In a brand new find out about, researchers have recognized a trio of proteins that function the important key in permitting sperm to fuse with an egg, a procedure that marks step one in developing new existence.
The researchers hired the bogus intelligence device AlphaFold to discover how sperm proteins have interaction on the molecular stage, dropping gentle on a basic side of fertilization shared throughout vertebrates.
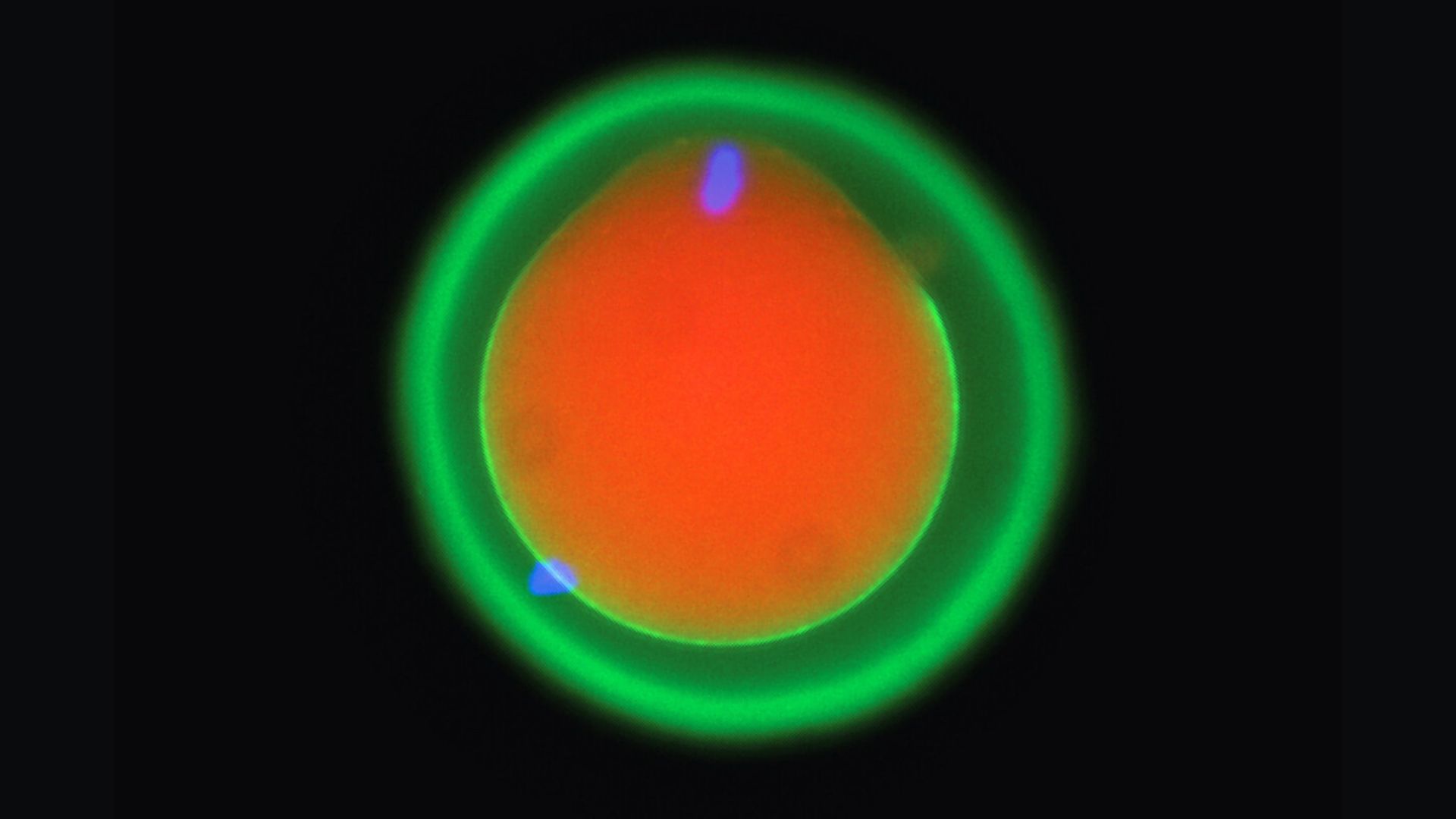 A microscope symbol from Osaka College (Oct 2024) presentations a fertilizing mouse egg in pink and inexperienced, with DNA highlighted in blue. Egg DNA is on the best, and sperm DNA is on the backside left.
A microscope symbol from Osaka College (Oct 2024) presentations a fertilizing mouse egg in pink and inexperienced, with DNA highlighted in blue. Egg DNA is on the best, and sperm DNA is on the backside left.
The sperm’s mysterious adventure to the egg
Fertilization starts when sperm navigate to an egg, guided through chemical alerts. When they achieve the egg, sperm bind to the egg’s floor, beginning a fusion in their genetic subject matter to shape a zygote. Alternatively, the fitting molecular mechanisms permitting this important interplay have remained elusive.
Andrea Pauli’s lab on the Analysis Institute of Molecular Pathology (IMP) in Vienna, along side global collaborators, applied AlphaFold Multimer to expect protein interactions that information sperm-egg fusion.
The group all in favour of sperm membrane proteins, the usage of AlphaFold to expect which proteins would possibly bind in combination. Their research published that two prior to now recognized proteins, Izumo1 and Spaca6, have interaction with a 3rd, newly found out protein: Tmem81.
We have been stunned to find a new protein that had by no means been characterized earlier than,” mentioned Andreas Blaha, co-first writer of the find out about. This new trimeric advanced—composed of Izumo1, Spaca6, and Tmem81—was once proven to play a important position in fertilization. When this advanced was once disrupted, male zebrafish and mice turned into infertile.
 Scanning electron microscopy symbol of a zebrafish sperm sure to the sperm-entry website of a zebrafish egg. (Credit score: IMP)
Scanning electron microscopy symbol of a zebrafish sperm sure to the sperm-entry website of a zebrafish egg. (Credit score: IMP)
The lock and key: A common mechanism for all vertebrates?
The researchers demonstrated that this sperm protein advanced interacts with the egg’s floor protein in zebrafish, referred to as Bouncer, which acts as a “lock”, permitting sperm to fuse with the egg. Bouncer’s position in zebrafish is similar to the serve as of Juno in mammals, even though those proteins are evolutionarily unrelated.
This discovery means that whilst sperm proteins have remained conserved throughout species, egg proteins have developed independently to facilitate fertilization in several vertebrates.
“The truth that it was once maintained over hundreds of thousands of years of evolution presentations simply how essential this lock-and-key procedure is,” mentioned Andrea Pauli, lead writer of the find out about.
This discovery is especially intriguing given the evolutionary divergence of egg proteins, which use species-specific locks—akin to Bouncer in zebrafish and Juno in mammals—to bind with the conserved sperm protein key.
The researchers validated their AI-generated predictions with experiments on dwelling organisms, confirming that this protein advanced exists no longer best in zebrafish but in addition in mice and people. This implies that the similar sperm protein advanced generally is a common characteristic of vertebrate fertilization.
Broader implications for reproductive science
This discovery opens new avenues for exploring fertility remedies and reproductive well being, because the proteins concerned are crucial for the fusion procedure. Researchers are desperate to discover how other species have developed numerous egg proteins to engage with a conserved sperm mechanism.
As scientists analysis the molecular underpinnings of fertilization additional, AI-powered gear like AlphaFold are offering insights into the elemental processes that power the advent of latest existence.
The id of this trimeric protein advanced no longer best advances our working out of reproductive biology but in addition raises intriguing questions in regards to the evolutionary range of fertilization mechanisms throughout species.
The find out about has been revealed in Cellular.
AI-powered discovery identifies lock-and-key procedure in sperm and egg