Antarctic sea ice is “behaving unusually” and may have entered a “new regime”, the director of america Nationwide Snow and Ice Information Centre (NSIDC) tells Carbon Transient.
Following an rock bottom most in September 2023, Antarctic sea ice has been monitoring at near-record-low extent for the previous six months. Final month, it hit its 2024 minimal extent, tying with 2022 for the second-lowest Antarctic minimal within the 46-year satellite tv for pc listing.
Dr Mark Serreze, director of the NSIDC tells Carbon Transient that extra heat ocean water is attaining the outside to soften ice and stay it from forming. He says that we “will have to wait and notice” whether or not it is a “transient impact” or whether or not the Antarctic has entered a “new regime”.
In the meantime, Arctic sea ice has reached its most extent for the 12 months, peaking at 15.01m sq. kilometres (km2) on 14 March. The provisional knowledge from the NSIDC displays that this 12 months’s Arctic iciness height, in spite of beneficial winds that inspired sea ice formation, was once 640,000km2 smaller than the 1981-2010 common most.
This 12 months’s most was once the 14th lowest within the satellite tv for pc listing.
“Total, the street stays downhill for Arctic sea ice, however it’s fairly bumpy alongside the best way,” every other scientist tells Carbon Transient. This moderately excessive iciness height is “notable and a just right reminder that we need to keep in touch and account for this kind of climate variability after we speak about Arctic local weather alternate”, he says.
He provides that even supposing the utmost is excessive in comparison to contemporary years, the ice continues to be “a lot thinner” than it was once a couple of a long time in the past. The “huge protection of this thinner ice” method overall Arctic sea ice quantity for the month of February was once the 1/3 lowest on listing.
Arctic iciness height
Arctic sea ice extent adjustments during the 12 months. It grows every iciness sooner than attaining its height for the 12 months in February or March after which melts during the spring and summer time against its annual minimal, normally round September.
The use of satellite tv for pc knowledge, scientists can observe the expansion and soften of sea ice, letting them decide the scale of the ice sheet’s iciness most and summer time minimal extent. Those are key metrics to observe the “well being” of the Arctic sea ice.
The NSIDC’s announcement says that this 12 months’s Arctic iciness height of 15.01m is “under common”. Clocking in at 640,000km2 under the 1981-to-2010 common most extent, it ranks because the 14th lowest within the satellite tv for pc listing.
The NSIDC provides that the date of the utmost this 12 months, 14 March, was once two days later than the 1981-to-2010 common date of 12 March.
The plot under displays Arctic sea ice extent on 14 March, with the typical sea ice extent for 1981-2010 proven by means of the orange line.
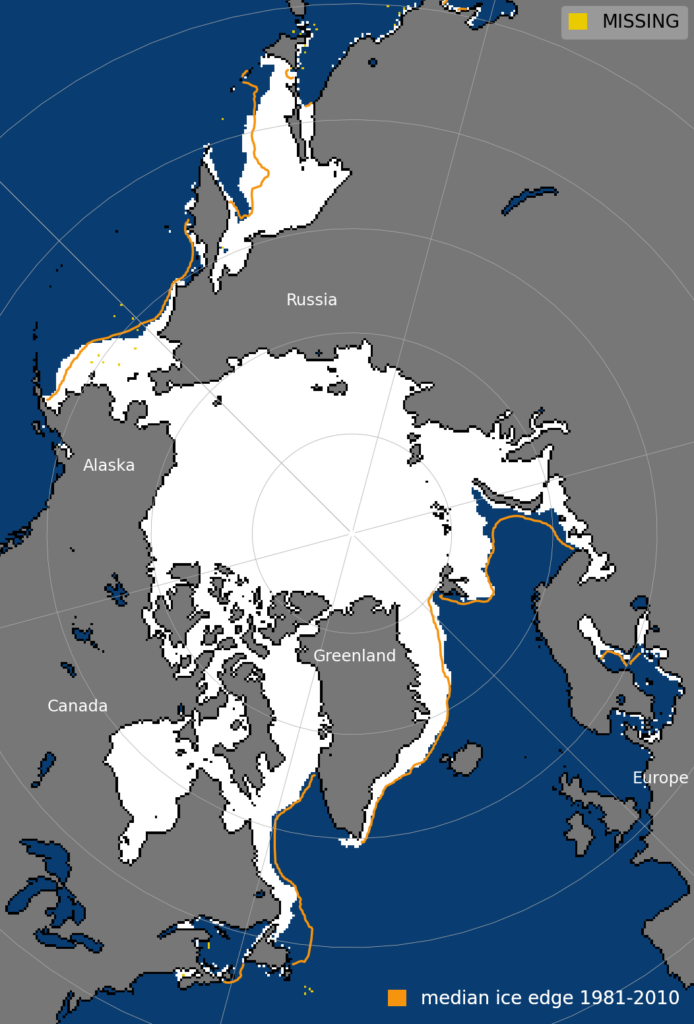 Arctic sea ice extent on 14 March 2024. Median sea ice edge for 1981-2010 is proven in orange. Supply: NSIDC.
Arctic sea ice extent on 14 March 2024. Median sea ice edge for 1981-2010 is proven in orange. Supply: NSIDC.
Arctic freeze
“The street stays downhill for Arctic sea ice, however it’s fairly bumpy alongside the best way,” Dr Zack Labe – a postdoctoral researcher running at NOAA Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory and the atmospheric and oceanic sciences programme at Princeton College – tells Carbon Transient. He provides:
“Whilst this iciness was once over again in keeping with the long-term pattern towards a hotter Arctic with much less ice, regional climate patterns can nonetheless give a contribution to ice enlargement and slower internet declines, particularly if the winds align from a north-to-south path.”
Arctic sea ice reached its minimal extent for 2023 on 19 September.
With an extent of four.23m km2, this was once the sixth-lowest minimal on listing and 1.99m km2 under the typical minimal recorded over 1981-2010.
Following its annual minimal, Arctic sea ice enlargement was once “slower than common”, resulting in the fifth-lowest September on listing, consistent with the NSIDC.
Labe tells Carbon Transient that the freeze season began with “well-liked open water around the Pacific facet of the Arctic, with large spaces of ice lacking north of Alaska”, which contributed to “well-above-average temperatures” within the area.
All over October, alternatively, sea ice extent higher by means of 119,800km2 in keeping with day – quicker than the 1981-2010 common of 89,200km2 in keeping with day, consistent with the NSIDC.
The Arctic freeze up was once “in particular fast” within the seas round Siberia. By means of the top of October, the ice quilt had reached the Siberian coast, even supposing open water remained within the Beaufort and Chukchi Seas.
Air temperatures over the Arctic Ocean, round 2,500 toes above floor stage, have been most commonly above common throughout October – in particular in and across the Canadian Archipelago, which noticed temperatures of 4-5C above common.
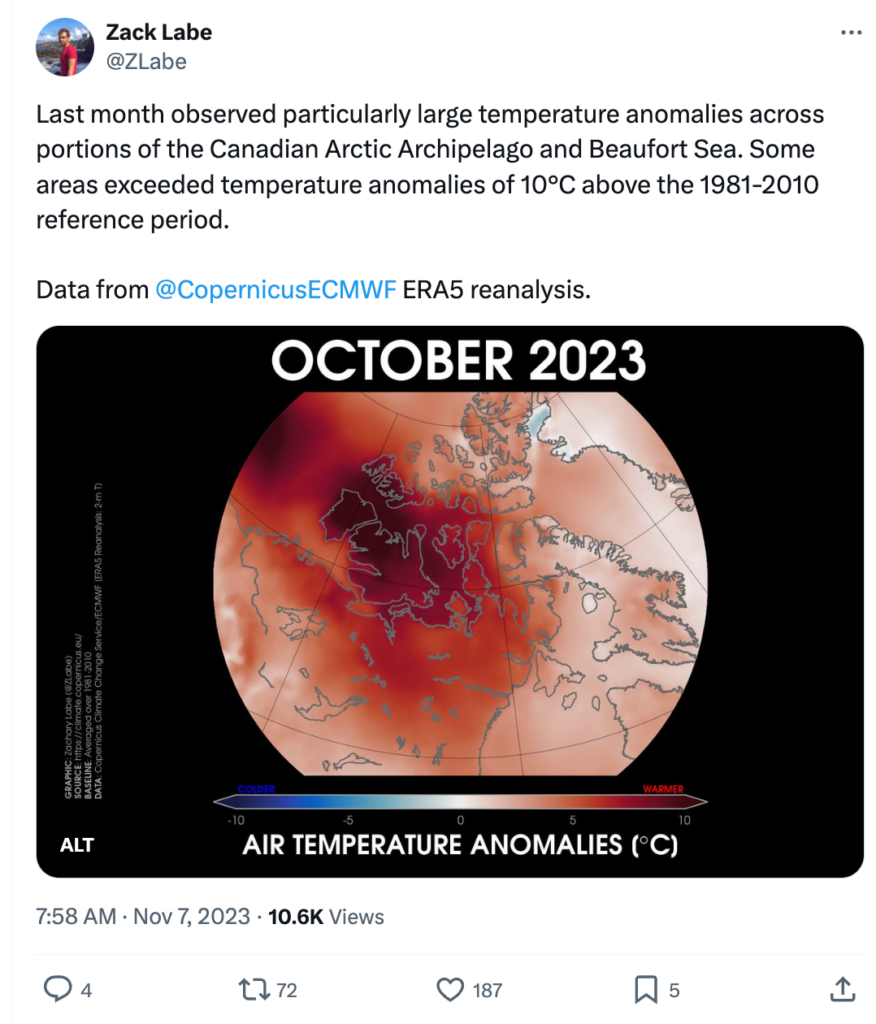
Labe tells Carbon Transient that, general, the Arctic iciness can also be characterized by means of “extraordinary heat within the northern Arctic, however higher overall ice extent”. This “counterintuitive” dynamic was once brought about by means of atmospheric circulate patterns, which resulted in “hotter, wet air blowing towards the north pole, whilst northerly winds give a contribution to increasing ice within the Greenland Sea and Sea of Okhotsk”, he says.
All over November, Arctic sea ice extent endured to extend quicker than common. Alternatively, the NSIDC says the freeze up “quickly stalled” for round 5 days from 22 November, as a sequence of 3 tropical cyclones introduced heat, wet air into the north Atlantic.
The NSIDC says {that a} aggregate of low strain to the north and west of Svalbard and a high-pressure centre to the south-east “created a powerful, continual drift from the south of moderately heat and wet air from the north Atlantic Ocean towards Svalbard”.
This drift of air can also be observed as “an extension of an atmospheric river into the Arctic”, it says. It provides that the sturdy winds “helped to push the ice edge within the east Greenland and Barents seas northwards, restricting new ice formation”.
The NSIDC notes that pauses in Arctic sea ice freeze up have took place in November sooner than, in 2013 and 2016, making such occasions “uncommon, however no longer unknown”.
Arctic sea ice extent endured to extend “markedly quicker” than same old during December, the NSIDC says. It provides that “sea ice formation in Hudson Bay was once surprisingly overdue, however the ice quilt expanded temporarily from west to east in mid-December”.
For December general, 2023 noticed the third-highest per 30 days acquire on listing, with 2.71m km2 of sea ice extent added during the month. Moderate Arctic sea ice extent over December 2023 was once the 9th lowest within the satellite tv for pc listing, at 12m km2.
Arctic sea ice extent endured to transport down the scores as the brand new 12 months rolled in, in spite of slower-than-average ice enlargement. Actually, the NSIDC says that Arctic sea ice extent in truth declined for a couple of days on the finish of the month, even supposing it notes that that is “no longer extraordinary right now of 12 months” and says it’s “brought about by means of climate techniques that quickly halt ice enlargement or push the ice northwards”.
The typical Arctic sea ice extent for January 2024 was once 13.92m km2 – the 20 th lowest on listing.
This relatively excessive sea ice extent is “notable and a just right reminder that we need to keep in touch and account for this kind of climate variability after we speak about Arctic local weather alternate”, Labe tells Carbon Transient.
Arctic sea ice extent endured to develop during February, gaining 15.3m km2 of ice during the month. The February 2024 extent of 14.61m km2 was once 690,000km2 under the 1981-2010 February common extent, and tied with 2022 because the fifteenth lowest on listing, consistent with the NSIDC.
Temperatures are normally “well-below freezing” over the Arctic Ocean in February, however the NSIDC notes that during 2024, they weren’t as little as same old for the time of 12 months. Over the central Arctic ocean, air temperatures at 2,500 toes above sea stage have been as much as 10C hotter than common.
Labe notes that even supposing sea ice extent was once excessive in comparison to contemporary years, the ice continues to be “a lot thinner” than it was once a couple of a long time in the past:
“General Arctic sea-ice quantity ended up because the 1/3 lowest on listing for the month of February because of the huge protection of this thinner ice.”
Variability and long-term decline of February #Arctic sea-ice thickness and sea-ice quantity… (anomalously low for 2024)+ Information data: percent.twitter.com/a51VTWKFVA— Zack Labe (@ZLabe) March 10, 2024
Antarctic ‘behaving unusually’
In the meantime, on the Earth’s different pole, Antarctic sea ice hit its summer time minimal sea ice extent on 20 February. With an extent of one.99m km2, this 12 months’s minimal ties with 2022 because the second-lowest on listing, the NSIDC studies.
The plot under displays Antarctic sea ice extent on 20 February 2024, with the median sea ice extent for 1981-2010 proven by means of the orange line.
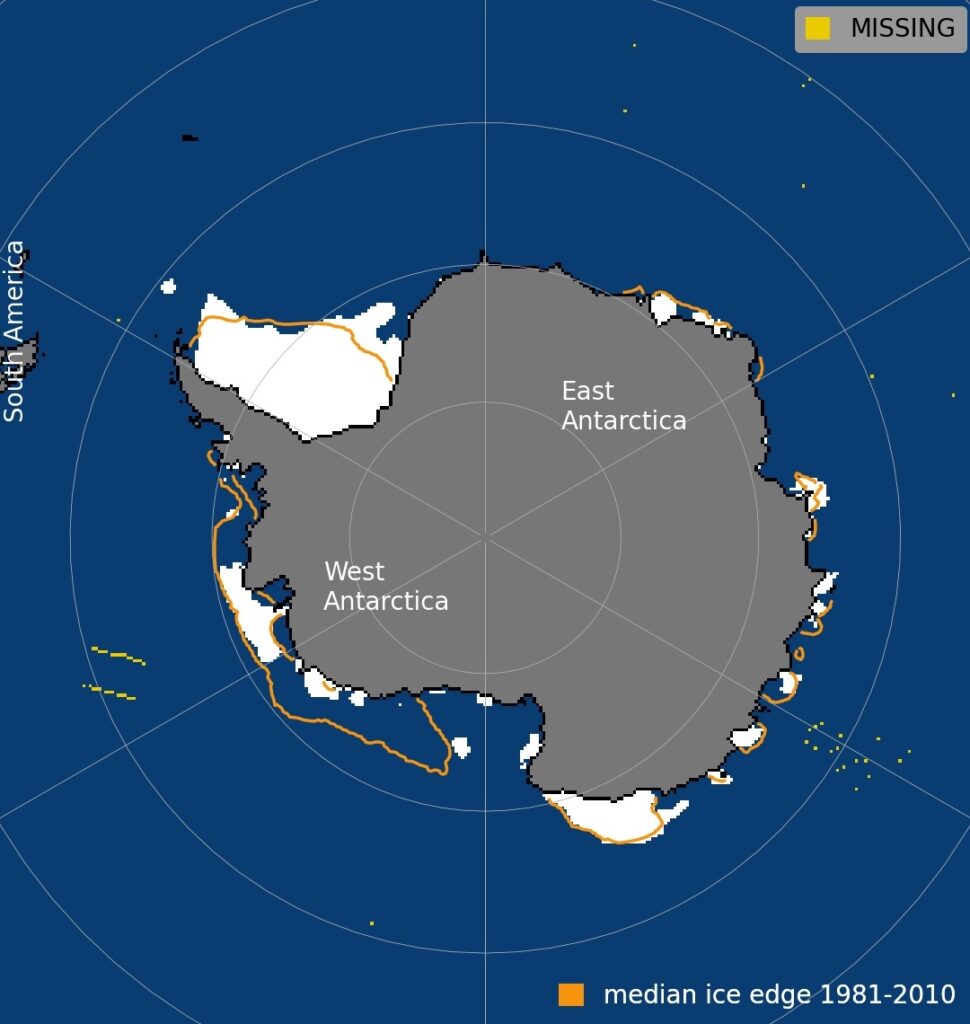 Antarctic sea ice extent on 20 February 2024. Median sea ice edge for 1981-2010 is proven in orange. Supply: NSIDC.
Antarctic sea ice extent on 20 February 2024. Median sea ice edge for 1981-2010 is proven in orange. Supply: NSIDC.
The Antarctic minimal was once 850,000km2 smaller than the 1981-to-2010 common summer time low of two.84m km2, however 200,000km2 higher than the former listing low set on 21 February 2023.
This 12 months marks the 1/3 consecutive minimal Antarctic sea ice extent under 2m km2. The desk under displays the 5 years with the bottom minimal Antarctic sea ice extent on listing, which contains 2022, 2023 and 2024 against the highest.
RankYearMinimum ice extent (m km2)Date
120231.7921 Feb
22022
1.9825 Feb
2=20241.9920 Feb
420172.113 March
520182.2221 Feb
“The Antarctic has been behaving unusually,” Dr Mark Serreze, director of the NSIDC, tells Carbon Transient. He continues:
“Up to now few years, [southern hemisphere] summer time extent has dropped to listing lows. Ahead of that, we noticed listing highs! What has modified?
“The solution turns out to lie within the ocean – extra heat water getting up the the outside to soften ice or stay it from forming. Is that this a brief impact, or, as many have argued, have we entered a ‘new regime’ during which the sea will proceed to strongly impact the ocean ice? Once more, we will have to wait and notice.”
Document-breaking Antarctic extent
Antarctic sea ice has been monitoring at or close to record-low ranges for months.
The Antarctic set a record-low most on 10 September 2023, with an extent of 16.96m km2. This was once “the bottom sea ice most within the 1979 to 2023 sea ice listing by means of a large margin”, and one of the most earliest, the NSIDC says.
Antarctic stipulations over 2023 have been “in point of fact outstanding” and “utterly outdoor the limits of normality”, one professional informed Carbon Transient.
As 2023 improved, Antarctic sea ice soften was once “slower than common”, the NSIDC says. The entire decline in Antarctic sea ice extent thru October was once 903,000km2, whilst the October common was once 985,000km2.
However, Antarctic sea ice extent endured to trace at a listing low. On 31 October 2023, Antarctic sea ice extent was once nonetheless monitoring at a record-low of 15.79m km2. That is 750,000km2 under the former 31 October listing low.
The decline in Antarctic sea ice paused for a couple of days from 9 November, permitting sea ice extent to creep above the November 2016 worth, the NSIDC says. This marked the primary time that the day-to-day 2023 Antarctic sea ice extent was once no longer the bottom within the listing since early Might 2023. By means of the beginning of December, Antarctic sea ice extent was once once more at a listing low, it notes.
The Antarctic noticed within the new 12 months with a sea ice extent of 6.37m km2, marking the sixth-lowest New Yr’s Day Antarctic sea ice extent on listing, the NSIDC says. Ice melted swiftly during the month, and by means of the top of January, day-to-day Antarctic sea ice extent reached 2.58m km2 – tying with 2017 for moment lowest on listing.
Sharelines from this tale














