A shocking new discovery of historical human stays in Africa — with remarkably well-preserved DNA — is redrawing the map of human populations in new and thrilling techniques.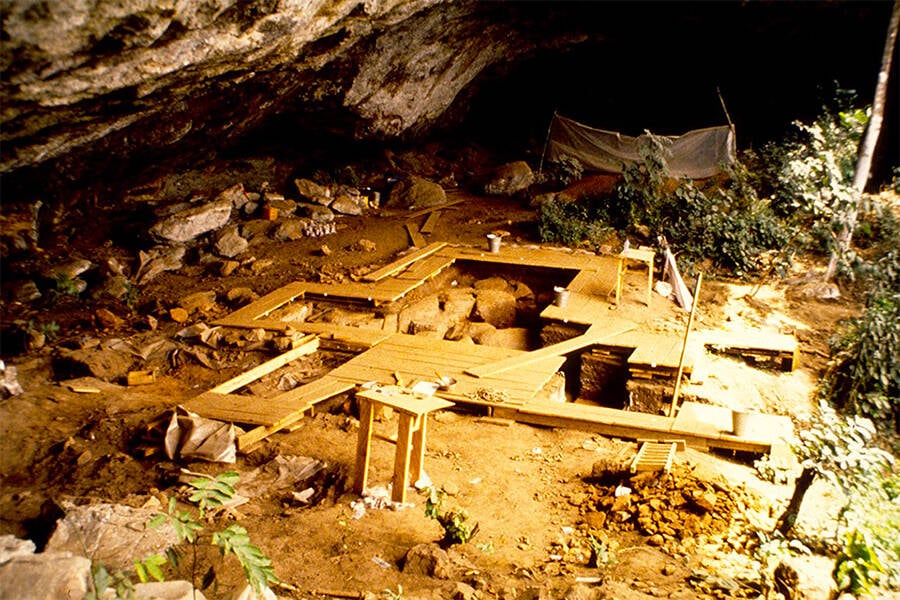 Pierre de Maret/St. Louis UniversityThe rock refuge at Shum Laka, the place the stays of 4 historical kids have been discovered.
Pierre de Maret/St. Louis UniversityThe rock refuge at Shum Laka, the place the stays of 4 historical kids have been discovered.
In finding out the origins of humanity, many mavens start in Africa, the place historical Homo sapiens arrived about 250,000 years in the past. On the other hand, one in an instant runs into an issue that has inhibited deeper analysis into humanity’s birthplace since we started in search of it.
The local weather of Central Africa used to be lengthy believed to be too scorching and humid for historical DNA to live to tell the tale. Previously, this has made detailed genetic examinations of prehistoric human stays — which can be very important equipment in monitoring ancient migration patterns — on this area very tricky.
However now, a burial website with 4 skeletons buried hundreds of years in the past has been present in Cameroon with remarkably well-preserved DNA. It now not handiest provides perception into the ancient variety of the realm, but additionally issues to a hidden “ghost inhabitants” of people in the past unknown to scientists.
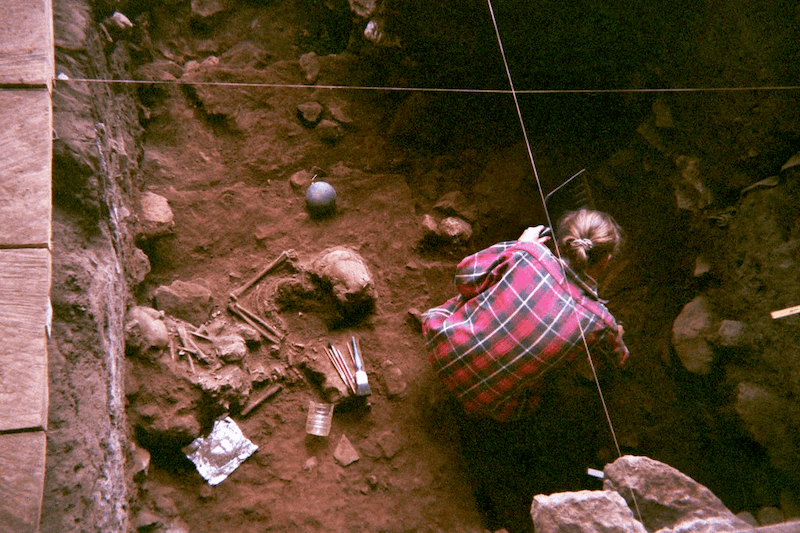
In a learn about printed within the magazine Nature, geneticists and archaeologists recovered DNA-rich samples from the interior ear bones of 4 kids buried at Shum Laka, a well-known archaeological website.
This website in western Central Africa sits in the midst of what researchers name the cradle of the Bantu languages, a linguistic base that bureaucracy a wide selection of African languages spoken via a few 3rd of the continent’s inhabitants.

 Isabelle RibotThe Shum Laka rock refuge in Cameroon, the place the traditional stays have been came upon.
Isabelle RibotThe Shum Laka rock refuge in Cameroon, the place the traditional stays have been came upon.
So it got here as a wonder when the researchers tested the DNA they accumulated from kids buried from about 3,000 to eight,000 years in the past on the website and located that their ancestry differed particularly from that of maximum Bantu-speakers residing as of late.
“This consequence means that Bantu-speakers residing in Cameroon and throughout Africa as of late don’t descend from the inhabitants to which the Shum Laka kids belonged,” mentioned Mark Lipson, Ph.D., Harvard Scientific College, who’s the learn about’s lead creator. “This underscores the traditional genetic variety on this area and issues to a in the past unknown inhabitants that contributed handiest small proportions of DNA to present-day African teams.”
Effects confirmed that the kids have been maximum carefully associated with hunter-gatherers just like the Baka and Aka teams historically referred to as “pygmies.” One of the vital samples additionally carried a unprecedented genetic marker within the Y-chromosome this is discovered nearly solely in the similar area as of late.
Because of this new to find, scientists now have a greater concept of the range of African teams that inhabited this a part of the continent prior to the Bantus started settling down within the grassy highlands.
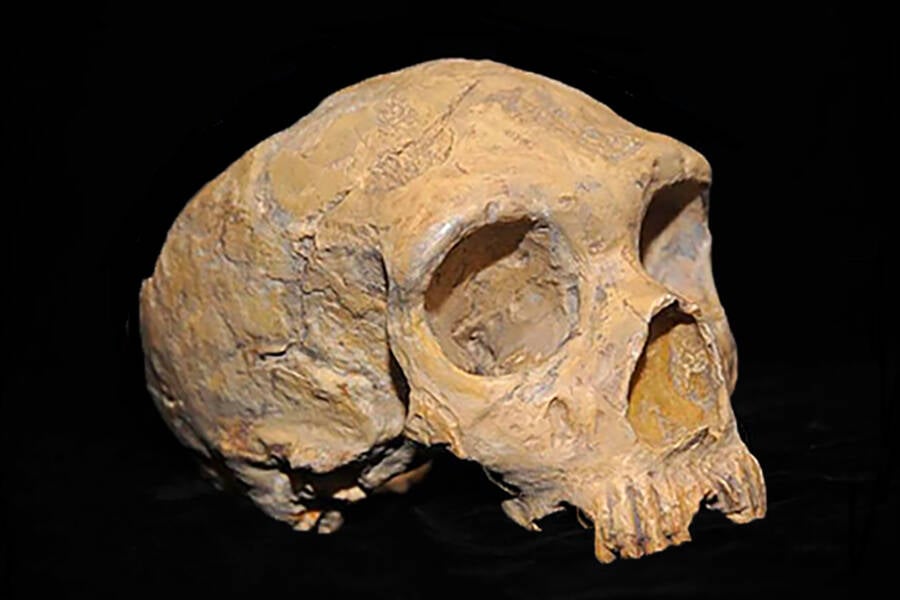
 Wikimedia CommonsOne of the primary Neanderthal fossils, present in Gibraltar close to North Africa in 1848.
Wikimedia CommonsOne of the primary Neanderthal fossils, present in Gibraltar close to North Africa in 1848.
“Those effects spotlight how the human panorama in Africa only a few thousand years in the past used to be profoundly other from what it’s as of late, and emphasize the facility of historical DNA to raise the veil over the human previous that has been forged via fresh inhabitants actions,” mentioned David Reich, Ph.D., the senior creator of the learn about.
The proof of any such “ghost inhabitants,” in the meantime, got here after the geneticists in comparison the kids’s DNA with any other historical DNA pattern taken from a 4,500-year-old specimen present in Mota Collapse Ethiopia and sequences from different historical and residing Africans.
The use of statistical comparisons, the crew used to be in a position to provide an interesting new style that pushes again the Central African hunter-gatherer origins from about 200,000 to 250,000 years in the past.
Now that you simply’ve examine this new discovery of historical African skeletons — and their ties to a conceivable “ghost” inhabitants of historical people — take a look at this tale of the oldest skeleton ever discovered out of doors of Africa. Then, take a look at this tale of the oldest virus ever pulled from a human skeleton — and the way it’s nonetheless affecting us even now.