If you find yourself looking to continue to exist within the freezing desolate tract of Antarctica, you wish to have all of the lend a hand you’ll get – and it kind of feels that some marine worms keep alive via forming relationships with micro organism that produce a type of herbal antifreeze.
Those micro organism finally end up dwelling within the worms, and in go back for the hospitality, they secrete protein components to give protection to towards the icy water temperatures.
It is crucial step ahead in our working out of the relationships between microbes and the organisms they’ve a mutually really helpful hyperlink to, in step with the group in the back of the learn about, which was once made up of researchers from a couple of establishments in Italy.
“Multicellular organisms within the oceans are living in shut affiliation with their microbiomes, which give their hosts with key purposes together with nutrient provide, protection mechanisms, or even further metabolic pathways,” write the researchers of their printed paper.
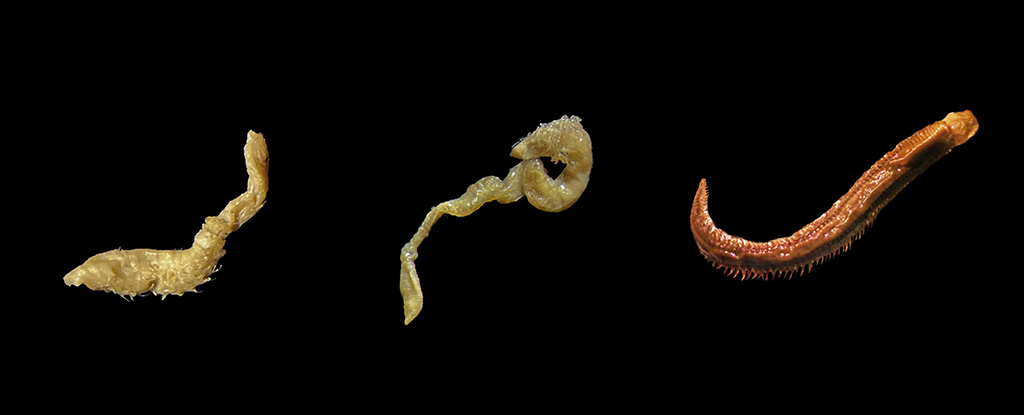
The group traveled to a number of coastal spaces in Antarctica to select up sediment samples, discovering the 3 worms: polychaetes (Leitoscoloplos geminus, Aphelochaeta palmeri, and Aglaophamus trissophyllus ). The common water temperature was once 1 °C beneath freezing, too chilly for those worms to continue to exist on their very own.
Input the Meiothermus and Anoxybacillus micro organism, running to struggle freezing from within the worms.
Particularly, proteins in those micro organism produce the chemical compounds proline and glycol, which decrease the freezing level in their inside liquids, combating ice from forming inside of their cells, simply as antifreeze does within liquids.
Different creatures in those excessive environments can produce identical antifreeze proteins themselves, with icefish being one instance. It will appear that those worms want somewhat symbiotic lend a hand from the native micro organism.
“Those findings recommend that the bacterial core contributors of Antarctic polychaetes are pushed via the organic interactions between hosts and related micro organism,” write the researchers.
The researchers assume this dating has been occurring for a protracted, very long time – most likely serving to those species to determine themselves in Antarctica – with generations of those marine worms passing the micro organism on down throughout the generations. On the other hand, extra analysis shall be had to ascertain that.
As for the way this new wisdom may well be implemented, one house the place it might be used is within the box of cryopreservation: holding cells preserved however alive in freezing temperatures. In fact, it additionally offers us recent perception into the sophisticated steadiness of marine lifestyles in Antarctica, a steadiness that is still threatened via expanding temperatures.
We all know that dwelling in those stipulations way quite a lot of sorts of adaptation to take advantage of what assets are to be had, and to struggle the stipulations that will in a different way make lifestyles within the icy wastes not possible.
“The findings of this learn about open wider views at the comprehension of the mechanisms of adaptation and cryo-resistance of marine invertebrates mediated via related micro organism,” write the researchers.The analysis has been printed in Science Advances.
Antarctic Worms Have an Superb Secret For Surviving Fatal Icy Water