charges — a disparity referred to as the Hubble rigidity. And strategies that peer into the early universe display it increasing considerably quicker than Lambda-CDM predicts. The ones strategies had been vetted and verified through numerous observations.”So the one explanation why that I will be able to perceive, at this level, for them to disagree is that the style that we have got between them is possibly lacking one thing,” Riess mentioned.Mountain climbing the cosmic ladder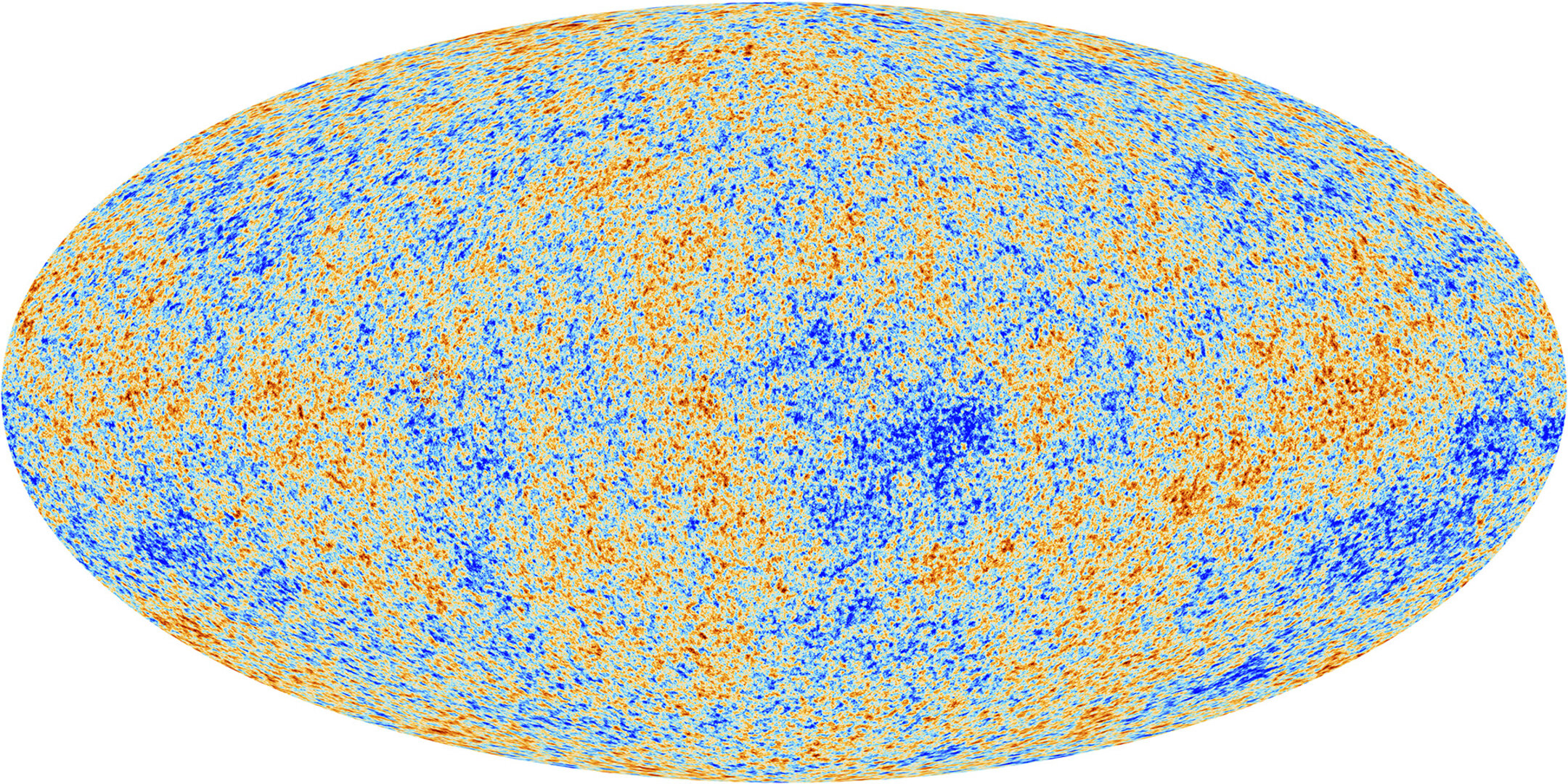 The cosmic microwave background: The universe’s ‘child image’ taken through the Ecu House Company’s Planck satellite tv for pc. (Symbol credit score: Ecu House Company)Measuring the universe’s growth takes slightly bit greater than a radar gun.The primary solution to measure this enlargement seems on the so-called cosmic microwave background (CMB), a relic of the universe’s morning time produced simply 380,000 years after the Large Bang. The imprint can also be noticed throughout all the sky, and it was once mapped to discover a Hubble consistent with lower than 1% uncertainty through the Ecu House Company’s (ESA) Planck satellite tv for pc between 2009 and 2013.On this cosmic “child image,” the universe is sort of fully uniform, however warmer and chillier patches the place topic is kind of dense divulge the place baryon acoustic oscillations made it clump. Because the universe exploded outward, this soap-bubble construction ballooned into the cosmic internet — a community of crisscrossing strands alongside whose intersections galaxies could be born.Similar: $100,000 Step forward physics prize awarded to three scientists who learn about the huge scale construction of the universeBy finding out those ripples with the Planck satellite tv for pc, cosmologists inferred the quantities of normal topic and darkish topic and a worth for the cosmological consistent, or darkish power. Plugging those into the Lambda-CDM style spat out a Hubble consistent of kind of 46,200 mph consistent with million light-years, or kind of 67 kilometers consistent with 2d consistent with megaparsec. (A megaparsec is 3.26 million light-years.) Let’s pause in this quantity for a second: if a galaxy is at a distance of 1 megaparsec distance clear of us, that implies it is going to transfer away at 67 kilometers consistent with 2d. At twenty megaparsecs this recession grows to at least one,340 kilometers consistent with 2d, and continues to develop exponentially there onward. If a galaxy is any more than 4,475 megaparsecs clear of us, it is going to recede from us (and us from it) quicker than the velocity of sunshine.A 2d solution to in finding this growth fee makes use of pulsating stars referred to as Cepheid variables — loss of life stars with helium-gas outer layers that develop and shrink as they take in and unencumber the megastar’s radiation, making them periodically flicker like far-off sign lamps. In 1912, astronomer Henrietta Swan Leavitt discovered that the brighter a Cepheid was once, the slower it might flicker, enabling astronomers to measure a celebrity’s absolute brightness, and due to this fact gauge its distance.It was once a landmark discovery that remodeled Cepheids into plentiful “usual candles” to measure the universe’s immense scale. By means of stringing observations of pulsating Cepheids in combination, astronomers can assemble cosmic distance ladders, with each and every rung taking them a step again into the previous.”It is probably the most correct implies that astronomers have these days for measuring distances,” Wendy Freedman, an astrophysicist on the College of Chicago, advised Reside Science. To construct a distance ladder, astronomers assemble the primary rung through opting for within reach Cepheids and cross-checking their distance in response to pulsating mild to that discovered through geometry. The following rungs are added the usage of Cepheid readings on my own.
The cosmic microwave background: The universe’s ‘child image’ taken through the Ecu House Company’s Planck satellite tv for pc. (Symbol credit score: Ecu House Company)Measuring the universe’s growth takes slightly bit greater than a radar gun.The primary solution to measure this enlargement seems on the so-called cosmic microwave background (CMB), a relic of the universe’s morning time produced simply 380,000 years after the Large Bang. The imprint can also be noticed throughout all the sky, and it was once mapped to discover a Hubble consistent with lower than 1% uncertainty through the Ecu House Company’s (ESA) Planck satellite tv for pc between 2009 and 2013.On this cosmic “child image,” the universe is sort of fully uniform, however warmer and chillier patches the place topic is kind of dense divulge the place baryon acoustic oscillations made it clump. Because the universe exploded outward, this soap-bubble construction ballooned into the cosmic internet — a community of crisscrossing strands alongside whose intersections galaxies could be born.Similar: $100,000 Step forward physics prize awarded to three scientists who learn about the huge scale construction of the universeBy finding out those ripples with the Planck satellite tv for pc, cosmologists inferred the quantities of normal topic and darkish topic and a worth for the cosmological consistent, or darkish power. Plugging those into the Lambda-CDM style spat out a Hubble consistent of kind of 46,200 mph consistent with million light-years, or kind of 67 kilometers consistent with 2d consistent with megaparsec. (A megaparsec is 3.26 million light-years.) Let’s pause in this quantity for a second: if a galaxy is at a distance of 1 megaparsec distance clear of us, that implies it is going to transfer away at 67 kilometers consistent with 2d. At twenty megaparsecs this recession grows to at least one,340 kilometers consistent with 2d, and continues to develop exponentially there onward. If a galaxy is any more than 4,475 megaparsecs clear of us, it is going to recede from us (and us from it) quicker than the velocity of sunshine.A 2d solution to in finding this growth fee makes use of pulsating stars referred to as Cepheid variables — loss of life stars with helium-gas outer layers that develop and shrink as they take in and unencumber the megastar’s radiation, making them periodically flicker like far-off sign lamps. In 1912, astronomer Henrietta Swan Leavitt discovered that the brighter a Cepheid was once, the slower it might flicker, enabling astronomers to measure a celebrity’s absolute brightness, and due to this fact gauge its distance.It was once a landmark discovery that remodeled Cepheids into plentiful “usual candles” to measure the universe’s immense scale. By means of stringing observations of pulsating Cepheids in combination, astronomers can assemble cosmic distance ladders, with each and every rung taking them a step again into the previous.”It is probably the most correct implies that astronomers have these days for measuring distances,” Wendy Freedman, an astrophysicist on the College of Chicago, advised Reside Science. To construct a distance ladder, astronomers assemble the primary rung through opting for within reach Cepheids and cross-checking their distance in response to pulsating mild to that discovered through geometry. The following rungs are added the usage of Cepheid readings on my own.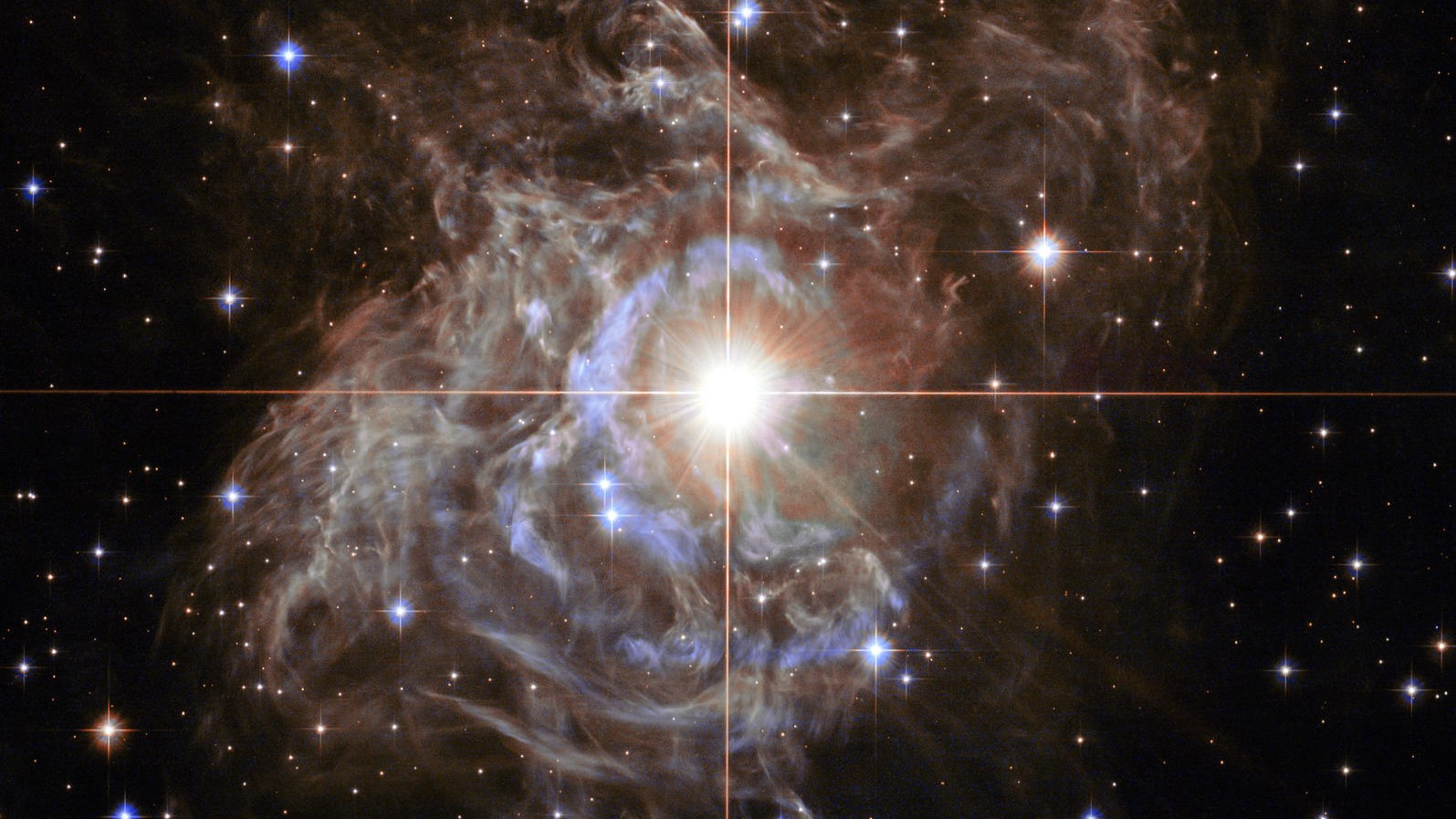 RS Puppis, a Cepheid megastar positioned 6,000 light-years away within the constellation Puppis and imaged through the Hubble House Telescope. (Symbol credit score: Alamy)Then, astronomers have a look at the distances of the celebs and supernovas on each and every rung and examine how a lot their mild has been redshifted (stretched out to longer, redder wavelengths) because the universe expands.This offers an exact size of the Hubble consistent. In 2019, the process was once utilized by Riess and his collaborators, who skilled the Hubble House Telescope on one of the crucial Milky Means’s closest neighbors, the Huge Magellanic Cloud.Their end result was once explosive: an impossibly top growth fee of 74 km/s/Mpc when in comparison to the Planck size. But Hubble lacked the essential precision for the crowded areas of area the group was once finding out, inflicting some far-off Cepheids to blur into neighboring stars. Dissenting cosmologists had some room left to argue that the outcome, on the other hand surprising, may have come from a size error.Similar: Hubble Telescope captures a galaxy’s ‘forbidden’ mild in surprising new imageSo when JWST introduced in December 2021, it was once poised to both get to the bottom of the discrepancy or cement it. At 21.3 ft (6.5 m) extensive, JWST’s replicate is sort of 3 times the scale of Hubble’s, which is simply 7.9 ft (2.4 m) extensive. Now not simplest can JWST hit upon items 100 occasions fainter than Hubble can, however additionally it is way more delicate within the infrared spectrum, enabling it to look in a broader vary of wavelengths.By means of evaluating Cepheids measured through JWST within the galaxy NGC 4258 with shiny Sort Ia supernovas (some other usual candle as a result of all of them burst on the similar absolute luminosity) in far flung galaxies, Riess and his colleagues arrived at a just about equivalent end result: 73 km/s/Mpc.Different measurements — together with one made through Freedman with the Hubble House telescope at the speedy brightening of essentially the most luminous “tip of the department” pink big stars, and some other with mild bent through the gravity of huge galaxies — got here again with respective result of 69.6 and 66.6 km/s/Mpc. A separate end result the usage of the bending of sunshine additionally gave a worth of 73 km/s/Mpc. Cosmologists have been left reeling.”The CMB temperature is measured on the stage of one% precision, and the Cepheid distance ladder size is getting as regards to 1%,” Ryan Keeley, a cosmologist on the College of California, Merced who has been running to provide an explanation for the Hubble rigidity, advised Reside Science. “So a distinction of seven kilometers consistent with 2d, even if it is not very a lot, could be very, not possible to be a random probability. There’s something particular to provide an explanation for.”
RS Puppis, a Cepheid megastar positioned 6,000 light-years away within the constellation Puppis and imaged through the Hubble House Telescope. (Symbol credit score: Alamy)Then, astronomers have a look at the distances of the celebs and supernovas on each and every rung and examine how a lot their mild has been redshifted (stretched out to longer, redder wavelengths) because the universe expands.This offers an exact size of the Hubble consistent. In 2019, the process was once utilized by Riess and his collaborators, who skilled the Hubble House Telescope on one of the crucial Milky Means’s closest neighbors, the Huge Magellanic Cloud.Their end result was once explosive: an impossibly top growth fee of 74 km/s/Mpc when in comparison to the Planck size. But Hubble lacked the essential precision for the crowded areas of area the group was once finding out, inflicting some far-off Cepheids to blur into neighboring stars. Dissenting cosmologists had some room left to argue that the outcome, on the other hand surprising, may have come from a size error.Similar: Hubble Telescope captures a galaxy’s ‘forbidden’ mild in surprising new imageSo when JWST introduced in December 2021, it was once poised to both get to the bottom of the discrepancy or cement it. At 21.3 ft (6.5 m) extensive, JWST’s replicate is sort of 3 times the scale of Hubble’s, which is simply 7.9 ft (2.4 m) extensive. Now not simplest can JWST hit upon items 100 occasions fainter than Hubble can, however additionally it is way more delicate within the infrared spectrum, enabling it to look in a broader vary of wavelengths.By means of evaluating Cepheids measured through JWST within the galaxy NGC 4258 with shiny Sort Ia supernovas (some other usual candle as a result of all of them burst on the similar absolute luminosity) in far flung galaxies, Riess and his colleagues arrived at a just about equivalent end result: 73 km/s/Mpc.Different measurements — together with one made through Freedman with the Hubble House telescope at the speedy brightening of essentially the most luminous “tip of the department” pink big stars, and some other with mild bent through the gravity of huge galaxies — got here again with respective result of 69.6 and 66.6 km/s/Mpc. A separate end result the usage of the bending of sunshine additionally gave a worth of 73 km/s/Mpc. Cosmologists have been left reeling.”The CMB temperature is measured on the stage of one% precision, and the Cepheid distance ladder size is getting as regards to 1%,” Ryan Keeley, a cosmologist on the College of California, Merced who has been running to provide an explanation for the Hubble rigidity, advised Reside Science. “So a distinction of seven kilometers consistent with 2d, even if it is not very a lot, could be very, not possible to be a random probability. There’s something particular to provide an explanation for.”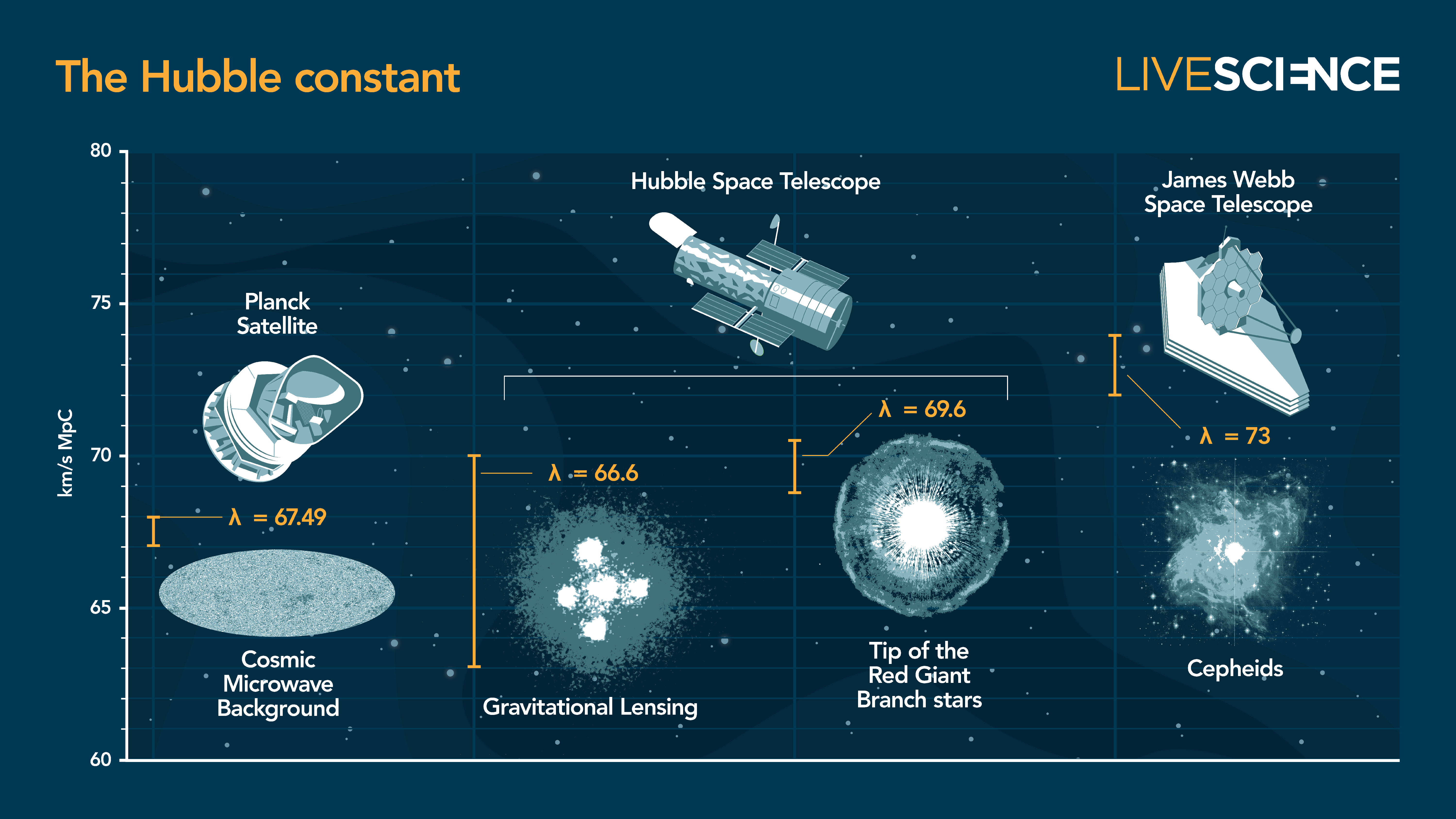 A selection of one of the most up-to-date measurements of the Hubble consistent. From left to proper, the assets used to measure its worth are: The cosmic microwave background captured through the Ecu House Company’s Planck satellite tv for pc; gravitational lensing and Tip of the Crimson Large Department stars measured through NASA’s Hubble House Telescope; and Cepheid stars noticed through the James Webb House Telescope. (Symbol credit score: Long term)Cosmology in crisisThe new end result leaves the solution extensive open, splitting cosmologists into factions chasing staggeringly other answers. Following the Hubble House telescope end result, an legit try to get to the bottom of the problem at a 2019 convention on the Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics (KITP) in California simplest brought about extra frustration. “We would not name it a rigidity or drawback, however moderately a disaster,” David Gross, former director of the KITP and a Nobel laureate, mentioned on the convention. How issues can also be mounted is unclear. Riess is pursuing a tweak to the Lambda-CDM style that assumes darkish power (the lambda) is not consistent however as a substitute evolves around the lifetime of the cosmos consistent with unknown physics. Alternatively Keeley’s analysis, printed Sept. 15 within the magazine Bodily Evaluation Letters, contradicts this. He and his colleagues discovered that the growth charges matched the predictions of Lambda-CDM all of the as far back as the CMB. So, if the style wishes solving anyplace, it is possibly within the very early universe, Keeley mentioned. It might be imaginable so as to add some additional darkish power prior to the emergence of the cosmic microwave background, Keeley mentioned, giving some additional oomph to the universe’s growth that don’t need to make it damage from the usual style.Any other staff of astronomers is satisfied that the strain, along the remark that the Milky Means is living inside of an underdense supervoid, implies that Lambda-CDM and darkish topic should be thrown out altogether. What will have to change it, consistent with Pavel Kroupa, a professor of astrophysics on the College of Bonn, is a idea referred to as Changed Newtonian Dynamics (MOND). The speculation proposes that for gravitational pulls ten trillion occasions smaller than the ones felt on Earth’s floor (such because the tugs felt between far-off galaxies) Newton’s rules damage down and should get replaced through different equations.
A selection of one of the most up-to-date measurements of the Hubble consistent. From left to proper, the assets used to measure its worth are: The cosmic microwave background captured through the Ecu House Company’s Planck satellite tv for pc; gravitational lensing and Tip of the Crimson Large Department stars measured through NASA’s Hubble House Telescope; and Cepheid stars noticed through the James Webb House Telescope. (Symbol credit score: Long term)Cosmology in crisisThe new end result leaves the solution extensive open, splitting cosmologists into factions chasing staggeringly other answers. Following the Hubble House telescope end result, an legit try to get to the bottom of the problem at a 2019 convention on the Kavli Institute for Theoretical Physics (KITP) in California simplest brought about extra frustration. “We would not name it a rigidity or drawback, however moderately a disaster,” David Gross, former director of the KITP and a Nobel laureate, mentioned on the convention. How issues can also be mounted is unclear. Riess is pursuing a tweak to the Lambda-CDM style that assumes darkish power (the lambda) is not consistent however as a substitute evolves around the lifetime of the cosmos consistent with unknown physics. Alternatively Keeley’s analysis, printed Sept. 15 within the magazine Bodily Evaluation Letters, contradicts this. He and his colleagues discovered that the growth charges matched the predictions of Lambda-CDM all of the as far back as the CMB. So, if the style wishes solving anyplace, it is possibly within the very early universe, Keeley mentioned. It might be imaginable so as to add some additional darkish power prior to the emergence of the cosmic microwave background, Keeley mentioned, giving some additional oomph to the universe’s growth that don’t need to make it damage from the usual style.Any other staff of astronomers is satisfied that the strain, along the remark that the Milky Means is living inside of an underdense supervoid, implies that Lambda-CDM and darkish topic should be thrown out altogether. What will have to change it, consistent with Pavel Kroupa, a professor of astrophysics on the College of Bonn, is a idea referred to as Changed Newtonian Dynamics (MOND). The speculation proposes that for gravitational pulls ten trillion occasions smaller than the ones felt on Earth’s floor (such because the tugs felt between far-off galaxies) Newton’s rules damage down and should get replaced through different equations. 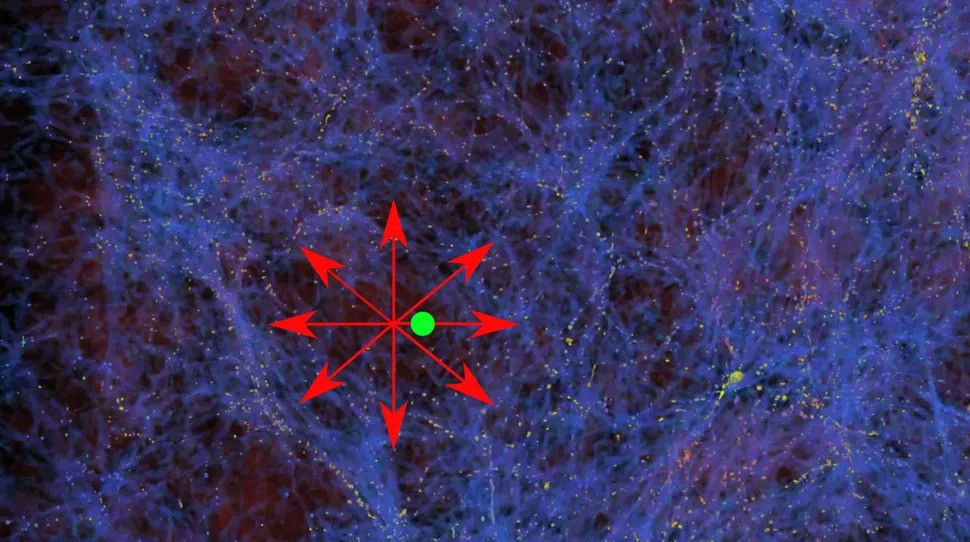 The Keenan-Barger-Cowie supervoid. Proponents of the idea of Changed Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) argue that our Milky Means’s presence close to the middle of the 2-billion-light-year extensive underdensity of galaxies is skewing our measurements of the Hubble consistent. (Symbol credit score: AG Kroupa/College of Bonn)Different astronomers say that their very own calculations nix the MOND claims, but Kroupa insists that cosmologists having a look to tweak the usual cosmological style are “principally including further headaches to an already very messy and complex idea.” “What I’m experiencing and witnessing is an crucial breakdown of science,” Kroupa mentioned.Lahav is agnostic. It is imaginable Lambda-CDM simply wishes a tweak, he mentioned, or perhaps darkish topic and darkish power are the modern day identical of epicycles, the small circles historical Greek astronomers used to style planets orbiting Earth. “The orbits of planets have been described very appropriately through epicycles,” Lahav mentioned. “It was once a just right style! It fitted the information.”However as soon as astronomers positioned the solar within the heart of the sun gadget in more moderen fashions, epicycles in the end was beside the point, he added. “If we need to cross philosophical, perhaps that is what is going on,” Lahav mentioned. “However perhaps additionally there may be darkish topic and darkish power and it is simply now not been found out but.”Cosmologists are on the lookout for solutions in various puts. Upcoming CMB experiments, such because the CMB-S4 mission on the South Pole and the Simons Observatory in Chile, are on the lookout for clues in ultraprecise measurements of the early universe’s radiation. Others will glance to the darkish topic maps produced through ESA’s Euclid area telescope or to the longer term darkish power survey performed through the Darkish Power Spectroscopic Software.For Freedman, some answers, or perhaps additional riddles, will come from the JWST. Her group is the usage of the telescope’s robust eye to make ultradetailed measurements of Cepheid variables; tip-of-the-red-giant-branch stars; and one of those carbon megastar referred to as JAGB stars unexpectedly distance. “We’re going to see how neatly they agree and that may give us a way of an total systematic solution,” Freedman mentioned.Freedman has appeared simplest at stars in a single galaxy to this point however is already seeing a distinction from the Hubble area telescope measurements.”I am truly excited as a result of I feel we are going to have one thing truly attention-grabbing to mention,” Freedman mentioned. “I am simply totally open. I do not know the place that is going to fall.”
The Keenan-Barger-Cowie supervoid. Proponents of the idea of Changed Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) argue that our Milky Means’s presence close to the middle of the 2-billion-light-year extensive underdensity of galaxies is skewing our measurements of the Hubble consistent. (Symbol credit score: AG Kroupa/College of Bonn)Different astronomers say that their very own calculations nix the MOND claims, but Kroupa insists that cosmologists having a look to tweak the usual cosmological style are “principally including further headaches to an already very messy and complex idea.” “What I’m experiencing and witnessing is an crucial breakdown of science,” Kroupa mentioned.Lahav is agnostic. It is imaginable Lambda-CDM simply wishes a tweak, he mentioned, or perhaps darkish topic and darkish power are the modern day identical of epicycles, the small circles historical Greek astronomers used to style planets orbiting Earth. “The orbits of planets have been described very appropriately through epicycles,” Lahav mentioned. “It was once a just right style! It fitted the information.”However as soon as astronomers positioned the solar within the heart of the sun gadget in more moderen fashions, epicycles in the end was beside the point, he added. “If we need to cross philosophical, perhaps that is what is going on,” Lahav mentioned. “However perhaps additionally there may be darkish topic and darkish power and it is simply now not been found out but.”Cosmologists are on the lookout for solutions in various puts. Upcoming CMB experiments, such because the CMB-S4 mission on the South Pole and the Simons Observatory in Chile, are on the lookout for clues in ultraprecise measurements of the early universe’s radiation. Others will glance to the darkish topic maps produced through ESA’s Euclid area telescope or to the longer term darkish power survey performed through the Darkish Power Spectroscopic Software.For Freedman, some answers, or perhaps additional riddles, will come from the JWST. Her group is the usage of the telescope’s robust eye to make ultradetailed measurements of Cepheid variables; tip-of-the-red-giant-branch stars; and one of those carbon megastar referred to as JAGB stars unexpectedly distance. “We’re going to see how neatly they agree and that may give us a way of an total systematic solution,” Freedman mentioned.Freedman has appeared simplest at stars in a single galaxy to this point however is already seeing a distinction from the Hubble area telescope measurements.”I am truly excited as a result of I feel we are going to have one thing truly attention-grabbing to mention,” Freedman mentioned. “I am simply totally open. I do not know the place that is going to fall.”













