It is almost certainly now not unexpected {that a} new learn about has related added sugar intake to an larger chance of middle illness, however a much less anticipated discovery is that those that have an occasional candy deal with seem to be at a discounted chance of cardiovascular issues.
Consuming a pastry, cake, or chocolate bar each and every so continuously could also be higher to your middle than a ‘zero-sugar’ vitamin, in step with the analysis workforce from Lund College in Sweden. On the other hand, this courting does not dangle for different kinds of sugar intake, like fizzy beverages or candy toppings.
“Essentially the most hanging discovering from our learn about is the divergent courting between other resources of added sugar and heart problems chance,” says epidemiologist Suzanne Janzi.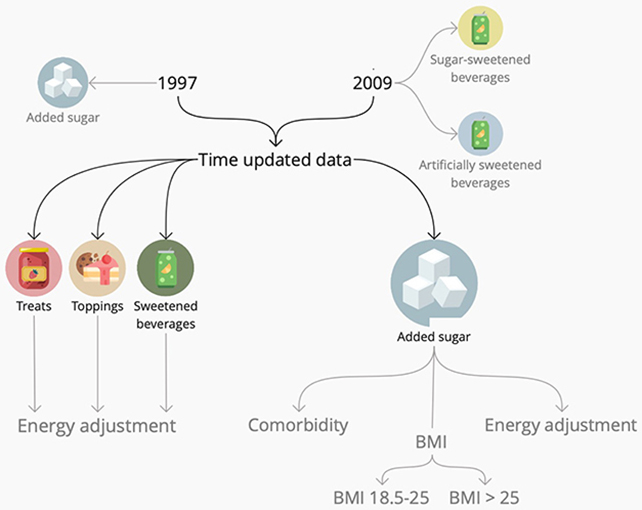 Added sugar consumption was once break up into 3 classes. (Janzi et al., Frontiers in Public Well being, 2024)”This unexpected distinction highlights the significance of making an allowance for now not simply the quantity of sugar fed on, however its supply and context.”
Added sugar consumption was once break up into 3 classes. (Janzi et al., Frontiers in Public Well being, 2024)”This unexpected distinction highlights the significance of making an allowance for now not simply the quantity of sugar fed on, however its supply and context.”
The researchers checked out information of 69,705 other people in Swedish public well being databases. The contributors, elderly between 45 and 83, have been quizzed on their vitamin and way of life in 1997 and 2009, then tracked as much as 2019.
Sugar consumption was once grouped into 3 classes: sugary toppings (like honey), candy treats (like pastries and candies), and sweetened drinks (like fizzy beverages).
Form of added sugar fed on was once then cross-referenced in opposition to seven kinds of cardiovascular illnesses, together with strokes and middle assaults, with a number of different chance elements (comparable to smoking) accounted for.
The associations various between sugar kind and middle illness kind; for instance, candy toppings have been related to an larger chance of an stomach aortic aneurysm (bulges in blood vessels). General although, the bottom dangers throughout all cardiovascular illnesses have been present in those that restricted themselves to a candy deal with each and every every so often.
There is a lot to believe relating to the alternative ways wherein we get our sugar: what different food and drink we’ve got with the sugar, for instance, in addition to how steadily we come with added sugar in our vitamin.
“Liquid sugars, present in sweetened drinks, most often supply much less satiety than cast bureaucracy – they make you’re feeling much less complete – doubtlessly resulting in overconsumption,” says Janzi.
“Context additionally issues – treats are continuously loved in social settings or particular events, whilst sweetened drinks may well be fed on extra steadily.”
Be mindful that those findings trace at relationships, relatively than proving motive and impact. Additionally they do not consider different well being penalties – like injury to enamel for instance – and want to be taken in context with what we already learn about sugar.
The researchers counsel long term research may glance in additional element at associations between sugar, middle illness, and weight problems, for instance.
Cultural elements additionally want to be thought to be: in Sweden, the place those learn about contributors have been from, there is a well-established customized of having in combination for espresso and pastry breaks referred to as ‘fika’, which could have some bearing at the effects.
Research on how loneliness and pressure have an effect on our well being point out there is doable middle advantages to this custom – common social interplay and taking time to calm down.
“Whilst our observational learn about can’t determine causation, those findings counsel that extraordinarily low sugar consumption might not be important or really helpful for cardiovascular well being,” says Janzi.The analysis has been printed in Frontiers in Public Well being.
An Occasional Deal with May just Be Higher For Your Center Than No Added Sugar at All