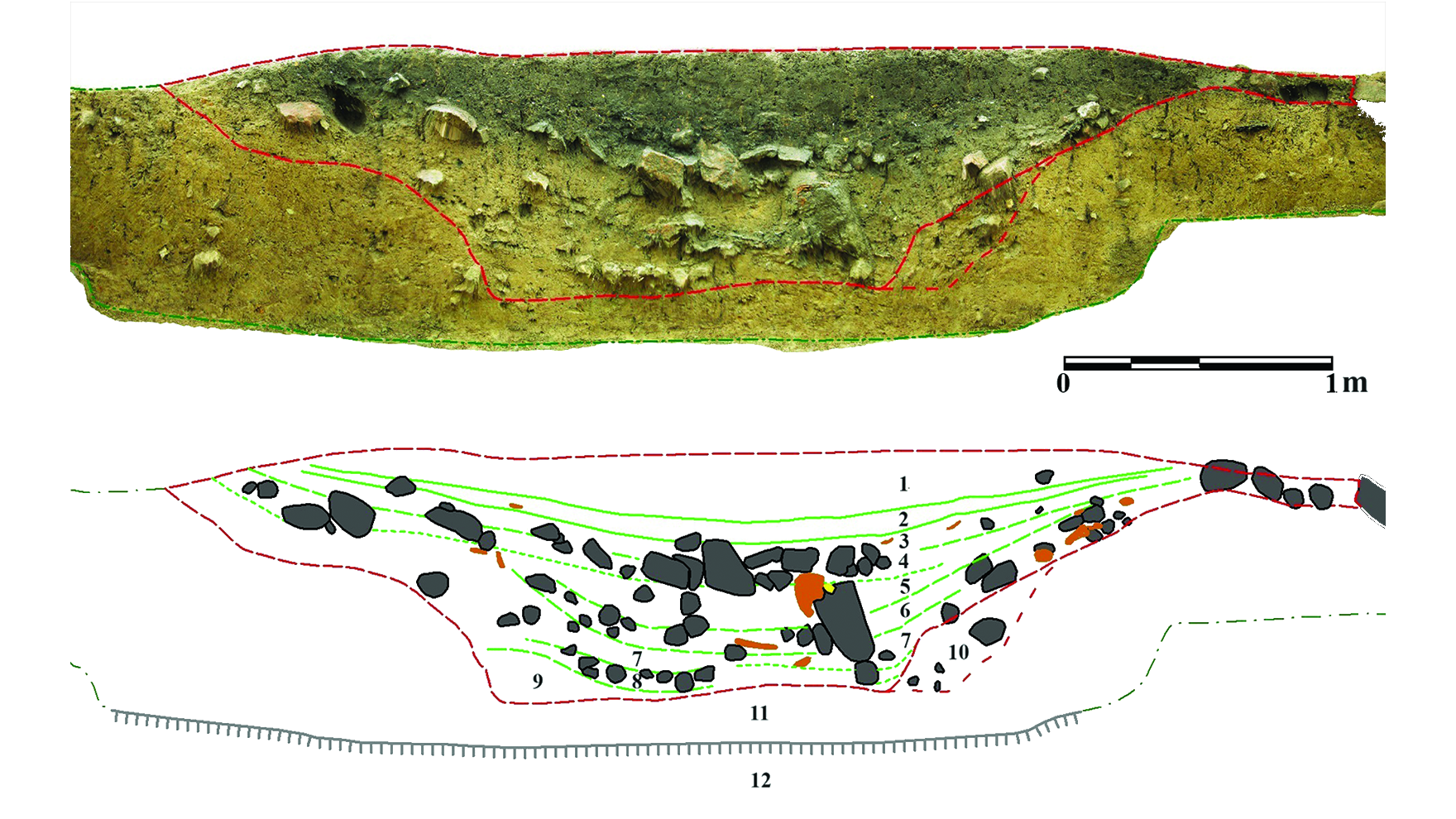
![]()
![]() A contemporary find out about printed in Social Neuroscience has supplied new insights into how alcohol use dysfunction (sometimes called alcoholism) interferes with the mind’s skill to procedure ethical cues. The researchers discovered that after people with alcohol use dysfunction had been proven ethical pictures paired with alcohol-related distractions, their brains confirmed much less process in areas related to ethical decision-making. This new working out may just lend a hand provide an explanation for probably the most behaviors noticed in people suffering with alcoholism.Ethical cognition—our skill to make choices about proper and fallacious—is a the most important side of social habits. It lets in us to serve as inside of society, balancing private targets towards the wishes of others. However for people with alcohol use dysfunction, the facility to procedure ethical eventualities could also be impaired, which might give a contribution to problematic or delinquent habits.Earlier analysis has proven that people with alcohol use dysfunction have a tendency to have altered mind process when confronted with emotional or ethical dilemmas, nevertheless it used to be unclear how alcohol in particular would possibly intrude with ethical processing. The researchers hypothesized that alcohol cues may just create one of those “consideration bias” that distracts the mind from processing ethical knowledge correctly. In different phrases, when alcohol is provide as a distraction, people with alcohol use dysfunction would possibly have extra bother that specialize in the ethical content material of a scenario.The purpose of the find out about used to be to inspect this possible “consideration bias” via the usage of a mixture of alcohol-related and impartial cues whilst measuring mind process. The researchers sought after to peer how alcohol use dysfunction would possibly disrupt the mind’s skill to procedure ethical eventualities and whether or not this interference may well be connected to precise patterns of mind process.“My background is in running with people concerned within the justice gadget, lots of whom have substance use problems,” mentioned find out about creator Samantha J. Fede, an assistant professor of mental sciences and head of the Social Cognition & Affective/Ethical Processing Imaging Lab Analysis Lab at Auburn College.“Substance use problems are frequently relatively harmfully and erroneously moralized in our society, so it’s an excessively subtle, nuanced query to invite what’s happening within the mind of a person with a substance use dysfunction, like alcohol use dysfunction, that would possibly give a contribution to socially damaging movements. It’s in particular vital to exhibit those processes are cognitive, and now not in particular ethical.”To research this, the researchers recruited 60 individuals—30 people with alcohol use dysfunction and 30 people with out the dysfunction—from the Washington D.C. space. The 2 teams had been matched for age and intercourse to make comparisons extra dependable. The individuals with alcohol use dysfunction had been break up between those that had been in inpatient remedy and people who weren’t searching for remedy on the time of the find out about. All individuals had been screened for eligibility to make sure they’d no different neurological prerequisites that would intrude with the effects.Individuals had been requested to accomplish a job whilst present process practical magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), a mind scanning method that measures process in several areas of the mind. The duty used to be designed to provide two pictures at a time: one used to be a distractor (both alcohol-related or impartial), and the opposite used to be a cue with ethical, emotional, or impartial content material.For instance, an ethical cue would possibly depict a damaging social scenario, like bullying, whilst a impartial cue would possibly display an individual staring at tv. Individuals had been requested to concentrate on figuring out whether or not the scene used to be indoors or open air, however the researchers had been essentially inquisitive about how the individuals’ brains reacted to the ethical and emotional content material.The duty used to be implicit, that means that the individuals weren’t informed to concentrate on the ethical or emotional content material of the photographs. This design used to be selected to steer clear of biasing their consideration, permitting the researchers to peer how their brains naturally spoke back to the cues and distractions.The effects confirmed that people with alcohol use dysfunction had decreased process in positive areas of the mind once they had been proven ethical cues paired with alcohol-related distractions. In particular, those people confirmed much less engagement within the medial prefrontal cortex, a area related to ethical decision-making, and the left amygdala, which performs a task in processing emotional responses. This decreased process used to be particularly noticeable in more youthful people with alcohol use dysfunction.This interference impact used to be noticed most effective when ethical cues had been paired with alcohol-related distractions. When the distractions had been impartial, the people with alcohol use dysfunction confirmed equivalent mind process to the keep watch over team with out the dysfunction. This implies that the presence of alcohol cues in particular interferes with the mind’s skill to procedure ethical knowledge.Throughout each teams, the researchers additionally spotted much less process within the center and awesome temporal gyri, areas thinking about working out social and emotional eventualities. This trend signifies that alcohol-related distractions might in most cases cut back the mind’s skill to have interaction with social and ethical content material, even in other folks with out alcohol use dysfunction, although the impact used to be a lot more pronounced in the ones with the dysfunction.“Our effects recommend that focus biases in opposition to alcohol cues intrude with processing of sociomoral footage,” Fede informed PsyPost. “To make use of a metaphor, in people with alcohol use dysfunction, alcohol cues are so loud that they drown out some other inputs (like ethical content material). That is vital, as a result of psychologists have already got interventions to make stronger consideration biases that may well be used to deal with this downside sooner or later.”Curiously, the impact of alcohol-related distractors on mind process in line with ethical cues used to be extra pronounced in more youthful people with alcohol use dysfunction. In particular, more youthful individuals on this team confirmed decreased process within the medial prefrontal cortex and the left amygdala when viewing ethical cues along alcohol distractions.The researchers additionally discovered that feminine individuals with alcohol use dysfunction had a more potent interference impact in comparison to men. Feminine individuals confirmed decreased process within the medial prefrontal cortex and the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex when ethical cues had been paired with alcohol-related distractions.“We noticed vital interactions with age and intercourse, nevertheless it’s tricky to mention precisely what the ones imply,” Fede defined. “Earlier research have proven that folks with alcohol use dysfunction range in the case of whether or not or now not they have got a powerful alcohol consideration bias. In the end, it’s a very powerful reminder that our effects aren’t going to use to everybody with alcohol use dysfunction.”Relating to long run instructions, the find out about opens up a number of fascinating avenues for additional investigation. One key query is whether or not remedies that focus on consideration bias, comparable to cognitive behavioral treatment or attentional bias amendment coaching, may just lend a hand repair commonplace ethical processing in people with alcohol use dysfunction or different substance use problems. Through lowering the power of substance-related distractions, those remedies would possibly permit people to focal point extra successfully at the social and ethical penalties in their movements.“My purpose is to increase those findings to different substance use problems and to provide people with substance use problems a device to scale back the affect in their use on others,” Fede mentioned.The find out about, “Alcohol consideration bias modulates neural engagement all through ethical processing,” used to be authored via Samantha J. Fede, Mallory A. Kisner, Sarah F. Dean, Emma Buckler, Robin Chholak, and Reza Momenan.
A contemporary find out about printed in Social Neuroscience has supplied new insights into how alcohol use dysfunction (sometimes called alcoholism) interferes with the mind’s skill to procedure ethical cues. The researchers discovered that after people with alcohol use dysfunction had been proven ethical pictures paired with alcohol-related distractions, their brains confirmed much less process in areas related to ethical decision-making. This new working out may just lend a hand provide an explanation for probably the most behaviors noticed in people suffering with alcoholism.Ethical cognition—our skill to make choices about proper and fallacious—is a the most important side of social habits. It lets in us to serve as inside of society, balancing private targets towards the wishes of others. However for people with alcohol use dysfunction, the facility to procedure ethical eventualities could also be impaired, which might give a contribution to problematic or delinquent habits.Earlier analysis has proven that people with alcohol use dysfunction have a tendency to have altered mind process when confronted with emotional or ethical dilemmas, nevertheless it used to be unclear how alcohol in particular would possibly intrude with ethical processing. The researchers hypothesized that alcohol cues may just create one of those “consideration bias” that distracts the mind from processing ethical knowledge correctly. In different phrases, when alcohol is provide as a distraction, people with alcohol use dysfunction would possibly have extra bother that specialize in the ethical content material of a scenario.The purpose of the find out about used to be to inspect this possible “consideration bias” via the usage of a mixture of alcohol-related and impartial cues whilst measuring mind process. The researchers sought after to peer how alcohol use dysfunction would possibly disrupt the mind’s skill to procedure ethical eventualities and whether or not this interference may well be connected to precise patterns of mind process.“My background is in running with people concerned within the justice gadget, lots of whom have substance use problems,” mentioned find out about creator Samantha J. Fede, an assistant professor of mental sciences and head of the Social Cognition & Affective/Ethical Processing Imaging Lab Analysis Lab at Auburn College.“Substance use problems are frequently relatively harmfully and erroneously moralized in our society, so it’s an excessively subtle, nuanced query to invite what’s happening within the mind of a person with a substance use dysfunction, like alcohol use dysfunction, that would possibly give a contribution to socially damaging movements. It’s in particular vital to exhibit those processes are cognitive, and now not in particular ethical.”To research this, the researchers recruited 60 individuals—30 people with alcohol use dysfunction and 30 people with out the dysfunction—from the Washington D.C. space. The 2 teams had been matched for age and intercourse to make comparisons extra dependable. The individuals with alcohol use dysfunction had been break up between those that had been in inpatient remedy and people who weren’t searching for remedy on the time of the find out about. All individuals had been screened for eligibility to make sure they’d no different neurological prerequisites that would intrude with the effects.Individuals had been requested to accomplish a job whilst present process practical magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), a mind scanning method that measures process in several areas of the mind. The duty used to be designed to provide two pictures at a time: one used to be a distractor (both alcohol-related or impartial), and the opposite used to be a cue with ethical, emotional, or impartial content material.For instance, an ethical cue would possibly depict a damaging social scenario, like bullying, whilst a impartial cue would possibly display an individual staring at tv. Individuals had been requested to concentrate on figuring out whether or not the scene used to be indoors or open air, however the researchers had been essentially inquisitive about how the individuals’ brains reacted to the ethical and emotional content material.The duty used to be implicit, that means that the individuals weren’t informed to concentrate on the ethical or emotional content material of the photographs. This design used to be selected to steer clear of biasing their consideration, permitting the researchers to peer how their brains naturally spoke back to the cues and distractions.The effects confirmed that people with alcohol use dysfunction had decreased process in positive areas of the mind once they had been proven ethical cues paired with alcohol-related distractions. In particular, those people confirmed much less engagement within the medial prefrontal cortex, a area related to ethical decision-making, and the left amygdala, which performs a task in processing emotional responses. This decreased process used to be particularly noticeable in more youthful people with alcohol use dysfunction.This interference impact used to be noticed most effective when ethical cues had been paired with alcohol-related distractions. When the distractions had been impartial, the people with alcohol use dysfunction confirmed equivalent mind process to the keep watch over team with out the dysfunction. This implies that the presence of alcohol cues in particular interferes with the mind’s skill to procedure ethical knowledge.Throughout each teams, the researchers additionally spotted much less process within the center and awesome temporal gyri, areas thinking about working out social and emotional eventualities. This trend signifies that alcohol-related distractions might in most cases cut back the mind’s skill to have interaction with social and ethical content material, even in other folks with out alcohol use dysfunction, although the impact used to be a lot more pronounced in the ones with the dysfunction.“Our effects recommend that focus biases in opposition to alcohol cues intrude with processing of sociomoral footage,” Fede informed PsyPost. “To make use of a metaphor, in people with alcohol use dysfunction, alcohol cues are so loud that they drown out some other inputs (like ethical content material). That is vital, as a result of psychologists have already got interventions to make stronger consideration biases that may well be used to deal with this downside sooner or later.”Curiously, the impact of alcohol-related distractors on mind process in line with ethical cues used to be extra pronounced in more youthful people with alcohol use dysfunction. In particular, more youthful individuals on this team confirmed decreased process within the medial prefrontal cortex and the left amygdala when viewing ethical cues along alcohol distractions.The researchers additionally discovered that feminine individuals with alcohol use dysfunction had a more potent interference impact in comparison to men. Feminine individuals confirmed decreased process within the medial prefrontal cortex and the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex when ethical cues had been paired with alcohol-related distractions.“We noticed vital interactions with age and intercourse, nevertheless it’s tricky to mention precisely what the ones imply,” Fede defined. “Earlier research have proven that folks with alcohol use dysfunction range in the case of whether or not or now not they have got a powerful alcohol consideration bias. In the end, it’s a very powerful reminder that our effects aren’t going to use to everybody with alcohol use dysfunction.”Relating to long run instructions, the find out about opens up a number of fascinating avenues for additional investigation. One key query is whether or not remedies that focus on consideration bias, comparable to cognitive behavioral treatment or attentional bias amendment coaching, may just lend a hand repair commonplace ethical processing in people with alcohol use dysfunction or different substance use problems. Through lowering the power of substance-related distractions, those remedies would possibly permit people to focal point extra successfully at the social and ethical penalties in their movements.“My purpose is to increase those findings to different substance use problems and to provide people with substance use problems a device to scale back the affect in their use on others,” Fede mentioned.The find out about, “Alcohol consideration bias modulates neural engagement all through ethical processing,” used to be authored via Samantha J. Fede, Mallory A. Kisner, Sarah F. Dean, Emma Buckler, Robin Chholak, and Reza Momenan.
Alcohol-related imagery disrupts ethical processing within the brains of other folks with alcoholism