It most effective took 3 items of proof, in combination, to fully revolutionize our image of the Universe within the early twentieth century. We had up to now assumed that the Universe was once static and unchanging, and that the whole thing of life was once contained inside the Milky Means. The spiral and elliptical nebulae within the sky had been assumed to be gadgets — most likely newly forming protostars — inside our personal galaxy. And but, through the past due Twenties, the blended details of:
Einstein’s normal relativity superseding Newton’s common gravitation as our concept of gravity,
person stars being seen in the ones spiral and elliptical nebulae, permitting us to substantiate their extragalactic nature and to compute the space to them,
and the observational moving of atomic traces towards both redder or bluer wavelengths from spiral and elliptical galaxies,
overturned that image completely. The Universe, at the biggest of cosmic scales, wasn’t static and unchanging in any respect, however moderately was once dynamically increasing.If that’s true, and the Universe is increasing, then what else is increasing at the side of it? Is our galaxy increasing? What in regards to the Sun Device, planet Earth, and even the atoms in our personal frame? That’s the subject of this week’s inquiry courtesy of Jim Robison, who asks:“We’re a part of the increasing universe. Does that imply we’re increasing with it? Is the space between the Earth and the Solar increasing, or between San Francisco and New York? Is the space between the atoms in my frame increasing? Is that why I desire a higher belt?”Whilst many people to find ourselves certainly combating our personal “fight of the bulge” as we age, you’ll be able to’t fairly blame that one at the increasing Universe. Right here’s how one can make sense of what’s — and isn’t — suffering from cosmic enlargement.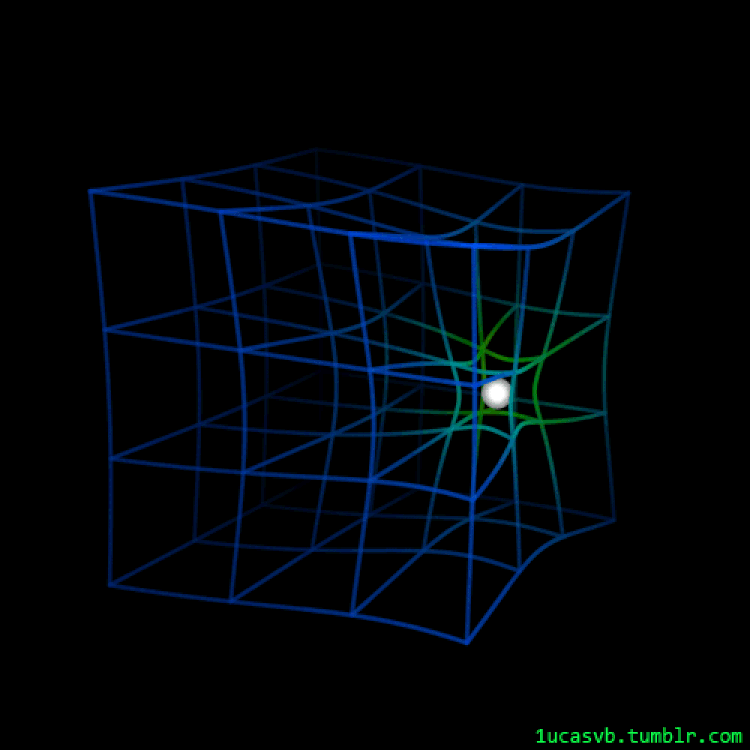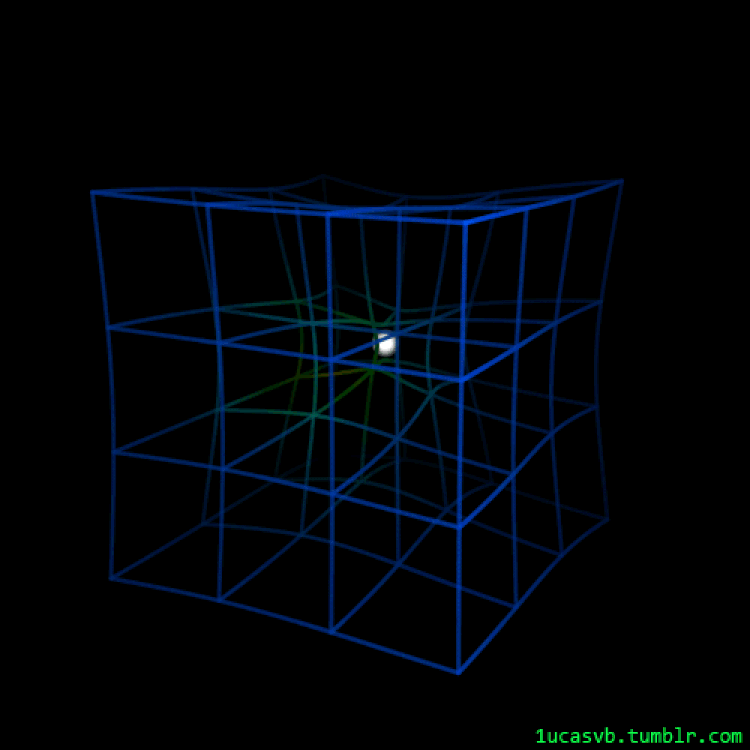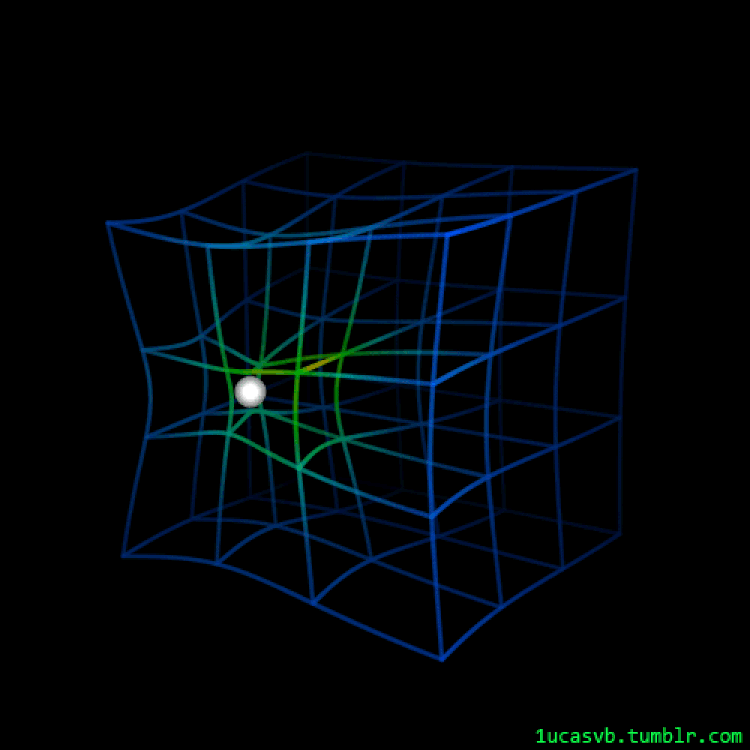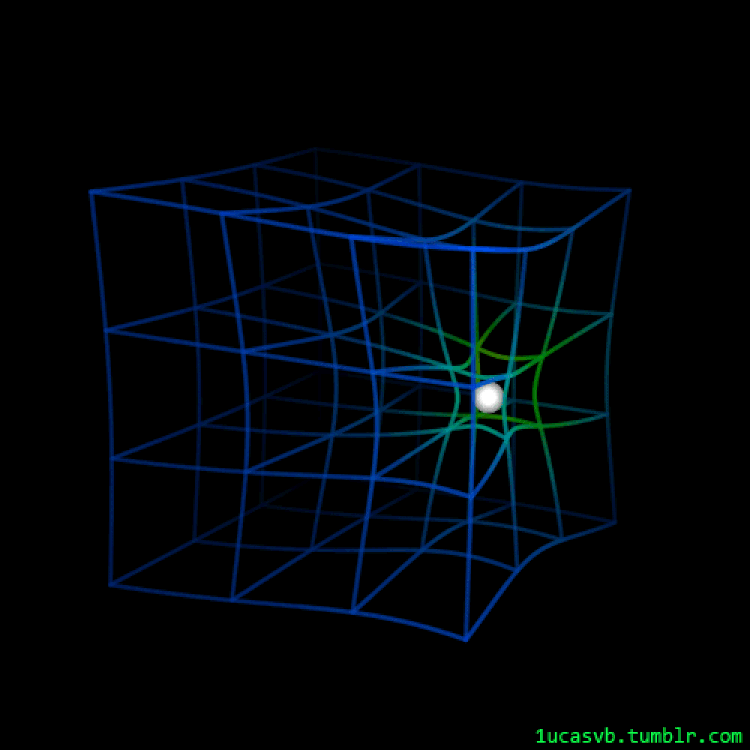 An animated have a look at how spacetime responds as a mass strikes via it is helping exhibit precisely how, qualitatively, it isn’t simply a sheet of material. As a substitute, all of three-D area itself will get curved through the presence and houses of the topic and effort inside the Universe. A couple of lots in orbit round one every other will motive the emission of gravitational waves, whilst any gentle passing via a area that accommodates this distorted spacetime will likely be bent, distorted, and most likely magnified through the consequences of curved area.
An animated have a look at how spacetime responds as a mass strikes via it is helping exhibit precisely how, qualitatively, it isn’t simply a sheet of material. As a substitute, all of three-D area itself will get curved through the presence and houses of the topic and effort inside the Universe. A couple of lots in orbit round one every other will motive the emission of gravitational waves, whilst any gentle passing via a area that accommodates this distorted spacetime will likely be bent, distorted, and most likely magnified through the consequences of curved area.
Credit score: LucasVB
Theoretical beginningsWhen Einstein first put forth his normal concept of relativity in past due 1915, it reimagined gravity no longer as an invisible, immediate pressure between two bodily separated large gadgets (what Newton referred to as “motion at a distance”), however moderately because of the curvature of the very cloth of spacetime itself. Mass and effort, in step with Einstein, would motive the material of spacetime to twist, bend, distort, or even evolve in a selected model, after which no matter construction that spacetime takes on determines how the matter-and-energy provide inside it strikes and evolves. To paraphrase John Wheeler, topic tells spacetime how one can curve, after which that curved spacetime tells topic how one can transfer.As a result of Einstein’s area equations are extraordinarily normal — and are in a position to describing any spacetime that would conceivably exist, even though most effective in our imaginations — it’s as much as us to extract what are referred to as “answers” to these equations. The most straightforward actual resolution is for totally empty, flat, non-evolving spacetime: the (Minkowski) spacetime of particular relativity. The following-simplest resolution, additionally derived through Einstein, was once for the weak-field restrict (i.e., being a long way away) from a unmarried level mass: the (nearly Newtonian-like) spacetime of a mass at a distance. However over the following couple of months and, later, years, quite a few essential, and unique, answers had been discovered.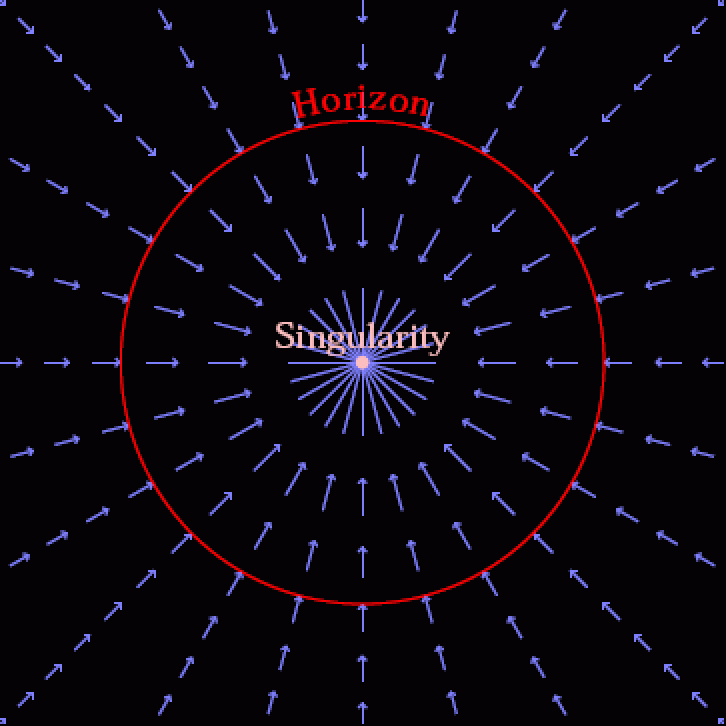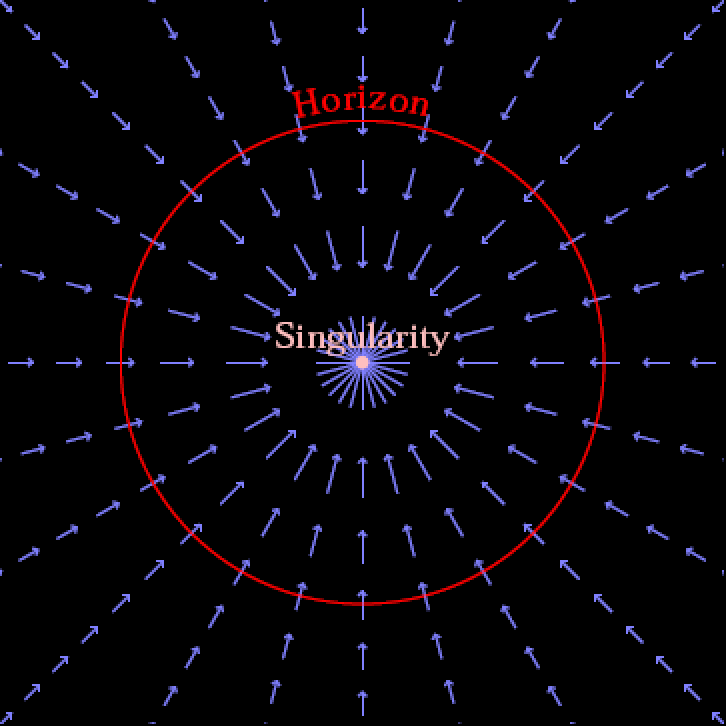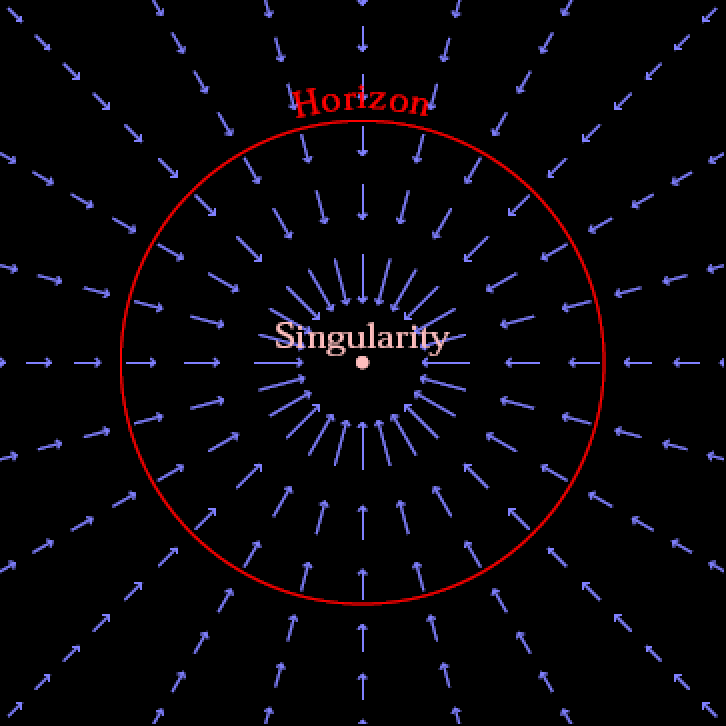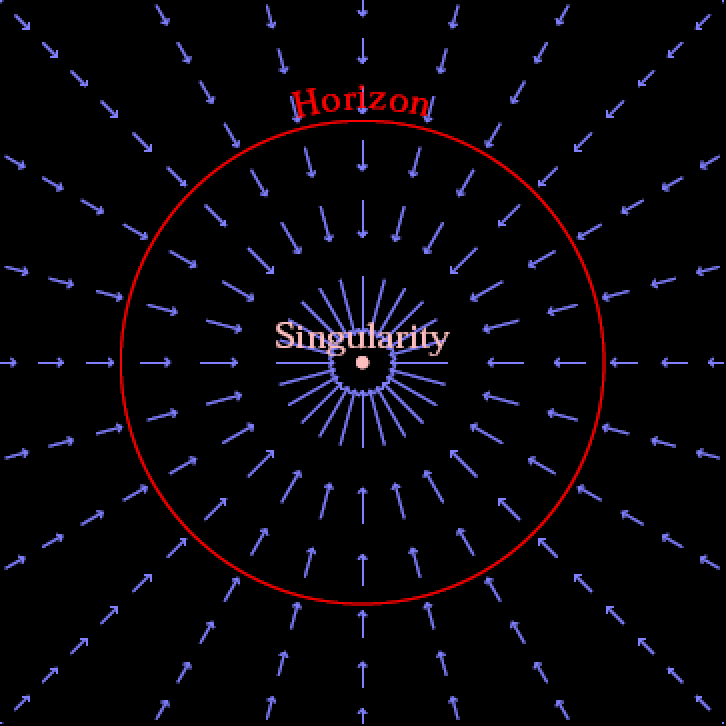 Each outside and inside the development horizon of a Schwarzschild black hollow, area flows like both a shifting walkway or a waterfall, relying on how you wish to have to visualise it. On the tournament horizon, even though you ran (or swam) on the pace of sunshine, there can be no overcoming the drift of spacetime, which drags you into the singularity on the middle. Outdoor the development horizon, regardless that, different forces (like electromagnetism) can often triumph over the pull of gravity, inflicting even infalling topic to flee.
Each outside and inside the development horizon of a Schwarzschild black hollow, area flows like both a shifting walkway or a waterfall, relying on how you wish to have to visualise it. On the tournament horizon, even though you ran (or swam) on the pace of sunshine, there can be no overcoming the drift of spacetime, which drags you into the singularity on the middle. Outdoor the development horizon, regardless that, different forces (like electromagnetism) can often triumph over the pull of gravity, inflicting even infalling topic to flee.
Credit score: Andrew Hamilton/JILA/College of Colorado
In 1916, Karl Schwarzschild wrote down the spacetime resolution for some degree mass with out being limited to weak-field assumptions: now equated with the case of a non-rotating black hollow.
In 1917, Willem de Sitter wrote down the spacetime resolution for a Universe stuffed with a cosmological consistent: what we now name de Sitter area, and which describes each cosmic inflation and darkish calories.
And in 1922, Alexander Friedmann wrote down the spacetime resolution for a Universe crammed — uniformly — with any species (and even more than one species) of topic and/or calories.
Relating to a black hollow, or every other spacetime that’s ruled through a sure construction, the spacetime doesn’t increase and gadgets inside it don’t recede from one every other. On the other hand, within the latter two instances, it seems that the spacetime for a Universe that’s crammed uniformly with “stuff,” whether or not a cosmological consistent, topic, radiation, or every other species of calories, can’t be static and solid, however will have to evolve: both increasing or contracting over the years.The perception that spacetime can evolve over the years, depending on what’s in it, is sort of as previous as normal relativity itself, and is one thing that sprang forth from Einstein’s equations without delay. That doesn’t imply it was once simply authorised, then again, together with through Einstein himself. As was once first famous through Vesto Slipher again within the 1910s, probably the most gadgets we follow display the spectral signatures of absorption or emission of explicit atoms, ions, or molecules, however with a scientific shift towards both the pink or blue finish of the sunshine spectrum. When blended with distance measurements for the ones gadgets, this information gave upward thrust to the preliminary concept of the increasing Universe: the farther away a galaxy is, the larger its gentle will seem redshifted to our eyes and tools.
As was once first famous through Vesto Slipher again within the 1910s, probably the most gadgets we follow display the spectral signatures of absorption or emission of explicit atoms, ions, or molecules, however with a scientific shift towards both the pink or blue finish of the sunshine spectrum. When blended with distance measurements for the ones gadgets, this information gave upward thrust to the preliminary concept of the increasing Universe: the farther away a galaxy is, the larger its gentle will seem redshifted to our eyes and tools.
Credit score: Vesto Slipher, 1917, Proc. Amer. Phil. Soc.
Observational confirmationIn the 1910s, astronomer Vesto Slipher used the methodology of spectroscopy to damage the sunshine from astronomical assets into its element wavelengths. As you’d be expecting, each time you carried out spectroscopy in a lab or on our personal Solar, you’d to find that atoms of a selected species — hydrogen, helium, calcium, potassium, and so on. — all the time each emitted and absorbed gentle on the identical set of wavelengths: wavelengths that corresponded to the quantum transition of electrons inside that atom.Whilst you as a substitute carried out spectroscopy on a kind of spiral or elliptical nebulae, then again, you’d see one thing other: all of those self same spectral traces nonetheless exist, however they’re all shifted through a multiplicative issue towards both longer wavelengths (if the issue is bigger than 1) or shorter wavelengths (if the issue is lower than 1). Shifts to longer wavelengths are referred to as redshifts, as a result of pink colours are at longer wavelengths, while shifts to shorter wavelengths are referred to as blueshifts, as blue colours are at shorter wavelengths.Now, right here was once the kicker to Slipher’s observations: the nebulae that glance higher and brighter within the sky — possibly as a result of they’re nearer — had been a mixture of redshifted and blueshifted, and most effective through small quantities, however the nebulae that glance smaller and fainter had been all redshifted, and through a lot larger quantities.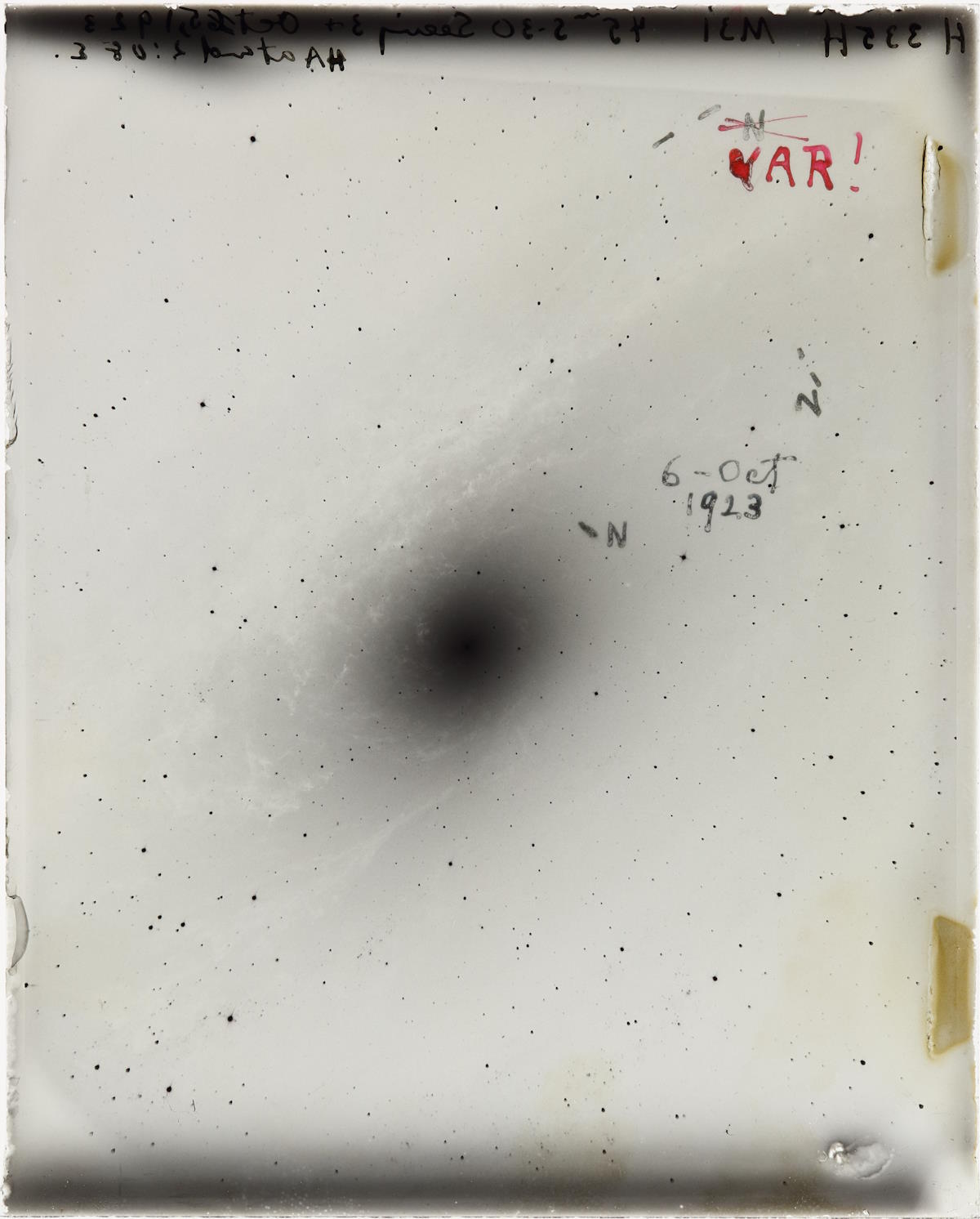 Most likely probably the most well-known photographic plate in all of historical past, this symbol from October of 1923 options the good nebula (now galaxy) in Andromeda at the side of the 3 novae that Hubble seen inside them. When a fourth brightening tournament took place in the similar location as the primary, Hubble identified this was once no nova, however a Cepheid variable megastar. The “VAR!” written in pink pen was once Hubble having a impressive realization: this supposed Andromeda was once an extragalactic object, positioned a long way past the Milky Means.
Most likely probably the most well-known photographic plate in all of historical past, this symbol from October of 1923 options the good nebula (now galaxy) in Andromeda at the side of the 3 novae that Hubble seen inside them. When a fourth brightening tournament took place in the similar location as the primary, Hubble identified this was once no nova, however a Cepheid variable megastar. The “VAR!” written in pink pen was once Hubble having a impressive realization: this supposed Andromeda was once an extragalactic object, positioned a long way past the Milky Means.
Credit score: Carnegie Observatories
What was once the rationale for this? We were given our subsequent clue in 1923, when Edwin Hubble came upon that faint “flares” within the Nice Nebula in Andromeda — in the beginning mis-identified as novae — if truth be told looked as if it would repeat: indicating their true nature as variable stars, moderately than as novae. On account of prior paintings through Henrietta Leavitt, which established the connection between a variable megastar’s periodicity and the intrinsic brightness of that megastar, lets measure the space to the place those stars are positioned.No longer most effective may just this system now be used to offer us a distance to Andromeda, confirming that the Nice Nebula in Andromeda was once if truth be told neatly out of doors of our Milky Means and was once in reality the Andromeda Galaxy, however lets then prolong it to measure the space to any nebula that contained those identical kinds of variable stars.As Hubble and his assistant, Milton Humason, persevered to measure the distances to quite a few nebulae, a number of different scientists put the important items in combination. First was once Belgian scientist Georges Lemaître, in 1927, who concluded that the Universe was once increasing. (Einstein would write to Lemaître and, dismissively and incorrectly, inform him his arithmetic was once right kind, however his physics was once abominable.) Subsequent was once American scientist Howard Robertson, who independently reached the similar conclusion in 1928. But if Hubble himself then revealed his maximum complete leads to 1929, little question remained: the Universe was once certainly increasing. Edwin Hubble’s unique plot of galaxy distances, from 1929, as opposed to redshift (left), organising the increasing Universe, as opposed to a extra trendy counterpart from roughly 70 years later (correct). Many various categories of gadgets and measurements are used to decide the connection between distance to an object and its obvious pace of recession that we infer from its gentle’s relative redshift with recognize to us. As you’ll be able to see, from the very within sight Universe (decrease left) to remote places over a thousand million light-years away (higher correct), this very constant redshift-distance relation continues to carry. Previous variations of Hubble’s graph had been composed through Georges Lemaître (1927) and Howard Robertson (1928), the use of Hubble’s initial knowledge.
Edwin Hubble’s unique plot of galaxy distances, from 1929, as opposed to redshift (left), organising the increasing Universe, as opposed to a extra trendy counterpart from roughly 70 years later (correct). Many various categories of gadgets and measurements are used to decide the connection between distance to an object and its obvious pace of recession that we infer from its gentle’s relative redshift with recognize to us. As you’ll be able to see, from the very within sight Universe (decrease left) to remote places over a thousand million light-years away (higher correct), this very constant redshift-distance relation continues to carry. Previous variations of Hubble’s graph had been composed through Georges Lemaître (1927) and Howard Robertson (1928), the use of Hubble’s initial knowledge.
Credit score: E. Hubble; R. Kirshner, PNAS, 2004
The fashionable pictureToday, we’ve got measured the redshifts and distance to loads of hundreds of gadgets within the within sight, intermediate, and ultra-distant Universe, from trendy instances the entire as far back as only some hundred million years after the Giant Bang. No longer most effective have we showed that the Universe is increasing, however we’ve used the facility of Friedmann’s unique 1922 equations to decide what the ratios are of the quite a lot of species of calories that permeate all the Universe. We’ve realized that the Universe is product of, nowadays:
68% darkish calories, behaving because the cosmological consistent tested through de Sitter,
27% darkish topic, which acts like a type of mass however that doesn’t enjoy any interplay rather then gravity,
4.9% commonplace topic, which incorporates protons, neutrons, electrons, and the whole lot they arrive to shape,
0.1% neutrinos, which behave as radiation when the Universe is sizzling and younger however then behave as topic when the Universe is chilly and previous,
and zero.01% photons, which all the time behave as radiation.
On cosmic scales, the Friedmann equations let us know what the connection is between the evolution of area — and in particular, the evolution of the space between any two issues in area — and the matter-and-energy contents of the Universe at any second in time. If you’ll be able to measure the growth fee nowadays and the way it’s developed over the years, you’ll be able to decide what’s for your Universe presently, in addition to what it was once like up to now and the way it is going to evolve into the long run. With excellent sufficient observations, we will decide our final destiny. A plot of the obvious enlargement fee (y-axis) vs. distance (x-axis) is in step with a Universe that expanded sooner up to now, however the place remote galaxies are accelerating of their recession nowadays. This can be a trendy model of, extending hundreds of instances farther than, Hubble’s unique paintings. Word the truth that the issues don’t shape a instantly line, indicating the growth fee’s trade over the years. The truth that the Universe follows the curve it does is indicative of the presence, and late-time dominance, of darkish calories.
A plot of the obvious enlargement fee (y-axis) vs. distance (x-axis) is in step with a Universe that expanded sooner up to now, however the place remote galaxies are accelerating of their recession nowadays. This can be a trendy model of, extending hundreds of instances farther than, Hubble’s unique paintings. Word the truth that the issues don’t shape a instantly line, indicating the growth fee’s trade over the years. The truth that the Universe follows the curve it does is indicative of the presence, and late-time dominance, of darkish calories.
Credit score: Ned Wright/Betoule et al. (2014)
However no longer the whole lot expandsAnd but, there are many galaxies that don’t obey the equations for the increasing Universe: a minimum of, no longer in any form of a precise model. As an example, take the galaxies which might be sure in combination within an enormous galaxy cluster. The nearest instance we’ve got is the Virgo cluster, positioned some 55-60 million light-years away. In keeping with our measurements of the increasing Universe and the space to the Virgo cluster, we’d anticipate finding the galaxies inside it receding from us at roughly 1200 km/s, give-or-take.
Go back and forth the Universe with astrophysicist Ethan Siegel. Subscribers gets the e-newsletter each Saturday. All aboard!
However that’s no longer what we measure after we pass forward and make the important observations.Within the Virgo cluster are hundreds of galaxies. A few of them are if truth be told headed towards us, with a small however measurable blueshift. Maximum are headed clear of us, however round part of the galaxies we discover have too low of a pace: between about 0 km/s and 1000 km/s. Additionally, about part of the galaxies we discover inside the Virgo cluster have a greater-than-predicted redshift: of greater than 1200 km/s and a few receding at much more than 2000 km/s. There’s crucial explanation why for this: the galaxies inside the Virgo cluster of galaxies are all gravitationally sure to each other and swarm round each and every different in a beehive-like model.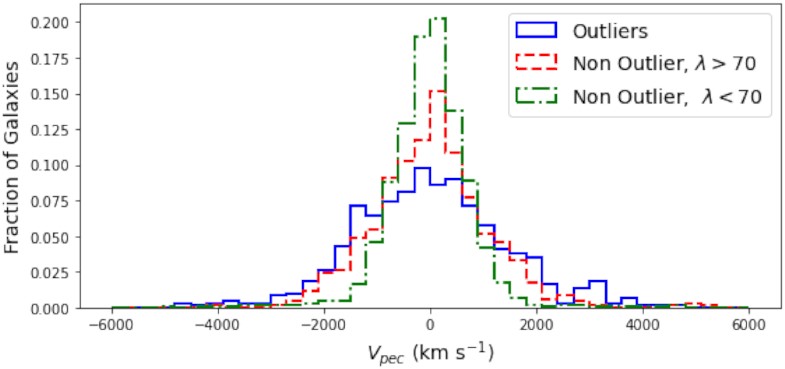 Compiling knowledge from many various galaxy clusters, it may be observed that particular galaxies inside the ones clusters could have bizarre velocities of as much as hundreds of km/s, indicating that inside those constructions, gravitational forces dominate. Best within the area between sure constructions does the growth of the Universe play a significant position.
Compiling knowledge from many various galaxy clusters, it may be observed that particular galaxies inside the ones clusters could have bizarre velocities of as much as hundreds of km/s, indicating that inside those constructions, gravitational forces dominate. Best within the area between sure constructions does the growth of the Universe play a significant position.
Credit score: V. Wetzell et al., Darkish Power Survey, MNRAS, 2022
We will most effective simply measure the line-of-sight motions of those galaxies: the element in their movement that’s directed both towards or clear of us. The transverse parts in their motions — the up-and-down or left-and-right motions of those galaxies — can’t be measured on mere century-like timescales, as galaxies are a long way too extensive and remote to be seen shifting in the ones dimensions. We will most effective take a short-term snapshot of what’s going down correct this second: when the sunshine from those remote gadgets is arriving at our eyes.So why are those galaxies no longer obeying Hubble’s legislation, and why are they in violation of the Friedmann equations’ predictions?For a similar causes that planets orbit the Solar within the Sun Device and stars transfer across the Milky Means within our galaxy: as a result of they’re all mutually sure in combination throughout the pressure of gravity. Those gravitational forces imprint what astronomers name a “bizarre pace” onto those gadgets: a pace starting from loads to hundreds of kilometers-per-second that will get superimposed on most sensible of the Hubble drift. All of spacetime doesn’t showcase the similar conduct as a result of some programs are sure — gravitationally or another way — whilst others are unbound, and it’s most effective the unbound programs that have the growth of the Universe. In between the good clusters and filaments of the Universe are nice cosmic voids, a few of which is able to span loads of tens of millions of light-years in diameter. The long-held concept that the Universe is held in combination through constructions spanning many loads of tens of millions of light-years, those ultra-large superclusters, has now been settled, and those huge web-like options are destined to be torn aside through the Universe’s enlargement.
In between the good clusters and filaments of the Universe are nice cosmic voids, a few of which is able to span loads of tens of millions of light-years in diameter. The long-held concept that the Universe is held in combination through constructions spanning many loads of tens of millions of light-years, those ultra-large superclusters, has now been settled, and those huge web-like options are destined to be torn aside through the Universe’s enlargement.
Credit score: Andrew Z. Colvin and Zeryphex/Astronom5109; Wikimedia Commons
What dominates, and the place?The massive query we want to ask ourselves, each time we’re making an allowance for what governs the conduct of area, is the query of what’s governing the form, curvature, and evolution of spacetime at the scales we’re making an allowance for. Although we’re a part of the increasing Universe, maximum of what we’re aware of isn’t, itself, increasing.
Atoms, sure in combination through the electromagnetic pressure, don’t increase.
Human beings, additionally sure in combination through electromagnetism, don’t increase with the increasing Universe.
Options on planet Earth, which is certain in combination through gravity, don’t increase with the increasing Universe. (If the Earth bodily expands, then again, because of components like thermal enlargement or core job, then the ones options would increase.)
The Earth-Solar distance, once more decided through gravity, does no longer increase because the Universe expands. (Because the Solar loses mass, then again, the Earth-Moon device spirals outward; a distinct impact dominates right here.)
The gap between stars inside the Milky Means, which is gravitationally sure, doesn’t increase because the Universe expands.
And the space between the Milky Means and the opposite galaxies within the Native Workforce, which once more is certain through gravity, doesn’t increase because the Universe expands.
It’s most effective when you get to a scale that’s higher than the most important sure construction you’re making an allowance for — constructions higher than galaxies, galaxy teams, and galaxy clusters — that the growth of the Universe performs a job in what you follow. This affiliation of 9 gamma-ray bursts, all positioned round 9 billion light-years away however separated through greater than 5 billion light-years from end-to-end, had been observed over a length of 8 years: from 2004 via 2012. The “hooked up superstructure” proven this is most effective an artist’s illustration; it’s undetermined whether or not there may be any bodily relation between the quite a lot of gamma-ray bursts and unknown whether or not any two of them are even a part of the similar cosmic construction. It is extremely most probably that they’re all mutually increasing clear of one every other: stuck up within the enlargement of the Universe.
This affiliation of 9 gamma-ray bursts, all positioned round 9 billion light-years away however separated through greater than 5 billion light-years from end-to-end, had been observed over a length of 8 years: from 2004 via 2012. The “hooked up superstructure” proven this is most effective an artist’s illustration; it’s undetermined whether or not there may be any bodily relation between the quite a lot of gamma-ray bursts and unknown whether or not any two of them are even a part of the similar cosmic construction. It is extremely most probably that they’re all mutually increasing clear of one every other: stuck up within the enlargement of the Universe.
Credit score: Pablo Carlos Budassi/Wikimedia Commons
Chances are you’ll understand a curious omission from the record of sure constructions above: galactic superclusters. It seems that the most important a sure construction may also be in our Universe, so far as we comprehend it, is someplace between about 1-and-2 billion light-years: no higher. The most important galaxy clusters are about this scale, as are a couple of galactic partitions. On the other hand, no constructions higher than this must be gravitationally sure in our darkish energy-dominated Universe. This contains our own residence supercluster, Laniakea, in addition to purported quasar and gamma-ray burst associations, which we can not scrupulously name “constructions” in their very own correct, as they’re undoubtedly increasing and don’t seem to be sure: both gravitationally or via every other mechanism.The person constructions that we’re aware of, together with atoms, people, planets, stars, galaxies, or even teams and clusters of galaxies, don’t seem to be increasing at the side of the increasing Universe. It’s most effective the distance that exists in between the most important sure constructions that seem on any scale — between unbound galaxies, galaxy teams, or galaxy clusters — that reveals the conduct of the increasing Universe. As physicist Richard Value quipped, “Your waistline could also be spreading, however you’ll be able to’t blame it at the enlargement of the Universe.”Ship for your Ask Ethan inquiries to startswithabang at gmail dot com!