An research of the genetic task of mind cells in people who have died with Alzheimer’s illness has published the situation progresses in two phases; a gradual build up in irritation, adopted by means of a extra fast degeneration.
Importantly, the primary of those stages is proscribed in its scope and occurs sooner than signs equivalent to reminiscence loss seem, indicating alternatives for analysis and remedy may happen at an previous level than they do recently.
The second one level ends up in a extra pronounced degree of destruction, that includes the infamous accumulation of protein plaques and tangles that coincide with serious injury to neurons that ends up in a lack of cognitive serve as.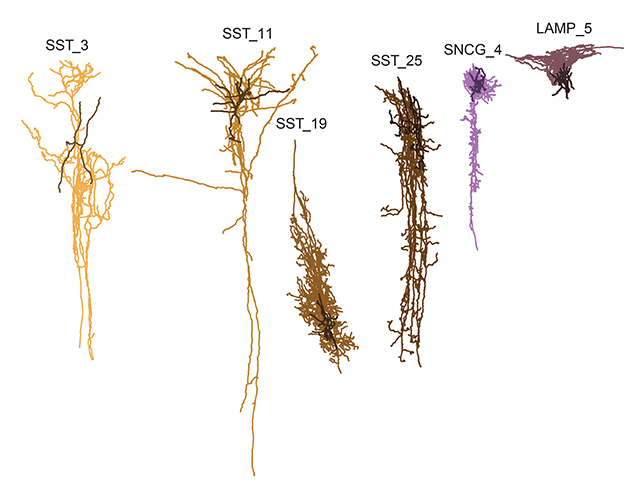 The find out about recognized the mobile varieties destroyed by means of Alzheimer’s first. (The Allen Institute, Seattle)The researchers, led by means of groups from the College of Washington and the Allen Institute for Mind Science, profiled the genetic acitivity of unmarried cells in a space of the mind referred to as the center temporal gyrus, the place key purposes of reminiscence, language, and imaginative and prescient are treated.
The find out about recognized the mobile varieties destroyed by means of Alzheimer’s first. (The Allen Institute, Seattle)The researchers, led by means of groups from the College of Washington and the Allen Institute for Mind Science, profiled the genetic acitivity of unmarried cells in a space of the mind referred to as the center temporal gyrus, the place key purposes of reminiscence, language, and imaginative and prescient are treated.
“This way supplies a complete figuring out of the particular, extremely granular mobile varieties affected over the process illness, the place the ones affected cells are positioned in tissue microarchitecture and when they’re affected as illness progresses,” write the researchers of their printed paper.
The group analyzed brains from 84 individuals who had died with Alzheimer’s, and who had a mean age of 88. Those readings and measurements had been then in comparison to brains from donors with out Alzheimer’s to spot essential variations.
Along with findings of distinct pathological stages, the researchers exposed explicit injury to cognitively-crucial inhibitory neuron within the first section. This can be how issues in neural circuitry are to start with caused, the group suggests.
Up to now, excitatory neurons – those who turn on different neurons – had been related to Alzheimer’s illness. Inhibitory neurons are those who deactivate or calm neurons, so the relationship to Alzheimer’s here’s a new and fascinating one.
The findings supply essential contributions to a complete and publicly to be had map of the wear and tear Alzheimier’s does to the mind referred to as the Seattle Alzheimer’s Illness Mind Cellular Atlas (SEA-AD). The hope is that by means of monitoring this trail of neuron destruction extra intently, we will be able to higher know how Alzheimer’s is taking cling – what stops it, and what lets in it to occur.
As our clinical generation will get extra complicated and extra succesful, we are finding out extra in regards to the complexities of Alzheimer’s – whether or not that is with triggers in other places within the frame, hyperlinks to different sicknesses, or a hidden preliminary section we in the past hadn’t came upon.
“The effects essentially adjust scientists’ figuring out of ways Alzheimer’s harms the mind and can information the improvement of latest therapies for this devastating dysfunction,” says Richard Hodes, the director of the NIH Nationwide Institute on Getting old, who wasn’t at once concerned within the find out about.The analysis has been printed in Nature Neuroscience.
Alzheimer’s Illness Harms The Mind in 2 Distinct Stages, Find out about Unearths








/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25752946/1183652392.jpg)