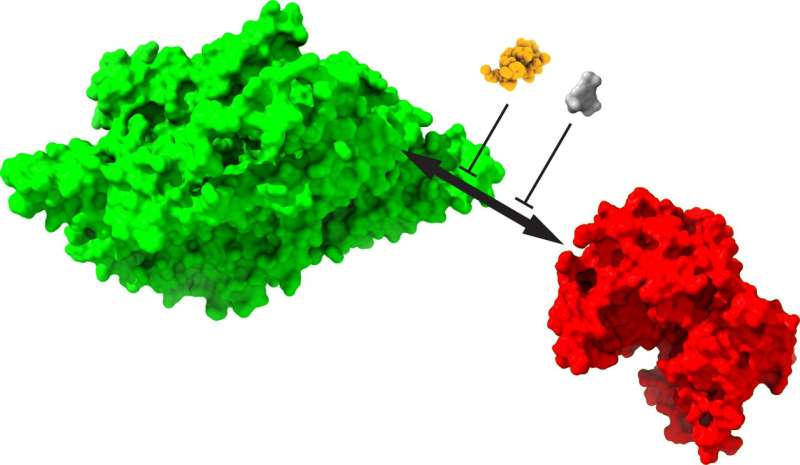
Reminiscences are saved by way of the interplay of 2 proteins: a structural protein, KIBRA (inexperienced), that acts as a power synaptic tag, and a synapse-strengthening enzyme, protein kinase Mzeta (pink). Medicine that disrupt the memory-perpetuating interplay (different colours) erase pre-established long-term and far flung reminiscences. Credit score: Changchi Hsieh, Ph.D.
Whether or not it is a first-time talk over with to a zoo or after we realized to experience a bicycle, we now have reminiscences from our childhoods stored neatly into grownup years. However what explains how those reminiscences remaining just about a whole lifetime?
A find out about within the magazine Science Advances, carried out by way of a workforce of world researchers, has exposed a organic cause of long-term reminiscences. It facilities at the discovery of the position of a molecule, KIBRA, that serves as a “glue” to different molecules, thereby solidifying reminiscence formation.
“Earlier efforts to know how molecules retailer long-term reminiscence targeted at the particular person movements of unmarried molecules,” explains André Fenton, a professor of neural science at New York College and probably the most find out about’s essential investigators. “Our find out about displays how they paintings in combination to make sure perpetual reminiscence garage.”
“A less assailable figuring out of the way we stay our reminiscences will lend a hand information efforts to remove darkness from and cope with memory-related afflictions one day,” provides Todd Sacktor, a professor at SUNY Downstate Well being Sciences College and probably the most find out about’s essential investigators.
It is been normal that neurons retailer data in reminiscence because the trend of robust synapses and vulnerable synapses, which determines the connectivity and serve as of neural networks. On the other hand, the molecules in synapses are volatile, regularly shifting round within the neurons, and dressed in out and being changed in hours to days, thereby elevating the query: How, then, can reminiscences be solid for years to a long time?
In a find out about the use of laboratory mice, the scientists targeted at the position of KIBRA, or kidney and mind expressed protein, the human genetic variants of that are related to each excellent and deficient reminiscence. They curious about KIBRA’s interactions with different molecules a very powerful to reminiscence formation—on this case, protein kinase Mzeta (PKMzeta). This enzyme is essentially the most a very powerful molecule for strengthening commonplace mammalian synapses this is identified, but it surely degrades after a couple of days.
Their experiments divulge that KIBRA is the “lacking hyperlink” in long-term reminiscences, serving as a “power synaptic tag,” or glue, that sticks to sturdy synapses and to PKMzeta whilst additionally fending off vulnerable synapses.
“Right through reminiscence formation the synapses concerned within the formation are activated—and KIBRA is selectively situated in those synapses,” explains Sacktor, a professor of body structure, pharmacology, anesthesiology, and neurology at SUNY Downstate. “PKMzeta then attaches to the KIBRA-synaptic-tag and assists in keeping the ones synapses sturdy. This permits the synapses to persist with newly made KIBRA, attracting extra newly made PKMzeta.”
Extra particularly, their experiments within the Science Advances paper display that breaking the KIBRA-PKMzeta bond erases outdated reminiscence.
Earlier paintings had proven that randomly expanding PKMzeta within the mind complements vulnerable or pale reminiscences, which was once mysterious as it must have achieved the other by way of performing at random places, however the power synaptic tagging by way of KIBRA explains why the extra PKMzeta was once reminiscence improving, by way of simplest performing on the KIBRA tagged websites.
“The power synaptic tagging mechanism for the primary time explains those effects which are clinically related to neurological and psychiatric issues of reminiscence,” observes Fenton, who may be at the school at NYU Langone Scientific Middle’s Neuroscience Institute.
The paper’s authors word that the analysis affirms an idea presented in 1984 by way of Francis Crick. Sacktor and Fenton indicate that his proposed speculation to give an explanation for the mind’s position in reminiscence garage regardless of consistent cell and molecular adjustments is a Theseus’s Send mechanism—borrowed from a philosophical argument stemming from Greek mythology by which new planks substitute outdated ones to deal with Theseus’s Send for years.
“The power synaptic tagging mechanism we discovered is similar to how new planks substitute outdated planks to deal with Theseus’s Send for generations, and permits reminiscences to remaining for years even because the proteins keeping up the reminiscence are changed,” says Sacktor.
“Francis Crick intuited this Theseus’s Send mechanism, even predicting the position for a protein kinase. Nevertheless it took 40 years to find that the elements are KIBRA and PKMzeta and to figure out the mechanism in their interplay.”
The find out about additionally integrated researchers from Canada’s McGill College, Germany’s College Health facility of Münster, and College of Texas Scientific Faculty at Houston.
Additional information:
Panayiotis Tsokas et al, KIBRA anchoring the motion of PKMζ maintains the endurance of reminiscence, Science Advances (2024). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adl0030. www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adl0030
Supplied by way of
New York College
Quotation:
Analysis uncovers ‘molecular glue’ that is helping be sure reminiscence formation and stabilization (2024, June 26)
retrieved 27 June 2024
from
This file is matter to copyright. Excluding any honest dealing for the aim of personal find out about or analysis, no
section could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions simplest.














